尿沈渣検査は,尿中に出現する成分を尿の遠心操作にて得られた沈殿物を観察する検査である。尿沈渣の標本作成における操作が単純であるにもかかわらず,尿沈渣に出現する成分は多種多様であるため,鑑別が非常に複雑である。その要因としては,尿沈渣に出現する尿中有形成分が,ひとつの成分においても様々な形態で存在することがある。たとえばシュウ酸カルシウム結晶では正八面体型とビスケット型,コマ型などが存在し,尿細管上皮細胞に至っては基本型,特殊型と細胞形態のバリエーションが多岐にわたる。このように尿沈渣検査では成分を正しく鑑別するための知識と技術が必要である。この部では,尿沈渣に出現する基本的な尿中有形成分を鑑別する知識を習得するために,最も基本となる成分の写真について「尿沈渣検査法2010」の尿沈渣アトラスを引用(一部改編)し掲載する。また「*」でマークした写真は,尿沈渣成分の新たな情報として追加したものである.この尿沈渣アトラスを利用し,各成分の特徴を捉えることをしっかりと身につけ,今後遭遇するであろう鑑別困難な成分に対しても対処できるよう,基礎知識を学習することを目的とする。

シュウ酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium oxalate crystals 40× No staining
正八面体の結晶で,弱酸性からアルカリ性まで広い範囲で観察される。酢酸に溶解せず,塩酸で溶解する。pH 6.5
These are regular octahedral crystals that can be observed in a wide range of pH from slightly acidic to alkaline. They do not dissolve in acetic acid but dissolve in hydrochloric acid. pH 6.5

シュウ酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium oxalate crystals 40× No staining
中央は正八面体の結晶で,背景にはビスケット状(円形)の結晶がみられる。塩酸で溶解する。pH 7.0
In the center, regular octahedral crystals are found, and in the background, biscuit-like (circular) crystals are observed. They dissolve in hydrochloric acid. pH 7.0

シュウ酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium oxalate crystals 40× No staining
コマ状の結晶で,シュウ酸カルシウム結晶は尿中のシュウ酸濃度やカルシウム濃度,各種イオン濃度により析出する形状が異なる。pH 7.0
Spinning top-shaped crystal. Calcium oxalate crystals differ in the shape due to the concentration of oxalic acid, calcium, and various ions in the urine. pH 7.0

シュウ酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium oxalate crystals 40× No staining
大小不同で楕円形の結晶である。ビスケット状(Figure 3.352)や楕円形の結晶は赤血球(矢印)と類似する場合がある。しかし,赤血球は淡黄色を呈するのに対し,この結晶は無色であり,また大小不同や光沢があることなどで鑑別できる。pH 6.5
Oval-shaped crystals of different sizes. Biscuit-like (Figure 3.352) and oval-shaped crystals may be similar to red blood cells (arrows). However, red blood cells exhibit a pale yellow color, whereas these crystals are colorless, of different sizes, and glossy. Thus, the crystals can be differentiated from red blood cells. pH 6.5

シュウ酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium oxalate crystals 40× No staining
楕円形の結晶がみられる。厚みがなく透明感のある結晶である。pH 7.0
Oval-shaped, transparent and thin crystals. pH 7.0

シュウ酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium oxalate crystals 40× No staining
亜鈴状(鉄アレイ状)の結晶で,炭酸カルシウム結晶も同様の形状を示す場合がある。しかし,炭酸カルシウム結晶は酢酸で気泡を産生しながら溶解する。pH 6.5
Dumbbell-shaped crystals. Calcium carbonate crystals may exhibit the same shape in some cases. However, calcium carbonate crystals dissolve while producing bubbles in acetic acid. pH 6.5

シュウ酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium oxalate crystals 40× No staining
ビリルビン陽性尿では,円形または楕円形の層状構造を示す結晶がしばしば観察される。色調はビリルビンに染まり黄褐色を呈する。pH 7.5
In bilirubin-positive urine, crystals exhibiting a circular- or oval-layered structure are often observed. The color tone is yellowish brown due to the presence of bilirubin. pH 7.5

シュウ酸カルシウム結晶 40× Alizarin red染色
Calcium oxalate crystals 40× Alizarin red staining
Figure 3.357の結晶をCalcium染色(Alizarin red染色)したもので,Calcium陽性の赤色に染色されている。
The crystal shown in Figure 3.357 is stained with calcium staining (alizarin red staining). It stained red and indicates calcium-positive.

シュウ酸カルシウム結石
Calcium oxalate calculi
体外衝撃波結石破砕術(ESWL)で採取されたシュウ酸カルシウム結石である。シュウ酸カルシウム結石は,黄褐色や黒褐色で,表面に凹凸を有する。
Calcium oxalate calculi collected with extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). Calcium oxalate calculi are yellowish brown or dark brown, with irregular surfaces.
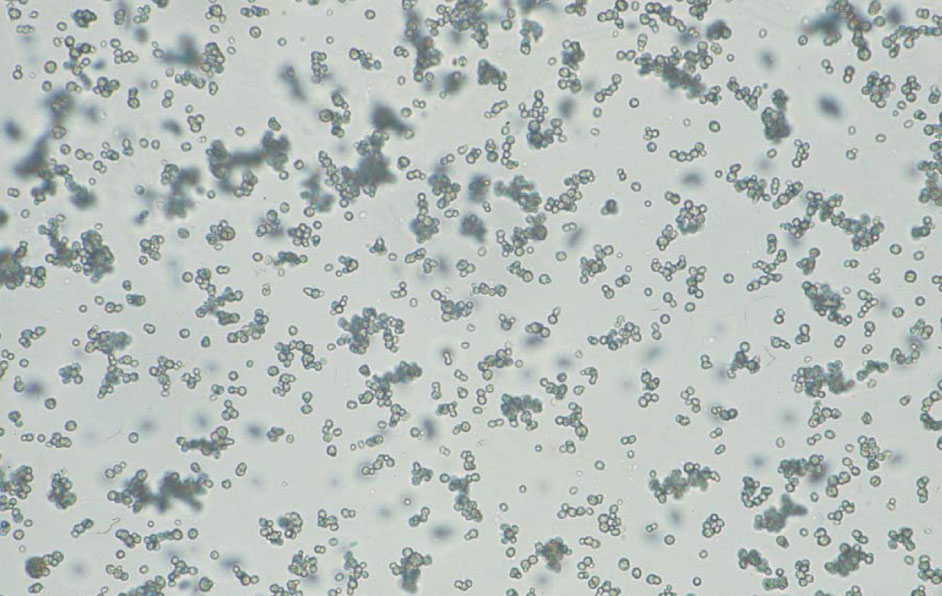
尿酸塩 40× 無染色
Urates 40× No staining
酸性尿で析出する褐色の無晶性塩類である。遠心後の尿の外観はレンガ色(紅色)を呈する。析出量が多い場合は,溶解後,観察するとよい。pH 6.5
Brown amorphous salts deposited from acidic urine. The urine after centrifugation is brick red in color. If a large amount of salt is deposited, it is better to perform observation after dissolving them. pH 6.5

尿酸塩 40× 無染色
Urates 40× No staining
酸性尿で析出する褐色の無晶性塩類である。大きくなると2,8-DHA結晶と類似するので加温またはEDTA加生理食塩水にて洗浄するなど鑑別を要する。pH 6.0
Brown amorphous salts deposited from acidic urine. When the deposition is large, it resembles a 2,8-DHA crystal. For differentiation, it is necessary to heat or wash the specimen with EDTA added physiological saline. pH 6.0

尿酸結晶 40× 無染色
Uric acid crystals 40× No staining
黄褐色で菱形の結晶である。尿酸結晶は酸性尿で析出する。水酸化カリウムで溶解する。pH 6.0
Yellowish brown rhomboid shape crystals. Uric acid crystals are deposited from acidic urine and dissolve in potassium hydroxide. pH 6.0

尿酸結晶 40× 無染色
Uric acid crystal 40× No staining
黄褐色で菊花状の結晶である。pH 5.5
A yellowish brown chrysanthemum blossom-shaped crystal. pH 5.5

尿酸結晶 40× 無染色
Uric acid crystal 40× No staining
黄褐色で亜鈴状(鉄アレイ状)の結晶である。pH 6.0
A yellowish brown dumbbell-shaped crystal. pH 6.0
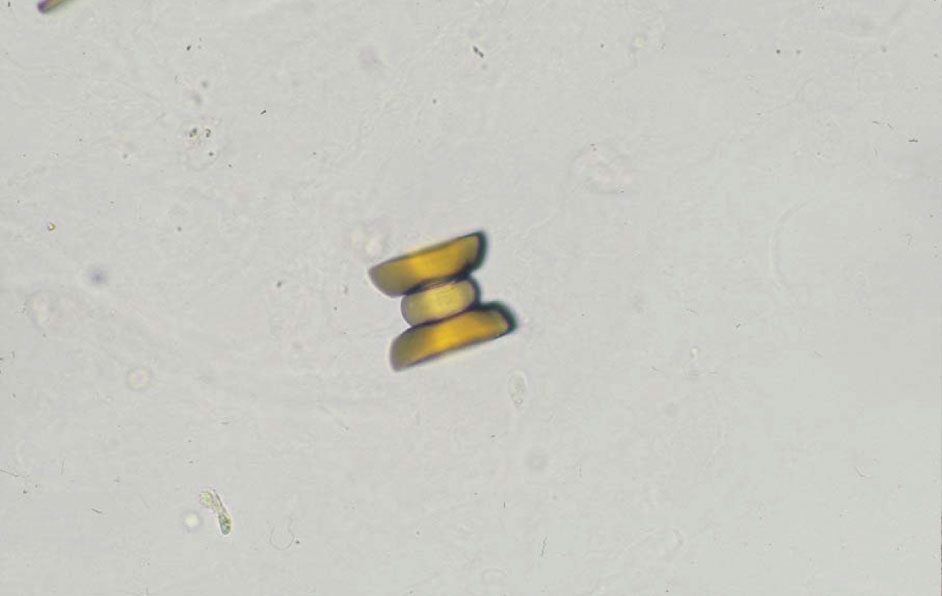
尿酸結晶 40× 無染色
Uric acid crystal 40× No staining
黄褐色で亜鈴状(鉄アレイ状)の結晶である。pH 5.5
A yellowish brown dumbbell-shaped crystal. pH 5.5

尿酸結晶 10× 無染色
Uric acid crystals 10× No staining
黄褐色で棒状の結晶である。比較的大型の結晶で肉眼でも観察可能な場合がある。カバーガラスを載せる際,上手く載せられないことがしばしばある。pH 5.5
Yellowish brown bar-shaped crystals. These are relatively large crystals and may be observed by the naked eye. It is often difficult to place the coverslip on such specimens. pH 5.5

リン酸塩 40× 無染色
Phosphates 40× No staining
無色~灰白色を呈し,多量に析出すると観察の妨げとなる。析出量が多い場合は,溶解後,観察するとよい。酢酸,塩酸で溶解する。pH 7.5
Phosphate appears colorless to whitish gray and obstructs observation when the deposition amount is large. In such cases, it is better to perform the observation after dissolving them in acetic or hydrochloric acid. pH 7.5

リン酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium phosphate crystals 40× No staining
無色~灰白色で菊花状の結晶である。背景には板状の結晶がみられる。酢酸,塩酸で溶解する。pH 8.0
A colorless to whitish gray crystal exhibiting a chrysanthemum blossom shape. There is a plate-shaped crystal in the background. It dissolves in acetic acid and hydrochloric acid. pH 8.0

リン酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium phosphate crystal 40× No staining
無色~灰白色で板状の結晶である。板の表面は顆粒状を呈する。pH 8.5
A plate-shaped crystal that appears colorless to whitish gray. The surface of the plate is granular. pH 8.5

リン酸アンモニウムマグネシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Magnesium ammonium phosphate crystal
40× No staining
無色~淡黄色で封筒状の結晶である。アルカリ性尿で観察される。ウレアーゼ産生菌による尿路感染症などで出現することがある。pH 8.5
A colorless to pale yellow envelope-shaped crystal observed in alkaluria. It may appear with a urinary tract infection with urease-producing bacteria. pH 8.5

リン酸アンモニウムマグネシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Magnesium ammonium phosphate crystals
40× No staining
無色~淡黄色で棒状の結晶である。背景には多数の細菌がみられる。pH 8.5
Colorless to pale yellow bar-shaped crystals. Many bacteria are observed in the background. pH 8.5

リン酸アンモニウムマグネシウム結晶 10× 無染色
Magnesium ammonium phosphate crystals
10× No staining
無色~淡黄色で棒状,封筒状の結晶である。比較的大型の結晶で肉眼でも観察可能な場合がある。pH 8.0
Colorless or pale yellow crystals appearing in a bar or envelope shape. They can be observed with the naked eye due to the relatively large size of the crystals. pH 8.0

リン酸アンモニウムマグネシウム結晶 20× 無染色
Magnesium ammonium phosphate crystal
20× No staining
無色~淡黄色で蝶の羽状の結晶である。pH 8.5
A colorless to pale yellow butterfly wing-shaped crystal. pH 8.5

尿酸アンモニウム結晶 40× 無染色
Ammonium urate crystals 40× No staining
褐色~淡黄色で棘を有する球状の結晶である。大小不同の棘が特徴で,一般にアルカリ性尿で観察されるが,しばしば酸性尿でも観察される。pH 8.5
Brown to pale yellow spherical crystals with thorns. Thorns of various sizes are characteristic. Generally, the crystals are observed in alkaluria; however, they can also be observed in acidic urine. pH 8.5

尿酸アンモニウム結晶 40× 無染色
Ammonium urate crystals 40× No staining
褐色~淡黄色で棘を有する球状の結晶である。尿路感染症と関連がある場合があり,背景に細菌を伴うことがしばしばある。pH 8.0
Brown to pale yellow spherical crystals with thorns that may be associated with urinary tract infections. Bacteria are often observed in the background. pH 8.0

酸性尿酸アンモニウム結晶 40× 無染色
Ammonium acid urate crystals 40× No staining
形態的には尿酸アンモニウム結晶と同様である。幼児の感染性胃腸炎や緩下剤の乱用時に本結石による腎後性急性腎不全の原因となる。pH 6.0
Ammonium acid urate crystals are morphologically similar to ammonium urate crystals. They may cause postrenal acute renal failure due to the calculi in young children with infectious gastroenteritis or people who abuse laxatives. pH 6.0

炭酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium carbonate crystals 40× No staining
無色~灰白色で亜鈴状(鉄アレイ状)の結晶である。酢酸,塩酸で気泡を産生しながら溶解する。pH 8.0
Colorless to whitish gray dumbbell-shaped crystals. They dissolve while producing bubbles with acetic acid and hydrochloric acid. pH 8.0

炭酸カルシウム結晶 40× 無染色
Calcium carbonate crystals 40× No staining
無色~灰白色で亜鈴状(鉄アレイ状)の結晶である。シュウ酸カルシウム結晶も,しばしば同様の形態を示す場合がある。酢酸や塩酸添加で気泡を産生する。pH 7.5
Colorless to whitish gray dumbbell-shaped crystals. Calcium oxalate crystals often exhibit a similar morphology. They produce bubbles when acetic acid or hydrochloric acid is added. pH 7.5

ビリルビン結晶 40× 無染色
Bilirubin crystals 40× No staining
黄褐色で針状の結晶である。放射状に集合したり,上皮細胞上に析出している場合がある。背景にみられる上皮細胞なども黄染する。pH 6.5
Yellowish brown needle-shaped crystals. They may aggregate radially or may be deposited on epithelial cells. Epithelial cells found in the background also turned yellow. pH 6.5

ビリルビン結晶 40× 無染色
Bilirubin crystals 40× No staining
上皮細胞上に析出した,黄褐色で針状の結晶である。pH 6.5
Yellowish brown needle-shaped crystals precipitated on an epithelial cell. pH 6.5

コレステロール結晶 40× 無染色
Cholesterol crystals 40× No staining
無色で歪んだ正方形や長方形の板状の結晶である。重なり合うと,シスチン結晶に類似する場合がある。シスチン結晶は六角形の輪郭を有する。pH 6.5
Colorless, distorted square or rectangular plate-like crystals. When overlapping, they may look similar to cystine crystals, but cystine crystals have a hexagonal contour. pH 6.5

コレステロール結晶 40× 無染色
Cholesterol crystals 40× No staining
無色で歪んだ正方形や長方形の板状の結晶である。重なり合った結晶である。pH 7.0
Colorless, distorted square or rectangular plate-shaped crystals that are overlapping. pH 7.0
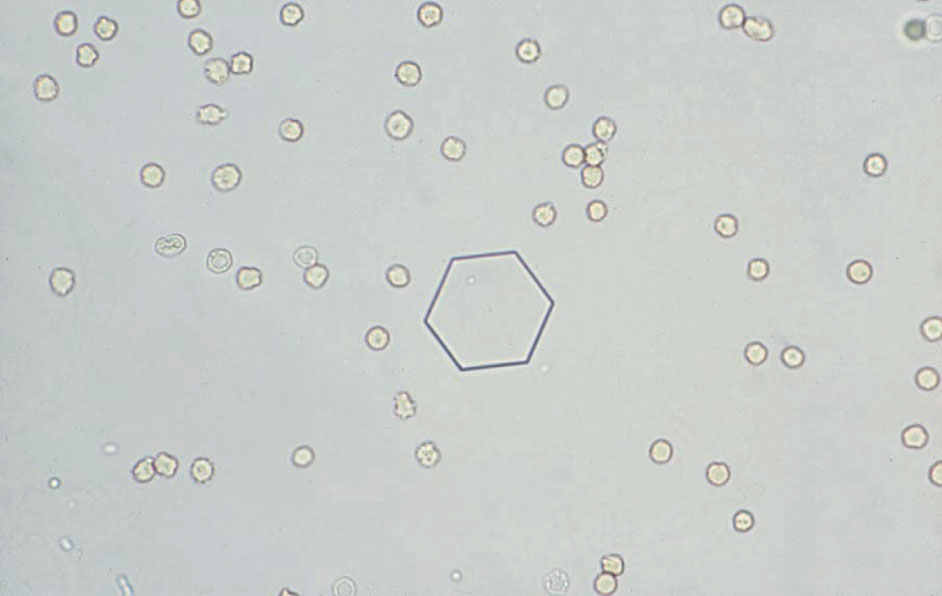
シスチン結晶 40× 無染色
Cystine crystals 40× No staining
無色で六角形の板状結晶である。いく層も重なり合うとコレステロール結晶に類似する場合がある。酸性尿でみられる。細菌尿では直ちに溶解し観察が困難な場合がある。pH 6.0
A colorless, hexagonal plate-shaped crystal. When the crystals overlap in many layers, they may look similar to cholesterol crystals. Cystine crystals are found in acidic urine. In bacterial urine, they may dissolve instantly, making them difficult to observe. pH 6.0

シスチン結晶 40× 無染色
Cystine crystals 40× No staining
無色で六角形の板状結晶である。重なり合った結晶である。六角形の輪郭が残る。結晶の角は120度である。pH 6.5
Colorless, hexagonal plate-shaped crystals that are overlapping. A hexagonal outline remains. The angle of the crystal is 120°. pH 6.5

2,8-ジヒドロキシアデニン結晶 40× 無染色
2,8-Dihydroxyadenine crystals 40× No staining
褐色で円形の結晶である。先天性プリン代謝異常のAPRT欠損症でみられる。水酸化カリウムで溶解する。pH 7.0
Brown, circular crystals found in cases of APRT deficiency of congenital purine metabolism abnormality. They dissolve in potassium hydroxide. pH 7.0

2,8-ジヒドロキシアデニン結石
2,8-Dihydroxyadenine calculus
2,8-ジヒドロキシアデニンは,腎臓より尿中に排泄されると結晶となり結石を形成する。この結石はX線透過性で,X線撮影では結石像は描出されない。
When 2,8-dihydroxyadenine is excreted in the urine from the kidney, it becomes crystalized and forms a calculus. As X-rays penetrate this stone, no stone image is produced via X-ray photography.

薬物結晶 40× 無染色
Drug crystals 40× No staining
投薬薬物によると思われる結晶である。多剤の投薬により薬物の同定は困難なことが多い。
A crystal that appears to be derived from medication. Causative drug identification is often difficult due to multidrug administration.

薬物結晶 40× 無染色
Drug crystal 40× No staining
投薬薬物によると思われる結晶である。
A crystal that appears to be derived from medication.

薬物結晶 40× 無染色
Drug crystal 40× No staining
投薬薬物によると思われる結晶である。
These crystals appear to be derived from medication.