-
Editor's pick
This pooled analysis of two phase 3 studies investigates efficacy and safety of vonoprazan-based quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication in Asian patients with peptic ulcers. The researchers compared vonoprazan based regimens to the lansoprazole-based quadruple therapy. The results demonstrate that vonoprazan-based therapy was effective and safe for eradicating H. pylori. The eradication rates achieved with vonoprazan-based quadruple therapy were noninferior to those achieved with lansoprazole-based quadruple therapy and exceeded clinically relevant threshold (90%) for efficacy. This finding suggests that vonoprazan-based quadruple therapy may be a valuable new treatment option for H. pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcers.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 8 Pages 1415-1421Activation of Mitochondria in Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Mitochondrial Delivery of Coenzyme Q10 Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
The authors previously developed a drug delivery system targeting mitochondria (MITO-Porter) by using a microfluidic device to encapsulate Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) on a large scale. Herein, the authors successfully activated mitochondrial functions in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) using this unique technique by controlling the amount of CoQ10 encapsulated in MITO-Porter. While the efficacy of MSC transplantation therapy has been reported for various diseases, it is still in the developmental stage. This mitochondrial-activated MSCs offers a promising tool to improve their transplantation therapy, with the potential to accelerate the clinical application of MSCs. -
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 8 Pages 1422-1428Refining Hepatocyte Models to Capture the Impact of CYP2D6*10 Utilizing a PITCh System Read moreEditor's pick
This groundbreaking study introduces a refined hepatocyte model that accurately replicates the impact of CYP2D6*10, a prevalent mutation in East Asian populations. Using the PITCh genome editing system, researchers successfully engineered HepG2 cells to express six key drug-metabolizing enzymes, including the CYP2D6*10 variant. The resulting CYP2D6*10 KI-HepG2 cells exhibited reduced CYP2D6 protein expression and metabolic activity, mirroring the mutation's effects in vivo. This novel model promises to enhance drug metabolism predictions and hepatotoxicity studies, particularly for East Asian populations, potentially revolutionizing drug development and safety assessments.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 8 Pages 1437-1446Bisdemethoxycurcumin Augments Docetaxel Efficacy for Treatment of Prostate Cancer Read moreEditor's pick
Prostate cancer is a common malignant tumor of the urinary tract in men. It is the fifth leading cause of cancer death in men worldwide and the second most common malignancy. The results of this study provide an effective way to improve the anti-cancer effect of docetaxel. Bisdemethoxycurcumin can be used as an anticancer adjuvant in combination chemotherapy. These authors suggest that the combination of bisdemethoxycurcumin and docetaxel may be more effective in treating prostate cancer than docetaxel alone. However, the development of bisdemethoxycurcumin as a sensitizer requires more detailed studies to evaluate the feasibility and benefits of its clinical use.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 8 Pages 1456-1459Association between Weight Gain and Sex-Related Differences through 5-Fluorouracil Administration Read moreEditor's pick
The authors investigated sex differences in weight gain induced by the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in mice. The results revealed a decrease in estradiol and an increase in ghrelin in female mice, along with elevated noradrenaline levels. The increase in noradrenaline inhibits the estradiol-producing enzyme aromatase and raises adrenergic receptors in the ovaries. This suggests that 5-FU treatment promotes weight gain in female mice by lowering estradiol levels and increasing ghrelin levels through sympathetic nerve stimulation, which enhances appetite. This study aims to elucidate the mechanism of 5-FU-induced weight gain in women with breast cancer, as reported in clinical practice.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 7 Pages 1282-1287Application of a Fluorescence Recovery-Based Polo-Like Kinase 1 Binding Assay to Polo-Like Kinase 2 and Polo-Like Kinase 3 Read moreEditor's pick
Affinity for target proteins and target selectivity are among the most important factors in drug development. The authors previously developed a fluorescence recovery-based polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) kinase domain-directed binding assay using an ATP-competitive Plk1 inhibitor-based fluorescent probe. Herein the authors expanded the assay system to other Plk family members by successfully constructing novel binding assay methodology for the kinase domains of Plk2 and Plk3. The authors also demonstrated that polo-box domain-directed affinity evaluation against full-length Plk’s 1–3 requires much higher affinity probes to overcome auto-inhibition.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 7 Pages 1314-1320EphA4 Induces the Phosphorylation of an Intracellular Adaptor Protein Dab1 via Src Family Kinases Read moreEditor's pick
Dab1 is an intracellular adaptor protein, and its tyrosine phosphorylation plays an important role in various events of brain development. Loss of Dab1 has been associated with the onset of neuropsychiatric disorders in humans. The authors demonstrate a novel mechanism for Dab1 phosphorylation by EphA4, a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase family. EphA4-mediated Dab1 phosphorylation requires autophosphorylation of EphA4 and activity of Src family tyrosine kinases. Cultured neurons expressed EphA4 and Dab1, but activation of EphA4 by ephrin A5 did not induce Dab1 phosphorylation, suggesting that Dab1 is localized in a different compartment in them.
-
Editor's pick
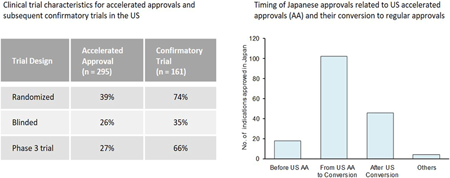
The Accelerated Approval (AA) Program of the United States (US) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) expedites access to new drugs for serious conditions, while Japan's conditional approval system remains underutilized. The authors analyzed postmarketing requirement compliance for AA drugs and their approval timing in Japan. These findings indicate that while the US AA program is well-managed, Japan needs improvements to actively utilize its conditional approval system, enabling rapid introduction of innovative drugs and timely confirmation of their efficacy and safety.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 7 Pages 1368-1375Difference in Contractile Mechanisms between the Early and Sustained Components of Ionomycin-Induced Contraction in Rat Caudal Arterial Smooth Muscle Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Vascular smooth muscle contraction has two phases, an early phase and a sustained phase. Using ionomycin, which increases cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) without membrane depolarization or receptor stimulation, the authors demonstrated that the early phase of contraction is due to activation of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) via Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM), and the sustained phase is due to activation of the CaM-independent RhoA/ Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) pathway via proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2). These findings suggest Pyk2 may be a new therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease. -
Editor's pick
18-β-Glycyrrhetinic acid (GA) is widely incorporated into hair care cosmetic products as an anti-inflammatory agent to maintain a healthy scalp. This study revealed that GA possesses anti-inflammatory effects on the scalp as well as novel effects on hair, including the stimulation of proliferation in human dermal papilla cells and human outer root sheath cells, and the inhibition of 5α-reductase. Promoting the proliferation of these two types of cells is influential in forming thicker and longer hair, while inhibiting 5α-reductase is effective in improving androgenetic alopecia.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 6 Pages 1119-1122Epigenetic Regulation of Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Expression by Nitric Oxide in Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells Read moreEditor's pick
S-Nitrosylation of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) inhibits its enzymatic activity, resulting in DNA hypomethylation and aberrant gene expression related to its pathogenesis. The authors demonstrated that nitric oxide epigenetically induces CA9 expression in human small airway epithelial cells through pharmacological evaluation using DBIC, a specific inhibitor of DNMT3B S-nitrosylation. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1α) is recruited to the CA9 promoter region via nitric oxide-induced epigenetic regulation. These findings indicate that nitric oxide is a key epigenetic regulator in normal human cells.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 6 Pages 1148-1153CRISPRa Analysis of Phosphoinositide Phosphatases Shows That TMEM55A Is a Positive Regulator of Autophagy Read moreEditor's pick
Transcriptional activation of endogenous genes using clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats activation (CRISPRa) is an excellent tool not only for biological research but also for treatment of diseases. The authors have successfully upregulated three endogenous genes encoding phosphoinositide phosphatases using the CRISPRa system targeting multiple promoter sites. The effects of gene upregulation on autophagy, a potential therapeutic target for various diseases, were investigated. The results showed that TMEM55A/PIP4P2, a phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 4-phosphatase, promotes autophagosome formation. It was also revealed that TMEM55B/PIP4P1 and SAC1 are involved in autolysosome formation.
-
Editor's pick
The increasing number of patients with depressive disorder is a serious socioeconomic problem worldwide, and effectiveness of several therapeutic agents used clinically is insufficient and thus discovery of novel therapeutic targets is desired. Focusing on dysregulation of neuronal purinergic signaling in depressive-like behavior, Nishioka et al. revealed that in astrocytes derived from cerebral cortex of chronic social defeat stress-susceptible mice, the expression levels of mRNAs for connexin 43 and P2X7 receptors were inversely correlated with mouse sociability. Together with recent findings, it is suggested that ATP channels expressed by cortical astrocytes might be potential therapeutic targets for depressive disorder.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 6 Pages 1209-1217Heterogenous Gene Expression of Bicellular and Tricellular Tight Junction-Sealing Components in the Human Intestinal Tract Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
This study revealed the gene expression profiles of bicellular and tricellular tight junction components in different segments of the human intestinal tract. Claudin-8, angulin-1 and -2 could be potential targets for intestinal permeation enhancers in the rectum. Claudin-2 and -15 may serve as targets for drug absorption enhancers in the upper intestine. Claudin-7, occludin, and tricellulin appear to be suitable targets for enhancing drug absorption throughout all intestinal segments. Furthermore, claudin-3, -4, and -7 modulators seem to be the most potent intestinal permeation enhancers. Thus, this study provides valuable insights for the development of intestinal drug permeation enhancers. -
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 6 Pages 1218-1223Omeprazole Induces CYP3A4 mRNA Expression but Not CYP3A4 Protein Expression in HepaRG Cells Read moreEditor's pick
Understanding the mechanisms behind the induction or inhibition of CYP enzymes, which are pivotal for drug metabolism, is essential for predicting drug-drug interactions (DDI). In this study, the authors demonstrate that omeprazole, a well-known inducer of CYP1A2, not only increased CYP1A2 mRNA expression but also elevated CYP3A4 mRNA levels. However, omeprazole treatment did not lead to an increase in CYP3A4 protein levels because it caused the CYP3A4 protein to degrade more quickly. These findings suggest that evaluating CYP protein degradation, in addition to CYP induction and inhibition, is crucial for more accurate DDI predictions.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 5 Pages 895-903New Directions for Advanced Targeting Strategies of EGFR Signaling in Cancer Read moreEditor's pick
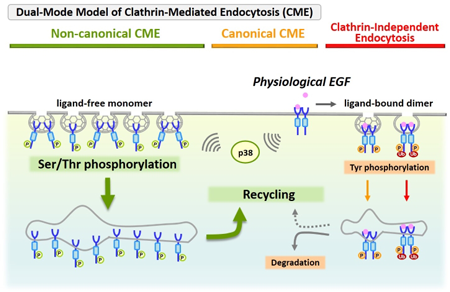
Since the first report of epidermal growth factor (EGF) in 1962, research on intracellular signaling through its receptor EGFR has greatly advanced. While the canonical activation of EGFR via tyrosine phosphorylation is well understood, the existence of a non-canonical activation via p38-dependent phosphorylation of serine/threonine residues has recently attracted attention. The authors have found that both of these mechanisms occur in parallel and are now analyzing them as a dual-mode activation model. This review summarizes new advances in EGFR signaling research and the latest status of EGFR inhibitor development for molecular targeted therapy of lung cancer.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 5 Pages 905-911From Glycolysis to Viral Defense: The Multifaceted Impact of Glycolytic Enzymes on Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Replication Read moreEditor's pick
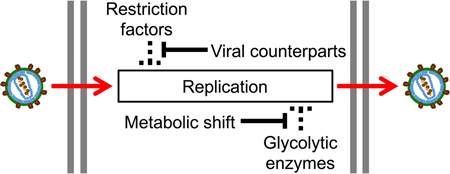
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) hijacks various cellular machinery to achieve efficient replication. HIV-1 infection induces a metabolic shift towards aerobic glycolysis as a cellular response to maintain homeostasis, yet the virus continues to replicate efficiently under these conditions. In this review, the authors introduce the regulatory role of glycolytic enzymes in HIV-1 replication and the impact of aerobic glycolysis on viral infection. In addition, the authors propose a novel strategy to eradicate latently HIV-1-infected cells.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 5 Pages 978-987The Influence of Emodin Succinyl Ethyl Ester on Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Induced by a Diet High in Fructose, Cholesterol, and Fat in Mice Read moreEditor's pick
[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a serious form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) that can lead to liver damage and inflammation. In this study, the authors focused on the therapeutic effects of emodin succinyl ethyl ester (ESEE) on NASH using a murine model induced by Special tailored diet. After four weeks of ESEE treatment, researchers observed significant improvements in glycolipid metabolism disorders, liver injury, and histopathological features of NAFLD/NASH. ESEE showed effectiveness in reducing cellular steatosis, inflammation, fat deposition in hepatocytes, and liver fibrosis in the model mice. These findings suggest that ESEE could serve as a novel therapeutic agent for NASH, providing protection against diet-induced liver abnormalities and injuries. -
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 5 Pages 1021-1027Short-Term Preexposure to Novel Enriched Environment Augments Hippocampal Ripples in Urethane-Anesthetized Mice Read moreEditor's pick
Exposure of animals to the enriched environments improves memory consolidation that requires extracellular ripples generated in the hippocampus during sleep. Natural sleep and general anesthesia are similar in terms of extracellular oscillations. However, whether the preexposure of animals to the enriched environment modulates neural activity in the hippocampus under subsequent anesthesia is not fully understood. The authors allowed mice to explore the enriched or standard environment, anesthetized them, and recorded local field potentials in the hippocampus, demonstrating that the amplitude of ripples and the number of successive ripples were larger in the novel enriched environment group.
-
Volume 47 (2024) Issue 4 Pages 868-871Carbon Monoxide Alleviates Post-ischemia–reperfusion Skeletal Muscle Injury and Systemic Inflammation Read moreEditor's pick
Carbon monoxide (CO) exhibits versatile bioactivities; its preventive effect on the progression of ischemia-reperfusion injury in various organs has been reported. The authors developed CO-bound red blood cells (CO-RBC) as a bioinspired CO delivery donor and investigated the therapeutic potential of CO-RBC against ischemia-reperfusion injury in the hind limbs of rats. As a result, CO-RBC alleviated the skeletal muscle injury and systemic inflammation following ischemia-reperfusion in the rat model. The present study significantly contributes to the advancement of CO-based therapeutic strategies for treating skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury.