Volume 2019, Issue 64
Displaying 1-12 of 12 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Paper
-
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 1-7
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (1276K) -
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 9-14
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (952K) -
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 15-21
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (1024K) -
Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of a Japanese bow (Nonlinear Spring Characteristics and Dynamic Behavior)2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 23-31
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (1229K) -
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 33-37
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (847K) -
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 39-44
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (900K) -
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 45-51
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (1153K) -
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 53-55
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (650K) -
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 57-70
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (1851K) -
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 71-77
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (1027K) -
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 79-87
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (1681K) -
2019Volume 2019Issue 64 Pages 89-94
Published: March 31, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2019
Download PDF (980K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|

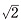 0 1], [
0 1], [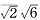 1], [
1], [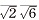 1] and the other of [001], [
1] and the other of [001], [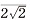 0 1], [
0 1], [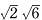 1], [
1], [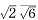 1]. The elastic recovery ratio improved from 27% to 36% at the reduction ratio (RR) at 20% , and to 40% at the RR 40% , however the shape recovery ratio was not improved. After the 600℃ annealing the shape recovery ratio improved from 20% to 33% in the RR 40% specimens. The cause of the elastic recovery ratio improvement is presumed that the cold rolling raised yield stress, and the expansion of martensite phase after bending test enhanced pseudoelastic effect. On the other hand, there are two reasons for improving the SME, one is the texture formation which promotes the martensitic transformation, and the other is the generation of austenite phase which easily transforms into martensite phase.
1]. The elastic recovery ratio improved from 27% to 36% at the reduction ratio (RR) at 20% , and to 40% at the RR 40% , however the shape recovery ratio was not improved. After the 600℃ annealing the shape recovery ratio improved from 20% to 33% in the RR 40% specimens. The cause of the elastic recovery ratio improvement is presumed that the cold rolling raised yield stress, and the expansion of martensite phase after bending test enhanced pseudoelastic effect. On the other hand, there are two reasons for improving the SME, one is the texture formation which promotes the martensitic transformation, and the other is the generation of austenite phase which easily transforms into martensite phase. parameter model was proposed. The relationship between defect size and fatigue limit can be predicted by this equation using the threshold stress intensity factor range of macro crack and the fatigue limit of non-defect specimen. The predicted fatigue limits were in good agreement with the experimental fatigue limit. Thus, the usefulness of this equation was demonstrated.
parameter model was proposed. The relationship between defect size and fatigue limit can be predicted by this equation using the threshold stress intensity factor range of macro crack and the fatigue limit of non-defect specimen. The predicted fatigue limits were in good agreement with the experimental fatigue limit. Thus, the usefulness of this equation was demonstrated.