-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 9 Pages 701-716Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Triaryl Derivatives with Readthrough-Inducing Activity Read moreEditor's pick
Readthrough therapy, which restores the biosynthesis of full-length proteins by incorporating an amino acid at a premature termination codon and allowing translation to continue, has recently been actively investigated for its application to nonsense mutation-related diseases. In this article, triaryl derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for the development of novel readthrough agents to treat mucopolysaccharidosis type I, which is caused by nonsense mutations in the IDUA gene. KY-516, a representative compound, exhibited excellent readthrough-inducing activity in the luciferase assay and significantly increased enzyme activity in mutant IDUA transgenic cells.
-
Editor's pick
In this Article, the authors investigated the effects of fluorine atoms introduced to the terminal positions of the side chain (26 and 27-positions) of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3) on vitamin D receptor (VDR) binding affinity, osteocalcin promoter transactivation activity, and levels of resistance against CYP24A1-dependant metabolism. They revealed that these biological activities were enhanced in the order of 26,27-difluoro, 26,26,27,27-tetrafluoro, and 26,26,26,27,27,27-hexafluoro-25(OH)D3. Introduction of fluorines at these positions lead to improvements on functions as VDR-ligands and biological activity. With regard to the VDR binding affinity, the authors considered those potency improvements might be attributed to the increased acidity of the 25-OH group.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 9 Pages 730-733Synthesis and in Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Jadomycins Read moreEditor's pick
The authors synthesized jadomycins and their structural analogues, evaluated their cytotoxic activity, and addressed structure-activity relationship study of jadomycins. They achieved the total synthesis of jadomycin T and jadomycin aglycons using L-threonine and 1-amino-2-propanol as nitrogen sources. When the cytotoxicity of jadomycins were evaluated in several tumor cells, the jadomycin aglycons tended to be more cytotoxic than the jadomycins. The authors also demonstrated the potential application of jadomycins as lead compounds for the treatment of brain tumors. This paper provides important insights into the total synthesis of other natural organic compounds, structure-activity relationship studies, and development of new therapeutic drugs.
-
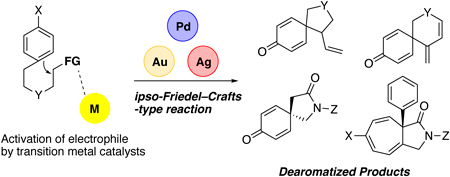
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 8 Pages 624-632Development of Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Dearomatization Reactions Read moreEditor's pick
To develop dearomatization reactions based on a nucleophilic activation of phenols, naphthols, and indoles, ipso-Friedel–Crafts-type C-alkylation must be selectively promoted over competitive O- or N-alkylation reactions. Resolving this chemoselectivity issue is essential for developing this class dearomatization reaction. Author’s research group found that various dearomatization reactions could be developed using appropriately designed aromatic substrates with an electrophilic moiety for intramolecular reactions. This review describes dearomatization reactions using Pd catalysis, Au catalysis, and Ag catalysis, which provided access to a wide variety of dearomatized products from planar aromatic compounds in a highly chemoselective manner.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 8 Pages 650-654Identification of Methylsulochrin as a Partial Agonist for Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptors and Its Antiviral and Anti-inflammatory Activities Read moreEditor's pick
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is known to be related to the metabolic pathway of xenobiotics but recent studies revealed that AhR is also associated with the life cycle of the virus and inflammatory reactions. In this article, the authors screened a natural product library and identified methylsulochrin as a partial agonist of AhR. Methylsulochrin exhibited antiviral activity against the hepatitis C virus and suppressed the production of an inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-6, in macrophages. These results suggested the possibility of methylsulochrin derivatives as anti-hepatitis C virus compounds with anti-inflammatory activity.
-
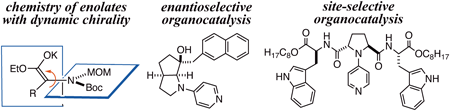
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 7 Pages 466-484Novel Strategies for Enantio- and Site-Selective Molecular Transformations Read moreEditor's pick
Two topics on novel synthetic strategy are shown. The first topic concerns enolate chemistry. The enolate structure has been long believed to be achiral because all four substituents are in the same enolate plane. From the viewpoint of dynamic chirality, however, the enolate can exist as an axially chiral form or a planar chiral form in a limited time scale. The author demonstrated that these chiral enolates can be employed as reliable intermediates for asymmetric synthesis. The second topic concerns catalyst function. 4-pyrrolidinopyridine (PPY) had been known to be the most active catalyst for acylation. Based on the PPY skeleton, strategies for enantio- and site-selective catalysis were proposed. The latter opened up a new way to total syntheses of natural glycosides in extremely short overall steps.
-
Editor's pick
This “Current Topics” contains one review and four regular articles describing the latest research on natural product chemistry that have been contributed by young researchers. These contents include computer science technology in natural products research, isolation of biological constituents from medicinal plants, evaluation of the biological activity of natural products, and synthesis of biological constituents from medicinal plants. These findings could be useful for the development of effective medicines from natural medicinal resources.
-
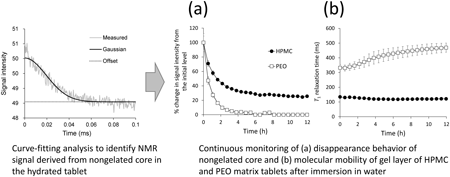
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 7 Pages 576-583Continuous Monitoring of the Hydration Behavior of Hydrophilic Matrix Tablets Using Time-Domain NMR Read moreEditor's pick
The hydration behavior of hydrophilic matrix tablets is a crucial process for the in vitro release of highly water-soluble drugs. This article presented a novel method for continuous monitoring of the hydration behavior by using time-domain nuclear magnetic resonance (TD-NMR). TD-NMR has an ability to identify the NMR signals corresponding to the nongelated core remaining in the sample from the measured T2 relaxation curves. The authors succeeded in characterizing fully the hydration behaviors of the model matrix tablets. The TD-NMR method is powerful to evaluate the hydration properties of hydrophilic matrix tablets.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 7 Pages 584-615Isosteric Replacement of Ester Linkage of Lysophospholipids with Heteroaromatic Rings Retains Potency and Subtype Selectivity Read moreEditor's pick
The authors have reported various derivatives of lysophosphatidylserine (LysoPS) as potent and selective agonists for each LysoPS receptor subtype. In order to further develop these LysoPS analogs to drug candidates, appropriate pharmacokinetic consideration is essential. They found that the ester bond of LysoPS is highly susceptible to metabolic degradation in mouse blood and examined isosteric replacement of the ester linkage with heteroaromatic rings. The resulting compounds showed excellent retention of potency and receptor subtype selectivity, as well as increased metabolic stability. This work provides a molecular basis for the design of phospholipid-based agonists with improved metabolic stability.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 6 Pages 435-440Establishment of One-Pot Disulfide-Driven Cyclic Peptide Synthesis with a 3-Nitro-2-pyridinesulfenate Read moreEditor's pick
In peptide drug discovery, it is important to develop efficient synthetic methodologies to access cyclic disulfide peptides with the expression of functional activity and resistance to metabolic enzymes. In this study, the authors developed a one-pot disulfide-driven cyclic peptide synthesis. The entire process is carried out using solid phase peptide synthesis, thus eliminating complicated work up procedures to remove by-products and enabling production of high-purity cyclic peptides by simple cleavage of a peptidyl resin. Consequently, the one-pot synthesis of oxytocin as a model cyclic disulfide peptide was successfully accomplished using this method. Their study has contributed for the preparation of more complex and artificial disulfide peptides.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 6 Pages 441-446Palatability of Aripiprazole Gummies Prepared from Commercially Available Products: Pharmaceutical Formulation for Improving Patient Adherence Read moreEditor's pick
Good adherence to medication is critical for successfully treating psychiatric disorders. The authors developed two types of aripiprazole gummies (ARP-Gs) with organoleptic masking, cocoa- and fruit-flavoured ARP-Gs using a commercially available ARP formulation. They evaluated the overall palatability and acceptability of the ARP-Gs by performing a gustatory sensation test in healthy volunteers. The both ARP-Gs exhibited superior palatability, and greatly exceeded the cut-off values of acceptability. The ARP-Gs could be alternative dosing forms in patients with schizophrenia, and pharmacists can prepare these formulations in pharmacies to enhance medication adherence and meet the specific needs of individual patients.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 6 Pages 447-450Substituent Effects at the N-Nitrosoaminophenol Moiety of a Photoinduced-Electron-Transfer-Driven Nitric Oxide Releaser Read moreEditor's pick
The authors have developed a series of photoinduced-electron-transfer-driven (PeT-driven) nitric oxide (NO) releasers that efficiently release NO upon irradiation with visible light. In this study investigating the substituent effects at the 2-position of the nitrosoaminophenol moiety, it was found that a methyl group had no significant effect on NO-releasing ability, while a nitro or methoxy group reduced it. The nitro group may suppress electron transfer to the antenna moiety, while the methoxy group may accelerate electron transfer but suppress deprotonation of nitrosoaminophenol. Understanding these structure-activity relationships could aid in further functionalizing PeT-driven NO releasers.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 5 Pages 354-359Mechanistic Insight into the TBHP-Mediated Decarboxylative Condensation of α-Ketoacids: Reaction Development and Application to Oligopeptide Synthesis Read moreEditor's pick
The development of peptide bond formation reaction enabling a convergent peptide fragment coupling is a major challenge of recent years for synthetic chemists due to the rapidly growing interest in the discovery of drugs base on the middle molecule peptides. The decarboxylative amidation recently reported by authors’ group is a potential solution to this problem. In this article, a mechanistic analysis and the further development of the t-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) mediated-decarboxylative amidation of α-ketoacids are described. A systematic examination and understanding of the reaction mechanism enabled a modified epimerization-free reaction whereby peptide fragment couplings using peptide α-ketoacids were successfully achieved.
-
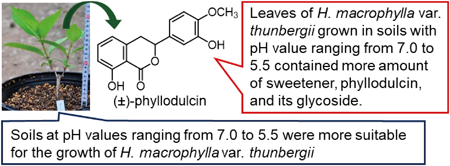
Editor's pick
The processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla Seringe var. thunbergii Makino is listed as a Sweet Hydrangea Leaf (Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium) in the 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. The authors reported soils with pH ranging from 7.0 to 5.5 was not only suitable for this plant growth but also increased the content of phyllodulcin as sweetener in the leaves. In addition, a correlation between the sweetness of the crude drug and phyllodulcin was shown. These findings could be useful for the development of the crude drug with high-quality.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 4 Pages 289-298Effects and Mode of Action of Oleic Acid and Tween 80 on Skin Permeation of Disulfiram Read moreEditor's pick
Oral disulfiram (DSF) has been used clinically for alcohol dependence and recently has been found to have antitumor activity. A transdermal delivery system would be useful for reducing the frequency of administration of DSF for cancer treatment. The authors found that the combination of oleic acid (OA) and Tween 80 further enhanced skin permeation of DSF compared with individual application. The peak of CH2 asymmetric stretching vibration was blue-shifted by the application of OA, and DSF solubility increased in response to Tween 80. Their study clarified the detailed mechanism of action of skin permeation and promoting effect of DSF through the combined use of OA and Tween 80.
-
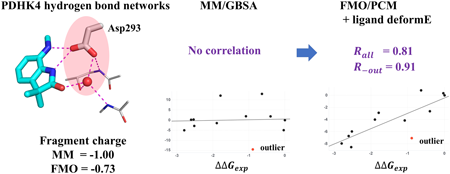
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 4 Pages 299-306Fragment Molecular Orbital Based Affinity Prediction toward Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinases: Insights into the Charge Transfer in Hydrogen Bond Networks Read moreEditor's pick
This computational paper describes the importance of treating electronic effects among hydrogen bond networks. Fragment Molecular Orbital (FMO) method, which is a fast quantum-mechanics method, was applied to the affinity prediction at the hydrogen bond networks of PDHK4. Authors found that the FMO calculation with the solvation method of polarizable continuum model (PCM) was important to increase the prediction accuracy. A considerable amount of charge was transferred among the target site in the FMO/PCM calculation, which was not described in the traditional molecular-mechanics method. These results highlight the importance of electronic effects in the affinity prediction toward hydrogen bond networks.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 3 Pages 213-219Bioequivalence Dissolution Test Criteria for Formulation Development of High Solubility-Low Permeability Drugs Read moreEditor's pick
The biowaiver scheme based on the biopharmaceutics classification system (BCS-BWS) is used not only as terms of regulatory submissions but also as an indicator for formulation development in drug discovery. The authors investigated the in vitro dissolution rates of formulations of a BCS class III drug and compared them with the criterion in the BCS-BWS. They also discussed the impact of dissolution rates on bioequivalence for BCS class III drugs by virtual simulation. These findings contribute to a better understanding of the biowaiver approach and would help researchers in the formulation development of BCS class III drugs.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 3 Pages 234-239Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Radioiodinated Triazole-Pyrolidine Derivative to Detect Orexin 2 Receptor in the Brain Read moreEditor's pick
The orexin 2 receptor plays a critical role in the arousal-promoting function. In vivo imaging of orexin 2 receptor is expected to contribute to elucidation of orexin systems and the development of drugs to treat sleep disorder. The authors newly developed a radioiodinated triazole-pyrolidine derivative to detect orexin 2 receptor in the brain. The authors described that an additional structure-activity relationship study based on the triazole-pyrolidine scaffold to improve brain pharmacokinetics may lead to the development of useful orexin 2 receptor imaging probes.
-
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 3 Pages 250-256An Amphipathic Structure of a Dipropylglycine-Containing Helical Peptide with Sufficient Length Enables Safe and Effective Intracellular siRNA Delivery Read moreEditor's pick
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are promising intracellular delivery tools for membrane-impermeable compounds such as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). In this study, the authors designed amphipathic CPPs containing unnatural amino acids dipropylglycine (Dpg) and explored the cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of peptide/siRNA complexes. The results suggested that the amphipathic structure of peptides played a key role in complexation with siRNAs and intracellular siRNA delivery. A Dpg-containing peptide formed an amphipathic a-helical structure and achieved effective intracellular delivery using small amounts of peptides with negligible cytotoxicity. These findings could be valuable for the design of novel CPPs for siRNA delivery.
-
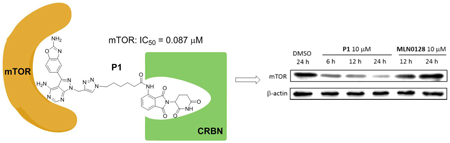
Volume 71 (2023) Issue 2 Pages 120-128Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of mTOR-Targeting PROTACs Based on MLN0128 and Pomalidomide Read moreEditor's pick
In this study, several novel PROTACs for the degradation of mTOR were designed based on MLN0128 (mTOR-binding ligand) and pomalidomide (E3 ligase CRBN ligand). PROTAC compounds exhibited mTOR inhibitory activity and suppressed MCF-7 cell proliferation. The representative compound P1 could degrade mTOR and reduce the expression of the mTOR downstream protein p-S6 (Ser240/244) and p-AKT (Ser473). Further studies showed that this compound could inhibit cancer cell growth by inducing autophagy, but it did not affect the cell cycle and apoptosis. This is the first mTOR PROTAC reported and these findings provide new insights in the study of mTOR inhibitors.