Volume 39, Issue 4
Displaying 1-27 of 27 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Regular Articles
-
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 457-465
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Advance online publication: January 28, 2016Download PDF (7097K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 466-472
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (1464K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 473-483
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (596K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 484-491
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Advance online publication: February 01, 2016Download PDF (908K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 492-501
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (1729K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 502-515
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (3266K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 516-523
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (940K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 524-531
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Advance online publication: January 23, 2016Download PDF (1122K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 532-539
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (1149K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 540-546
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (930K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 547-555
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (1477K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 556-563
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (1503K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 564-569
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (10235K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 570-577
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Advance online publication: January 23, 2016Download PDF (1454K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 578-586
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (2372K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 587-592
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (566K) Full view HTML -
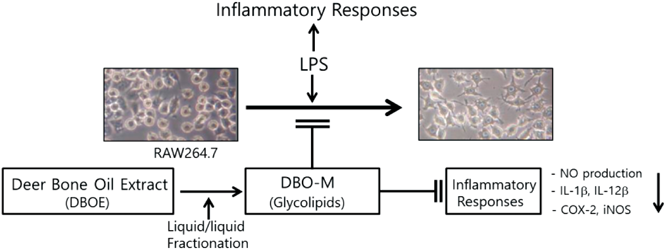
Deer Bone Oil Extract Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW264.7 Cells2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 593-600
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (738K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 601-610
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (1957K) Full view HTML
Notes
-
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 611-614
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (343K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 615-619
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (410K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 620-624
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (424K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 625-630
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Advance online publication: January 28, 2016Download PDF (592K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 631-635
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Advance online publication: January 09, 2016Download PDF (1332K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 636-640
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Advance online publication: January 26, 2016Download PDF (671K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 641-647
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (1332K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 648-651
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (287K) Full view HTML
Errata
-
2016 Volume 39 Issue 4 Pages 652
Published: April 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2016
Download PDF (72K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|