-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 11 Pages 1660-1668Feasibility Study of Dendrimer-Based TTR-CRISPR pDNA Polyplex for Ocular Amyloidosis in Vitro Read moreEditor's pick
Hereditary amyloidogenic transthyretin (ATTR) ocular amyloidosis, an intractable disease, is caused by ATTR production from retinal cells. Therefore, development of novel therapeutic agents is urgently needed. In this study, folate-modified dendrimer/cyclodextrin conjugates (FP-CDE) were prepared and their ability to deliver plasmid DNA encoding the TTR-targeted genome editing CRISPR-Cas9 system (TTR-CRISPR pDNA) was investigated. As a result, FP-CDE/TTR-CRISPR pDNA complex was taken up by retinal pigment epithelial cells, exerted ATTR amyloid suppression, and inhibited TTR production through genome editing effect. Taken together, FP-CDE may be useful as a novel therapeutic TTR-CRISPR pDNA carrier in the treatment of ATTR ocular amyloidosis.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 11 Pages 1678-1683Light-Touch-Induced Afterdischarge Firing in the Superficial Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurons in Hairless Mice with Irritant Contact Dermatitis Read moreEditor's pick
Cutaneous hypersensitivity (e.g., alloknesis) was observed in mice with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-induced dermatitis. Repeated application of SDS increased the expression of c-Fos-positive neurons in the superficial spinal dorsal horn (SDH). In vivo extracellular recording revealed afterdischarge responses following stimulation with light touch were also observed in the superficial SDH neurons. Authors found: 1) relation between the alloknesis responses and the afterdischarge responses, and 2) correlation between the intensity of the afterdischarge responses and depth of the recording site. These findings suggest afterdischarge responses can be an index of alloknesis responses.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 11 Pages 1699-1705Distinct Pharmacological Profiles of Monosulfide and Trisulfide in an Experimental Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Reactive sulfur species including monosulfides and persulfides/polysulfides are increasingly recognized to play important roles in (patho)physiological events in various organ systems. Authors compared the effects of monosulfide and trisulfide as therapeutic agents for intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Monosulfide alleviated neurological deficits after ICH and prevented ICH-induced neuronal death, axon degeneration and chemokine production. Trisulfide partially mimicked the effect of monosulfide and was more effective than monosulfide in suppressing recruitment of inflammatory cells, while having no effect on neurological functions. These findings underscore different pharmacological properties of individual sulfur species in regulation of brain pathology.
-
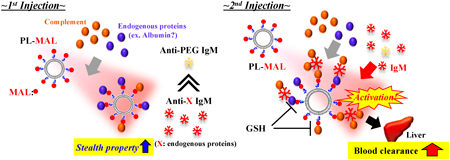
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 10 Pages 1518-1524A Maleimide-Terminally Modified PEGylated Liposome Induced the Accelerated Blood Clearance Independent of the Production of Anti-PEG IgM Antibodies Read moreEditor's pick
PEGylated liposomes (PL) lose their long-circulating characteristic when administered repeatedly, called the accelerated blood clearance (ABC) phenomenon. A PEG lipid with a maleimide (MAL) group at the PEG terminal, MAL-PEG-DSPE, is used in various studies as a linker for ligand-bound liposomes such as antibody-modified liposomes. However, most ABC phenomenon research used PL with a terminal methoxy group. In this study, authors prepared MAL-PEG-DSPE liposomes (PL-MAL) to evaluate the effect of PL-MAL on the ABC phenomenon induction. These findings indicate PL-MAL induced the ABC phenomenon independent of the production of IgM antibodies against PEG. This study provides valuable findings for further studies using ligand-bound liposomes.
-
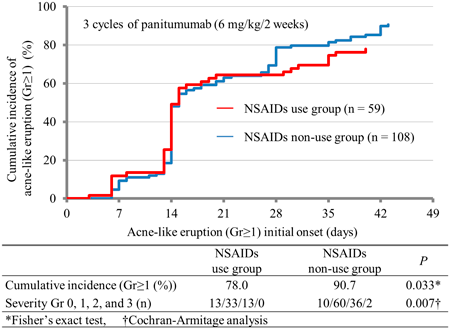
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 10 Pages 1531-1536Prevention of Acne-Like Eruption Caused by Panitumumab Treatment through Oral Administration of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Read moreEditor's pick
Acne-like eruption caused by anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibodies such as panitumumab reduces treatment adherence and patient quality of life; an alternative therapy is desired. Although the mechanism underlying acne-like eruption associated with anti-EGFR antibody remains unclear, previous studies have suggested that the inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 is effective to acne-like eruption caused by low-molecular-weight EGFR inhibitors such as erlotinib. Authors aimed to investigate whether the concurrent use of oral Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and EGFR antibodies and presented preliminary evidence that oral NSAIDs may help prevent acne-like eruptions caused by panitumumab.
-
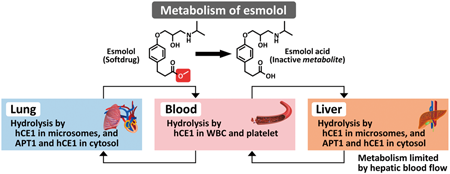
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 10 Pages 1544-1552Esterases Involved in the Rapid Bioconversion of Esmolol after Intravenous Injection in Humans Read moreEditor's pick
Esmolol, an antedrug, is clinically used for long period due to its rapid onset of action and elimination at a rate greater than cardiac output. The authors found the esterases involved in the hydrolysis of esmolol. Esmolol was hydrolyzed by human carboxylesterase 1 (hCE1) in leukocytes and platelets. The human hepatic clearance limited by hepatic blood flow was obtained by microsomal hydrolysis by hCE1 and cytosolic hydrolysis by acyl protein thioesterase 1 (APT1). The expression of hCE1 and APT1 in human lung might cause the high total clearance of esmolol, which is 3.5-fold greater than cardiac output.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 10 Pages 1559-1563Dihydroceramide Δ4-Desaturase 1 Is Not Involved in SARS-CoV-2 Infection Read moreEditor's pick
Hayashi Y, et al. have already reported that N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-retinamide (4-HPR) inhibits dihydroceramide Δ4-desaturase 1 (DEGS1) enzymatic activity, and suppresses SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here, the authors describe the generation of DEGS1 knockout VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells and their use to evaluate the infectivity and the effect of 4-HPR on SARS-CoV-2 infection. This study reports that DEGS1 is not involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection, including viral replication and the release of viral progeny. Further investigation is needed to elucidate the exact mechanism underlying the inhibition in SARS-CoV-2 infection by 4-HPR. 4-HPR has been extensively studied for cancer treatment. Therefore, the results of this study, along with accumulated clinical data on the safety of 4-HPR, are potential candidates for the treatment of COVID-19.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 10 Pages 1572-1580SNAP23-Mediated Perturbation of Cholesterol-Enriched Membrane Microdomain Promotes Extracellular Vesicle Production in Src-Activated Cancer Cells Read moreEditor's pick
Cancer cells secrete large numbers of small extracellular vesicles (sEVs). These vesicles are derived from intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) and contribute to cancer progression by forming the tumor microenvironment. In this study, Mitani et al. demonstrated a novel role for SNAP23 in Src-dependent EV secretion: in Src-transfected cells, SNAP23 translocates to non-rafts and causes cholesterol depletion, resulting in the upregulation of ILV. They also found that pancreatic cancer patients with high SNAP23 expression have a poor prognosis. These findings suggest that the Src-SNAP23-sEV axis contributes to cancer progression.
-
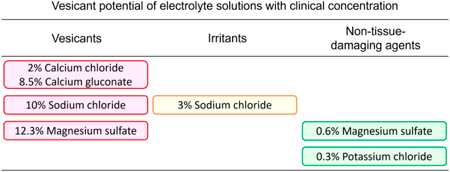
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 9 Pages 1254-1258Classification of Skin Injury Risk Caused by Extravasation of Electrolyte Solutions or Infusions in a Rat Model Read moreEditor's pick
Cytotoxic agents are classified according to the severity of skin injury after extravasation. However, injuries caused by extravasation of noncytotoxic agents have not been sufficiently investigated. In this study, the authors focused on noncytotoxic electrolyte solutions and infusions and evaluated skin injuries macroscopically and histopathologically using extravasation model rats. As a result, the electrolyte solutions and infusions were classified into three categories (vesicants, irritants, and non-tissue-damaging agents) depending on the degree of skin injury. The characteristic symptoms and severity of each drug extravasation revealed in this study will provide basic information for preparation of guidelines for treatment of extravasation.
-
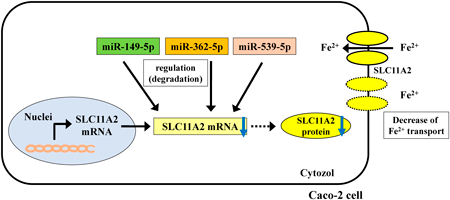
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 9 Pages 1291-1299Regulation of Iron-Ion Transporter SLC11A2 by Three Identical miRNAs Read moreEditor's pick
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are known “key regulator” of numerous gene expressions. In this study, authors determined the effects of three miRNAs, miR-149-5p, miR-362-5p, and miR-539-5p, on iron-ion transporter, SLC11A2 mRNA using the cultured human colon carcinoma cell line. Authors found that they regulate SLC11A2 gene expression and iron-ion transporting function in an in vitro system. Authors believe that this study makes a significant contribution to the literature because the use of these three miRNAs as surrogate biomarkers could significantly advance the development of therapies for the treatments of diseases caused by transporter disorders, such as anemia.
-
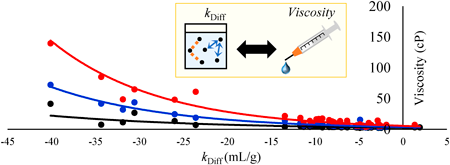
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 9 Pages 1300-1305Estimation of the Viscosity of an Antibody Solution from the Diffusion Interaction Parameter Read moreEditor's pick
In antibody drugs, estimating the viscosity at high concentrations is crucial in terms of designing drug formulations since high viscosity could limit the choice of administration routes. The authors hypothesized that the diffusion interaction coefficient may be a key factor in estimating the viscosity and analyzed the relation between them. Not only have the results showed the viscosity can be estimated by using the diffusion interaction coefficient, but it has also succeeded in setting criterions for the feasibility of high concentration formulations. Such findings will deepen the understanding of the physicochemical properties, leading to the promotion of future drug development.
-
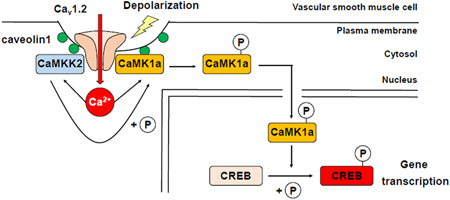
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 9 Pages 1354-1363Local Ca2+ Signals within Caveolae Cause Nuclear Translocation of CaMK1α in Mouse Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Read moreEditor's pick
An increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration activates Ca2+-sensitive enzymes such as Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinases (CaMK) and induces gene transcription in various types of cells through excitation-transcription (E-T) coupling. In this study, the authors revealed that CaMK1α can be fully activated by both Ca2+ influx through of L-type Ca2+ channels, Cav1.2, and phosphorylation by CaMKK2 within caveolae in mouse vascular smooth muscle cells. This activated (phosphorylated) CaMK1a can translocate from the cytosol to the nucleus. These findings strongly suggest that CaMK1a can transduce Ca2+ signaling generated within or very near caveolae to the nucleus and thus, promote E-T coupling.
-
Editor's pick
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) are widely used in Japan. PPIs or PCAB is known to have cardiovascular risk. Authors revealed the cardiovascular risk in each PPI or PCAB components using a large claims data in 91,098 working-age workers. Finally, authors reveal that lansoprazole, a higher CYP2C19 inhibition activity as compared other PPIs or PCAB, is a higher risk for cardiovascular risk.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 8 Pages 1124-1132Autism Spectrum Disorder Model Mice Induced by Prenatal Exposure to Valproic Acid Exhibit Enhanced Empathy-Like Behavior via Oxytocinergic Signaling Read moreEditor's pick
ASD are neurodevelopmental disorders characterized by impairments in social behavior and repetitive interests. Individuals with ASD often also display decreased empathy, while recent report indicates that individuals with ASD show enhanced emotional empathy than typically developed individuals. In this study, Takayama et al. assessed socially transmitted fear in observational fear learning paradigm as a proxy of emotional empathy in VPA-treated mice, ASD model mice. The authors found that hyperactivity of oxytocin neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus in VPA-treated mice enhanced empathy-like behaviors in observational fear learning paradigm.
-
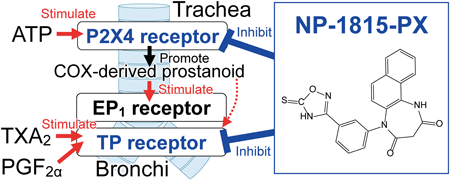
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 8 Pages 1158-1165Effects of NP-1815-PX, a P2X4 Receptor Antagonist, on Contractions in Guinea Pig Tracheal and Bronchial Smooth Muscles Read more
-
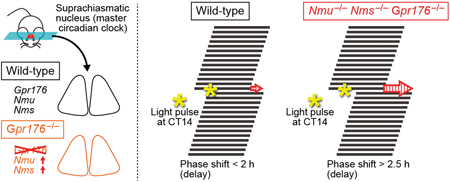
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 8 Pages 1172-1179Nmu/Nms/Gpr176 Triple-Deficient Mice Show Enhanced Light-Resetting of Circadian Locomotor Activity Read moreEditor's pick
Circadian clock disruption has been linked to diseases ranging from metabolic syndrome to cancer. Therefore, the circadian system has become an attractive target for research and clinical care innovations. The authors show that the orphan G-protein-coupled receptor Gpr176 is involved in light entrainment of the circadian clock through a mechanism requiring two related neuropeptides, neuromedin U and neuromedin S. It is suggested by the authors that simultaneous modulation of these neuropeptides and Gpr176 may constitute a potential therapeutic option for modulating the circadian clock.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 7 Pages 806-812Health Effects and Safety Assurance of Nanoparticles in Vulnerable Generations Read moreEditor's pick
Despite the usefulness of nanoparticles, there are now safety concerns about their use. Therefore, the importance of evaluating the safety of vulnerable generations such as pregnant women and infants, who are highly sensitive to chemical substances, has been pointed out worldwide. From this perspective, to analyze the risk from nanoparticles to vulnerable generations, nano-safety science and nano-safety design research has been conducted. The findings of these studies will lead not only to develop a nanotechnology that will enable the sustainable use of nanoparticles; they will also contribute to future developments in the field of health science.
-
Editor's pick
Recently, therapeutic drug monitoring is recommended for many drugs even though the procedure is not covered by health insurance. This Current Topic focuses on four areas: (1) anticancer drugs, (2) anti-infective agents, (3) antipsychotics/antidepressants, and (4) antibody drugs. Among the drugs that are not approved for insurance coverage in Japan, the drugs for which TDM is recommended and drugs that are likely to be approved in the future are summarized in a review, which include their pharmacokinetic characteristics and the usefulness of TDM.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 7 Pages 851-855More than 370-Fold Increase in Antibody Affinity to Estradiol-17β by Exploring Substitutions in the VH-CDR3 Read moreEditor's pick
Antibodies that specifically target biomarkers are essential in clinical diagnosis. Genetic engineering has assisted in designing novel antibodies that offer greater antigen-binding affinities, thus providing more sensitive immunoassays. Authors have succeeded in generating a single-chain Fv fragment (scFv) targeted estradiol-17b (E2) with more than 370-fold improved affinity (Ka 3.2 ´ 1010 M-1), based on a strategy focusing the complementarity-determining region 3 in the VH domain (VH-CDR3). This improvement is the greatest reported for mutagenesis targeting anti-steroid antibodies. The scFv mutant enabled an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that provided sensitive dose-response curves for determining E2, the midpoint of which was 4.46 pg/assay.
-
Volume 45 (2022) Issue 7 Pages 881-887Hospital-Wide Surveillance of Fracture Risk Assessment by Both FRAX and Medication Patterns in Acute Care Hospital Read moreEditor's pick
Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) is a well-known scoring system for predicting the probability of fragility fractures (FF). However, among the factors used in FRAX, glucocorticoid is the only medication factor. Authors assessed the risk of FF at each clinical department using FRAX and medication patterns. As a result, the departments included in the high-risk group by FRAX were not necessarily the same as the departments included in the top group, based on the administered medications. Authors recommend the use of FRAX together with prescribed medications on hospital-wide surveillance of fracture risk assessment.