Abstract
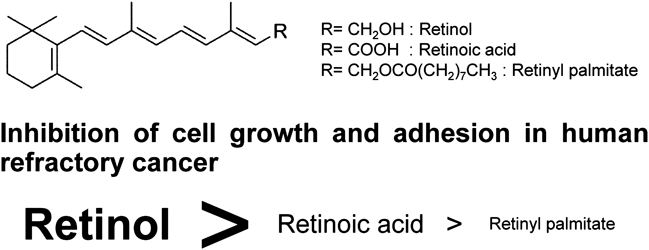
Vitamin A constituents include retinal, which plays a role in vision, and retinoic acid (RA), which has been used in the therapy of human acute promyelocytic leukemia. However, the effects on cancer of retinol (Rol) and its ester, retinyl palmitate (RP) are not known well. In the current study, we examined the effects of these agents on proliferation and adhesion of various cancer cells. Rol exhibited dose-dependent inhibition of the proliferation of human refractory and prostate cancer cells, while RA and RP showed little or no effect. In contrast, RA inhibited the growth of human breast cancer cells to a greater extent than Rol at low concentrations, but not at high concentrations. Rol suppressed adhesion of refractory and prostate cancer cells to a greater extent than RA, while it suppressed adhesion of breast cancer cells as well as RA and of JHP-1 cells less effectively than RA. These results indicate that Rol is a potent suppressor of cancer cell growth and adhesion, which are both linked to metastasis and tumor progression. Rol might be useful for the clinical treatment of cancer.