-
Volume 72 (2024) Issue 3 Pages 311-312Effect of Two-Photon Excitation to 8-Azacoumarin Derivatives as Photolabile Protecting Groups Read moreEditor's pick
Photolabile protecting groups (PPGs) have been utilized in many research fields such as organic synthesis and chemical biology because their fast and selective photocleavage proceeds under mild conditions. The authors previously reported the design and synthesis of 8-azacoumarin-type PPGs based on the alkene-to-amide replacement of the 6-bromo-7-hydroxy-coumarin-4-ylmethyl (Bhc) group. The characteristic feature of these PPGs is their aqueous solubility, which is remarkably higher than that of Bhc. The authors found that 8-azacoumarin-type PPGs can also be used as two-photon excitation sources because the photolytic efficiency for two-photon excitation showed preferable physicochemical values for applications in cells and tissues.
-
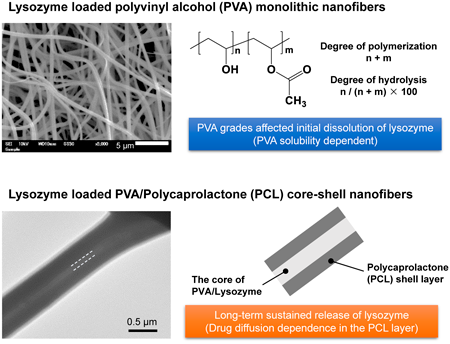
Volume 72 (2024) Issue 3 Pages 324-329Controlled Release of Lysozyme Using Polyvinyl Alcohol-Based Polymeric Nanofibers Generated by Electrospinning Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
The authors investigated the use of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibers for the drug delivery of lysozyme (LZM), focusing on how different PVA grades affect drug release characteristics. PVA nanofibers with a 50% LZM content achieved efficient encapsulation and quick release within 30 minutes. Using fully hydrolyzed PVA led to more controlled release due to its reduced water solubility. Notably, the study highlighted coaxial electrospinning to create PVA/LZM nanofibers coated with polycaprolactone, facilitating extended drug release. This approach clarified the relationship between the characteristics of PVA in nanofibers and drug release properties, offering promising insights for pharmaceutical nanofibers. -
Volume 72 (2024) Issue 3 Pages 336-339Synthesis of 2-Substituted Indoles via Migration Reaction of 3-Substituted Indoles with Triflic Acid Read moreEditor's pick
Indole is a crucial heterocycle found in various biologically active natural products and medicinal compounds. Therefore, developing convenient methodologies for modifying the indole structure is an interesting topic for the discovery of pharmaceuticals and functional materials. In this context, the authors report trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (2.1 equiv) efficiently facilitates the 1,2-migration reaction of the substituent from C3- to C2- position of the indole structure. Alkyl, aryl groups such as benzyl, isopropyl, phenyl were tolerated for this reaction (up to 98% yield).
-
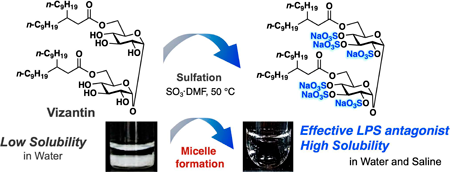
Volume 72 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 226-233Development of a Water Soluble Self-assembling Analogue of Vizantin Read moreEditor's pick
Vizantin is a TLR-4 antagonist developed in the author's laboratory. In this article, to improve the water solubility of vizantin, the authors designed a new vizantin derivative in which all hydroxyl groups of the sugar unit were sulfated. It has been confirmed that the synthesized vizantin derivative spontaneously forms string-like micelles and dissolves in water. The authors also report that string-like micelles of more uniform size are formed in physiological saline than in distilled water, making it possible to prepare an ideal injection solution.
-
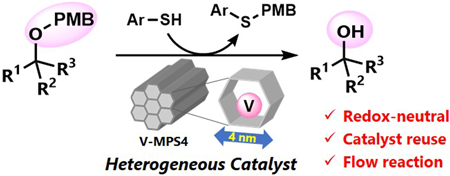
Volume 72 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 213-219Nucleophilic Deprotection of p-Methoxybenzyl Ethers Using Heterogeneous Oxovanadium Catalyst Read moreEditor's pick
Heterogeneous catalysis has gained increasing interest in the growing demand of sustainable manufacturing of pharmaceutically relevant compounds. The authors report herein a mesoporous silica-supported oxovanadium (V-MPS4)-catalyzed nucleophilic removal of the p-methoxybenzyl (PMB) protective group on alcohols under mild and redox-neutral conditions. The method has a wide reaction scope, including primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols with various functional groups. The catalyst was reused six times without a significant loss in the conversion. The advantages of using the heterogeneous catalyst were further demonstrated by conducting the deprotection reaction in a flow process, which showed significantly higher turnover frequency compared to the batch reactions.
-
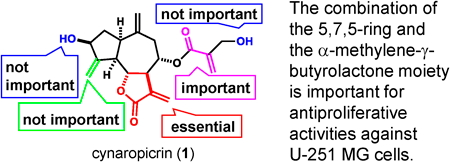
Volume 72 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 200-208Antiproliferative Activities of Cynaropicrin and Related Compounds against Cancer Stem Cells Read moreEditor's pick
The guaianolide sesquiterpene lactone cynaropicrin and its derivatives showed antiproliferative activity against human glioblastoma U-251 MG cells and their cancer stem cells. Accordingly, the authors synthesized several derivatives of cynaropicrin and investigated their structure-activity relationships. The authors conclude that the α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone moiety involved in the Michael addition reaction and the 5,7,5-ring are both important for antiproliferative activities. The results of this study suggest guaianolide sesquiterpene lactones are useful for developing anticancer drugs targeting glioblastoma.
-
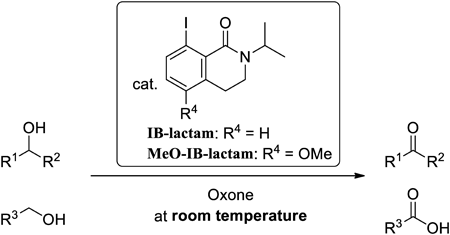
Volume 72 (2024) Issue 2 Pages 234-2398-Iodoisoquinolinone, a Conformationally Rigid Highly Reactive 2-Iodobenzamide Catalyst for the Oxidation of Alcohols by Hypervalent Iodine Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Catalytic hypervalent iodine oxidation reactions have recently attracted attention to as an environmentally benign and safe method. The authors now report the first lactam-type 2-iodobenzamide catalysts, 8-iodoisoquinolinones (IB-lactams), that can act as a catalyst at room temperature for the oxidation of alcohols with Oxone (2KHSO5·KHSO4·K2SO4) and show the highest reactivity among their previously reported ones. They have a conformationally rigid 6/6 bicyclic lactam structure. The lactam structure could form an efficient intramolecular I---O interaction in its hypervalent species. The interaction could stabilize them to achieve rapid oxidation to pentavalent iodine species, which can oxidize alcohols to carbonyl compounds. -
Volume 72 (2024) Issue 1 Pages 28-35Analysis of Factors Related to Variation in Dissolution Profiles Estimated from Continuously Conducted Dissolution Tests of Generic Products Read moreEditor's pick
The authors focus on the long-term consistency of dissolution profiles of generic pharmaceutical products. By analyzing a vast dataset of 1675 products across 127 ingredients, the study uncovers the intricate factors influencing changes in dissolution profiles post-approval. It emphasizes the significance of co-development in the increase of dissimilar dissolution products, the pivotal role of API particle size in poorly soluble drugs, and the impact of acidic or basic residues on dissolution changes at specific pH levels. These findings highlight the necessity for proper development that consider formulation and process variables to ensure the sustained bioequivalence of generic drugs.
-
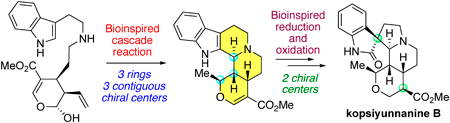
Editor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Kopsiyunnanine B was isolated from Yunnan Kopsia arborea and possesses a unique folded and complex pentacyclic structure containing six contiguous chiral centers. In this article, the authors reported the asymmetric total synthesis of Kopsiyunnanine B, along with their originally proposed biosynthetic pathway. The key transformation is an impressive cascade reaction that constructs three ring structures and three chiral centers in one step. Following the stereoselective reduction of the β-acrylate and oxidation to oxindole, the natural product is synthesized over 14 steps. Their careful consideration of the biosynthetic hypothesis has resulted in an exceptionally efficient synthesis with a minimal number of steps. -
Volume 72 (2024) Issue 1 Pages 80-85Five New Analogs of Streptogramin Antibiotic Viridogrisein Isolated from Streptomyces niveoruber Read moreEditor's pick
Given the spread of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria (AMR), there is an urgent need for the ongoing search for novel antibacterial natural products. The authors discovered five new viridogrisein congeners from Streptomyces niveoruber with potent antibacterial activities against Gram-positive bacteria. Additionally, co-treatment with griseoviridin, another natural product from the same producer, enhanced the activity. Biosynthetic studies have revealed that SgvY, encoded in the viridogrisein biosynthetic gene cluster, detoxifies viridogrisein against Staphylococcus aureus by linearization, suggesting its role in the self-resistance system in S. niveoruber. These results could facilitate the understanding of antimicrobial-resistant mechanism for developing the countermeasures against AMR.
-
Volume 72 (2024) Issue 1 Pages 86-92Derivation of the Extended Kawakita Equation for Estimating the Yield State of Powder in Die Read moreEditor's pick
The Kawakita equation has been used for estimating yield pressure and porosity of compressed powder in the die. This equation assumes the compression pressure is homogeneously distributed. However, in actual powders, it is not homogeneously distributed due to the friction on the die wall. The authors extended the Kawakita equation by accounting for the inhomogeneous distribution of compression pressure. The extended Kawakita equation theoretically explained the powder behavior yielding sequentially from the loading punch to fixed punch due to the spatial limitation of particle rearrangement. Therefore, the extended Kawakita equation advances understanding of powder compaction in die.
-
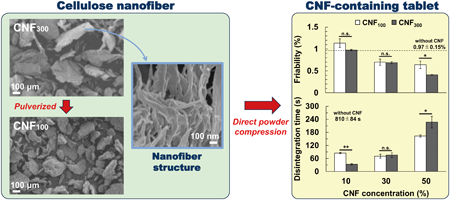
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 12 Pages 887-896Effect of Powdered Cellulose Nanofiber with Different Particle Sizes on the Physical Properties of Tablets Manufactured via Direct Compression Read moreEditor's pick
While the addition of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) to tablet formulations during direct compression has attracted increasing attention as a means for enhancing tablet strength and disintegration, they are also known to increase the variation in tablet weight and drug content. This study evaluated the effect of pulverized CNF on the variation in tablet weight and drug content. The pulverized CNF reduced both weight and drug content variation to a larger extent than untreated CNF. Further, either CNF achieved sufficient tablet strength and short disintegration time. Thus, the authors provided evidence that CNF is useful as a multifunctional additive.
-
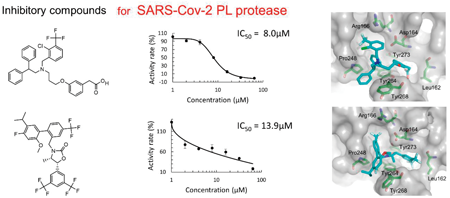
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 12 Pages 897-905In Silico Identification of Inhibitory Compounds for SARS-Cov-2 Papain-Like Protease Read moreEditor's pick
Computational screening is a powerful technique for drug discovery today. In this work, a virtual screening was performed to find SARS-Cov-2 PL protease inhibitors, utilizing a chemical database consisting of approved and investigational drugs. A key issue for successful virtual screening is the accuracy of computational predictions for the binding pose and score of each compound to the target. The authors applied their original software program, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2017, 65, 461, for calculating the score. Their approach identified five inhibitory compounds against the PL protease. The inhibitory activities were evaluated by an enzymatic assay with the FRET technique.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 819-823Exosome-Hijacking Drug Delivery System with Branched Arginine Linker Effectively Deliver Antisense Oligonucleotides into Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells Read moreEditor's pick
Exosomes, a kind of extracellular vesicles, have actively been researched as the drug delivery system (DDS) for nucleic acid drugs. The authors previously reported exosome-hijacking antibody-oligonucleotide conjugate “ExomiR-Tracker”, which is consisting of cationic oligoarginine linker-introduced anti-exosome antibody (anti-Exo) and nucleic acid drugs. In this article, it was revealed that the intracellular delivery capability of nucleic acid drugs and the functional inhibition of target gene in lung adenocarcinoma cells was significantly improved by branched oligoarginine adapted ExomiR-Tracker (Branch ExomiR-Tracker) as compared to conventional one. Their findings demonstrate the promising potential of ExomiR-Tracker as a tool for delivering nucleic acid drugs and provide novel insights into the exosome-hijacking DDS.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 11 Pages 838-842Determination of the Solid Content of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Powders in Suspension-Type Pharmaceutical Oral Jelly Using Time-Domain NMR Read moreEditor's pick
This study utilized low-field time-domain NMR (TD-NMR) to ascertain the solid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) content in suspension-type pharmaceutical oral jellies. The authors prepared and tested jellies containing various APIs, such as acetaminophen (APAP), indomethacin (IMC), and L-valine. The authors determined that precise API content measurement in jellies was achieved by utilizing NMR signal intensity measured through the solid-echo pulse sequence. Additionally, the authors observed that smaller API particle sizes resulted in faster T2 relaxation rates. In summary, TD-NMR proves to be a robust tool for evaluating the dispersion state of API powders in pharmaceutical oral jellies.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 10 Pages 775-781Regiocontrol Using Fluoro Substituent on 3,6-Disubstituted Arynes Read moreEditor's pick
To enhance the structural diversity in aryne-based products, the aryne precursors bearing various functional groups have been continuously developed. However, the use of unsymmetrically substituted arynes is frequency constrained by the low regioselectivity. Authors achieved the regiocontrol by introducing a fluoro-substituent in unsymmetrically 3,6-disubstituted arynes as a directing group. Particularly, the use of 3,6-disubstituted aryne having fluorine and bromine atoms led to the good degree of regiocontrol in several reactions. These results consist with aryne distortion models reported by Garg and Houk’s group.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 10 Pages 792-797Lithium Binaphtholate-Catalyzed Asymmetric Michael Reaction of Acrylamides Read moreEditor's pick
A chiral lithium binaphtholate base catalyst effectively mediates the asymmetric Michael addition of ketones to less reactive acrylamides in a highly enantioselective manner. A small excess of lithium tert-butoxide relative to the binaphthol is used to facilitate the enolization of the ketone, thereby improving conversion of the asymmetric Michael reaction. Computational studies support that the 3- and 3'-phenyl groups of the binaphtholate catalyst control the orientation of the lithium enolate and the subsequent approach of acrylamide to achieve high enantioselectivity.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 9 Pages 687-694Effects of Granulated Lactose Characteristics and Lubricant Blending Conditions on Tablet Physical Properties in Direct Powder Compression Read moreEditor's pick
This study evaluated the effects of different forms of granulated lactose (GL) on the physical properties of tablets and the effect of magnesium stearate on each type of GL. The different forms of GL such as agitated granulation (GL-AG), spray-dried granulation (GL-SD), and fluidized bed granulation (GL-FB) were added as excipients during direct powder compression. When tablets with the same blending conditions were compared, the tensile strength and disintegration time followed the order as GL-FB > GL-SD > GL-AG. The authors presented selection criteria for the suitability of different forms of GL during tableting by examining the relevance between the type of GL and properties of the tablets produced.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 9 Pages 701-716Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Triaryl Derivatives with Readthrough-Inducing Activity Read moreEditor's pick
Readthrough therapy, which restores the biosynthesis of full-length proteins by incorporating an amino acid at a premature termination codon and allowing translation to continue, has recently been actively investigated for its application to nonsense mutation-related diseases. In this article, triaryl derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for the development of novel readthrough agents to treat mucopolysaccharidosis type I, which is caused by nonsense mutations in the IDUA gene. KY-516, a representative compound, exhibited excellent readthrough-inducing activity in the luciferase assay and significantly increased enzyme activity in mutant IDUA transgenic cells.
-
Editor's pick
In this Article, the authors investigated the effects of fluorine atoms introduced to the terminal positions of the side chain (26 and 27-positions) of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3) on vitamin D receptor (VDR) binding affinity, osteocalcin promoter transactivation activity, and levels of resistance against CYP24A1-dependant metabolism. They revealed that these biological activities were enhanced in the order of 26,27-difluoro, 26,26,27,27-tetrafluoro, and 26,26,26,27,27,27-hexafluoro-25(OH)D3. Introduction of fluorines at these positions lead to improvements on functions as VDR-ligands and biological activity. With regard to the VDR binding affinity, the authors considered those potency improvements might be attributed to the increased acidity of the 25-OH group.