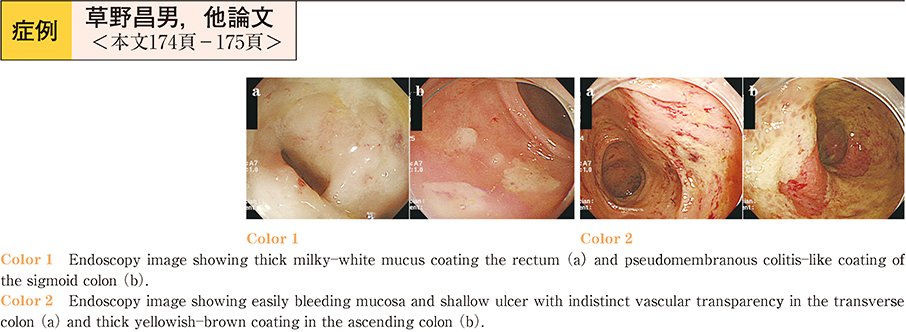
症例
内視鏡で経過が追えたcollagenous colitisの1例
草野 昌男, 駒沢 大輔, 渡部 敬之, 伊藤 広通, 土佐 正規, 大楽 尚弘, 池田 智之, 上野 孝治, 池谷 伸一, 中山 晴夫, 樋渡 信夫, 浅野 重之
著者情報
-
草野 昌男
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
駒沢 大輔
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
渡部 敬之
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
伊藤 広通
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
土佐 正規
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
大楽 尚弘
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
池田 智之
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
上野 孝治
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
池谷 伸一
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
中山 晴夫
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
樋渡 信夫
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/消化器内科
-
浅野 重之
いわき市立総合磐城共立病院/病理科
キーワード:
collagenous colitis,
ランソプラゾール
ジャーナル
フリー
2013 年 83 巻 1 号 p. 174-175
詳細
- 発行日: 2013/12/14 受付日: - J-STAGE公開日: 2013/12/21 受理日: - 早期公開日: - 改訂日: -
PDFをダウンロード (530K)
メタデータをダウンロード
RIS形式
BIB TEX形式
テキスト
メタデータのダウンロード方法
発行機関連絡先
(EndNote、Reference Manager、ProCite、RefWorksとの互換性あり)
(BibDesk、LaTeXとの互換性あり)