-
Editor's pick
Molecular space chemistry is an important concept for the design of novel functional materials and catalysts. The research group “Molecular space chemistry for the chemical conversion” was established by the member who advocate that the organic integration of supramolecular chemistry and catalytic chemistry enables flexible chemical conversion in multi-component molecular ensembles. It is noteworthy that most of the member got a position of full professor (or similar position) in these few years. To this volume of Chem. Pharm. Bull., four of the members, who have deep connection with the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, contribute their cutting-edge results.
-
Editor's pick
This report describes the synthesis of novel dual-purpose reagents, p-methoxybenzyl N-acetylcarbamate potassium salt (PM-BENAC-K) and 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl N-acetylcarbamate potassium salt (2,4-DM-BENAC-K). The BENAC-Ks were stable colorless powders synthesized via a simple three-step procedure without column chromatography, which can be easily scaled-up. The BENAC-Ks reacted with various alkyl halides and sulfonates to form substituted products that were converted to N-alkylacetamides via acid-mediated deprotection. Simultaneously, p-methoxybenzyl and 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl carbamates were obtained via base-mediated deacetylation. Thus, the BENAC-Ks are worth remembering as simple reagents for synthesis of acetamides and benzyl carbamates.
-
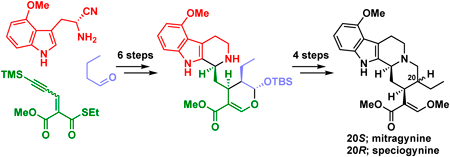
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 9 Pages 662-668Asymmetric Total Syntheses of Mitragynine, Speciogynine, and 7-Hydroxymitragynine Read moreEditor's pick
Mitragyna speciosa, which belongs to the Rubiaceae family, contains several corynantheine-type monoterpenoid indole alkaloids that exhibit potent biological activity, including analgesic activity. In this article, the authors reported the asymmetric total syntheses of such Mitragyna alkaloids mitragynine, speciogynine, and 7-hydroxymitragynine. These syntheses were accomplished via asymmetric organocatalytic Michael reaction, diastereoselective Pictet-Spengler cyclization, and biogenetically inspired chemical transformations within 12 steps and in >11% overall yield from commercially available materials. These syntheses will strongly promote the structure-activity relationship study of Mitragyna alkaloids.
-
Editor's pick
Biomembranes constitute the boundary between the living organism and the external environment, and their function is essential for maintaining biological activities. Quantitative understanding and precise control of the transport and conversion of various substances across biomembranes are important issues in biophysics and cell biology, but dealing with biomembranes, which are multi-component, heterogeneous, and complex systems, is not an easy task. In the Current Topics, investigators who are boldly tackling this area of research introduce recent advances in biophysical and molecular biological aspects and technology.
-
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 8 Pages 540-543Site-Selective α-Alkylation of 1,3-Butanediol Using a Thiophosphoric Acid Hydrogen Atom Transfer Catalyst Read moreEditor's pick
The linear 1,3-diol structure is a common motif in biologically active molecules. C-H functionalization at an α-position of alcohols leads to efficient synthesis of sugars and polyols. However, regioselective conversions at the alcohol α-position of linear 1,3-diols have been limited. Nakao et al. developed secondary-alcohol-selective C-H alkylation of 1,3-butane diol by combining an acridinium photoredox catalyst and a thiophosphoric acid hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) catalyst. The use of DCM as a solvent with a relatively small dipole moment improved secondary α-alkoxy C-H selectivity by making the C-H abstraction process the rate-limiting step.
-
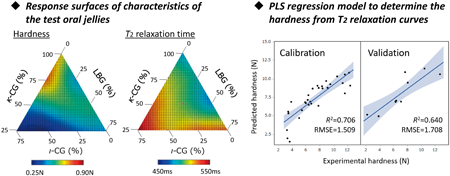
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 8 Pages 558-565Determination of Hardness of a Pharmaceutical Oral Jelly by Using T2 Relaxation Behavior Measured by Time-Domain NMR Read moreEditor's pick
Hardness is a critical quality characteristic of pharmaceutical oral jelly. The purpose of this study is to determine the hardness using time-domain NMR (TD-NMR). After measurement of the T2 relaxation curves of the test jellies by TD-NMR, the acquired data were analyzed by partial least squares (PLS) regression analysis. Eventually, an accurate and reliable PLS model was created that enabled accurate assessment of the hardness of the test jellies. TD-NMR enables the measurement of samples nondestructively and rapidly with low cost, and so could be a promising method for evaluation of the hardness of pharmaceutical oral jellies.
-
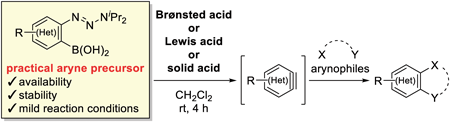
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 8 Pages 566-572Aryne Generation from o-Triazenylarylboronic Acids Induced by Brønsted Acid Read moreEditor's pick
This paper describes acid-mediated aryne generation from o-triazenylarylboronic acids. The authors previously reported these practical aryne precursors generate arynes by the treatment with silica gel. In this paper, they reported acids including Brønsted acids, Lewis acids, and solid acids are also effective for aryne generation from the precursors. In particular, the use of camphorsulfonic acid provided high yields in reactions with a range of arynophiles, and enabled chemoselective reaction with a furan in the presence of an amine. Hammett plot analyses revealed that an aryne generation mechanism induced by the acid is distinct from the mechanism induced by silica gel.
-
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 7 Pages 458-468Progress in Chiral Stationary Phases Based on Proteins and Glycoproteins Read moreEditor's pick
The ligand-binding sites of F1*S and A variants of human α-acid glycoprotein (hAGP), and chicken AGP were completely different. The former sites were located in lobs I-III including W122, while the later ones were located near W26. Both (R)- and (S)-benzoin were docked onto a cavity of the generated model structure of cAGP. In addition to hydrophobic interactions, some of hydrogen bonding interactions worked for chiral recognition of (R)- and (S)-benzoin. (R)-Benzoin bound to cAGP more tightly than (S)-benzoin. The elution order of benzoin enantiomers on chiral stationary phases based on cAGP in LC were consistent with the docking results.
-
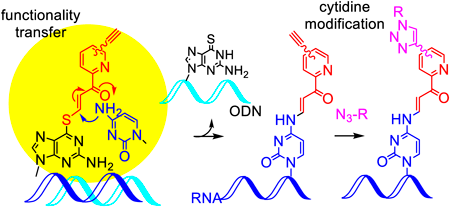
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 7 Pages 498-504Application of the Functionality Transfer Oligodeoxynucleotide for the Site-Selective Modification of RNA with a Divers Molecule Read moreEditor's pick
Due to the importance of chemical modification of RNA, methods for chemical modification at a predetermined site in an internal position of RNA have attracted much attention. The authors have developed an original method for the base- and sequence-specific modification by transferring the functional group of the oligonucleotides to RNA through the formation of hybrid complexes. To achieve further modification by copper-catalyzed alkyne-azide cycloadditions, the authors investigated transfer groups with the tri-, tetra- and pentaethylene glycol-linked alkynes. As a result, the transfer groups with tetra- and pentaethylene linkers were determined to be promising compounds to internally modify long RNA.
-
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 6 Pages 420-426Enhancing Anticancer Potency of a 13-Substituted Berberine Derivative with Cationic Liposomes Read moreEditor's pick
This paper reports the successful use of a cationic liposomal-encapsulated novel 13-substituted berberine derivative for the targeted cell uptake and delivery to the cancer cell nucleus. Additionally the liposome also assists with stabilization of the selectively toxic anticancer berberine derivative with respect to oxidative cleavage in solution. Liposomes derived from a cholesterol-based lipid with a polar side chain which would become cationic after amine protonation, were of particular interest. Enhanced cancer cell toxicity was seen in vitro with the cationic liposomal formulation of the berberine derivative possibly via inhibitory interactions with the cell’s telomere/telomerase system.
-
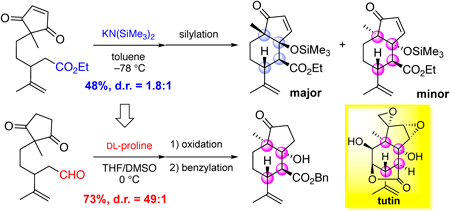
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 6 Pages 435-442Model Synthetic Study of Tutin, a Picrotoxane-Type Sesquiterpene: Stereoselective Construction of a cis-Fused 5,6-Ring Skeleton Read moreEditor's pick
This paper describes a stereoselective synthesis of a cis-fused 5,6-ring skeleton in picrotoxane-type sesquiterpenes. This bicyclic skeleton is a synthetic challenging structure because of the presence of multiple consecutive stereocenters including two tetrasubstituted carbons at the angular positions. The authors developed a synthetic method of the core structure via DL-proline-mediated intramolecular aldol reaction accompanied with the desymmetrization of the 2-methyl-1,3-cyclopentanedione moiety and the construction of four contiguous stereocenters. This reaction can be also applied to the kinetic resolution using L-proline, implying that the established method would be useful for the synthesis of natural products classified as picrotoxane-type sesquiterpenes.
-
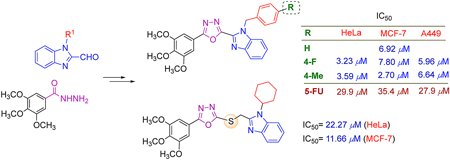
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 6 Pages 448-453Design, Synthesis and Cytotoxicity Evalufation of Substituted Benzimidazole Conjugated 1,3,4-Oxadiazoles Read moreEditor's pick
Many drugs being used in chemotherapy of cancer has nitrogen-containing heterocyclic moieties as their basic structure, and the authors extensively focused on the 1,3,4-oxadiazole and benzimidazole scaffolds. In this article, two series of novel hybrids combining the 1,2-disubstituted benzimidazole and 1,3,4-oxadiazole or thioether linked 1,3,4-oxadiazole were designed and successfully synthesized. The in vitro cytotoxicity bioassays came up with the discovery of three lead compounds which displayed 4.5-13 fold increase in activity compared to 5-FU against the three human cancer cell lines (HeLa, MCF-7, A549), meriting further characterization and serving as promising scaffolds in the discovery of new potent anticancer agents.
-
Editor's pick
The authors had held a symposium, “New modalities and strategies in drug delivery and discovery”, in the 36th Annual Meeting of the Academy of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, Japan (APSTJ) in Tokushima (online), Japan, 2021. In the symposium, the active young researchers from the Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences of Tokushima University presented various topics on their own researches. This Current Topics accumulated the review articles from the invited speakers of the symposium. These reviews will provide a wide range of intimate information regarding new modalities and strategies in drug delivery and discovery.
-
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 5 Pages 362-368Monitoring and Predicting the Size of Fine Particles Prepared in a Fluidized-Bed Granulator Using a Handheld-Type Raman Spectrometer Read moreEditor's pick
Particle size-monitoring method using a handheld-type Raman spectrometer is proposed in this study. Two types of fine particles with the same formulation under different operating conditions were prepared for calibration purposes. There was a relationship between particle size and Raman intensity during processing and calibration curves could be obtained in both operating conditions. Two other types of fine particles with the same formulation, but on different scales or using different processing mechanisms were also prepared for verification purposes. The particle size could be successfully predicted using the calibration curve obtained taking powder porosity into consideration.
-
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 5 Pages 383-390Mechanism of Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs Triggered by Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks Read moreEditor's pick
The authors elucidated the mechanism of solubilization of poorly water-soluble drugs using zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs), a member of metal-organic frameworks. The solubility of ZIF-trapped drugs was enhanced compared to the raw drugs. The authors focused on 2-methylimidazole (2-MIM), used as an organic ligand in ZIFs. Drugs were easily dissolved by the addition of 2-MIM, suggesting that the presence of 2-MIM enhanced the drug solubility. The findings of this study demonstrated the solubilization mechanism of poorly water-soluble drugs using ZIFs. ZIFs are expected to be used as drug carriers to maximize the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs.
-
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 5 Pages 391-399Lipase-Catalyzed Kinetic Resolution of C1-Symmetric Heterocyclic Biaryls Read moreEditor's pick
The highly enantioselective lipase-catalyzed kinetic resolution (KR) of racemic C1-symmetric biaryl compounds including heterocyclic moieties, such as carbazole and dibenzofuran, has been achieved for the first time. This enzymatic esterification was accelerated by the addition of disodium carbonate while maintaining its high enantioselectivities (up to 99% ee), and was particularly effective for biaryls having N-substituted carbazole moieties. Furthermore, mesoporous silica-supported oxovanadium-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling of 3-hydroxycarbazole and 2-naphthol was followed by the lipase-catalyzed KR in one-pot to synthesize the optically active heterocyclic biaryl compounds with high optical purity.
-
Editor's pick
Biopharmaceutical dry powder inhaler (Bio-DPI) is an attractive formulation for non-invasive administration method for biopharmaceutical compounds. In Bio-DPI to ensure spray stability, it is important to control the powder caking risk of the formulation. To detect powder caking risk, Void Forming Index (VFI) is a useful method for DPI formulation study. The authors conducted formulation screening using VFI, to develop a high-dose Bio-DPI formulation containing 50 mg of lysozyme per capsule. As a result, VFI clarified the powder caking risk of each formulations and contributed to selection of high spray stability formulation.
-
Editor's pick
This paper describes the synthesis of new derivatives of habiterpenol and their structure-activity relationships. Habiterpenol is a G2 checkpoint inhibitor that has recently attracted attention as a new vital molecular-targeting therapeutic agent. Combination therapy using low-doses of anticancer agents and G2 checkpoint inhibitors has great potential as an effective treatment for cancer because it minimizes the dosage of the DNA-damaging anticancer agents and results in fewer side effects. The authors have independently developed a total synthesis to obtain new habiterpenol derivatives that cannot be derived from natural products, and have further studied their structure-activity relationships.
-
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 4 Pages 283-285Caulophyine A, a Rare Azapyrene Alkaloid from the Roots of Caulophyllum robustum Read moreEditor's pick
This paper reports one rare azapyrene alkaloid named caulophyine A along with six known compounds identified from the roots of Caulophyllum robustum Maxim., which was collected on Taibai mountain, the highest peak of the Qinling mountains, Shaanxi province, China. Caulophyine A is a nitrogen containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, possess a naphtho[2,1,8-def]isoquinoline fragment. This is the first report of the nitrogen containing azapyrene alkaloid identified from plant. The in vitro bioassays revealed that caulophyine A displayed weak acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory activity.
-
Volume 70 (2022) Issue 4 Pages 304-308Isolation of Natural Prodrug-Like Metabolite by Simulating Human Prodrug Activation in Filamentous Fungus Read moreEditor's pick
The authors successfully demonstrated that expression of a hCYP gene in a filamentous fungus led to the identification of a bioactive natural product from a strain previously not reported to produce the compound, and a prodrug-like secondary metabolite that can be activated by an hCYP. Our approach can be further developed by employing other types of CYPs and prodrug-activating enzymes in combination with microbes, with differing secondary metabolite biosynthetic potentials, to explore a wider biosynthetic space for identification of interesting prodrug-type natural products.