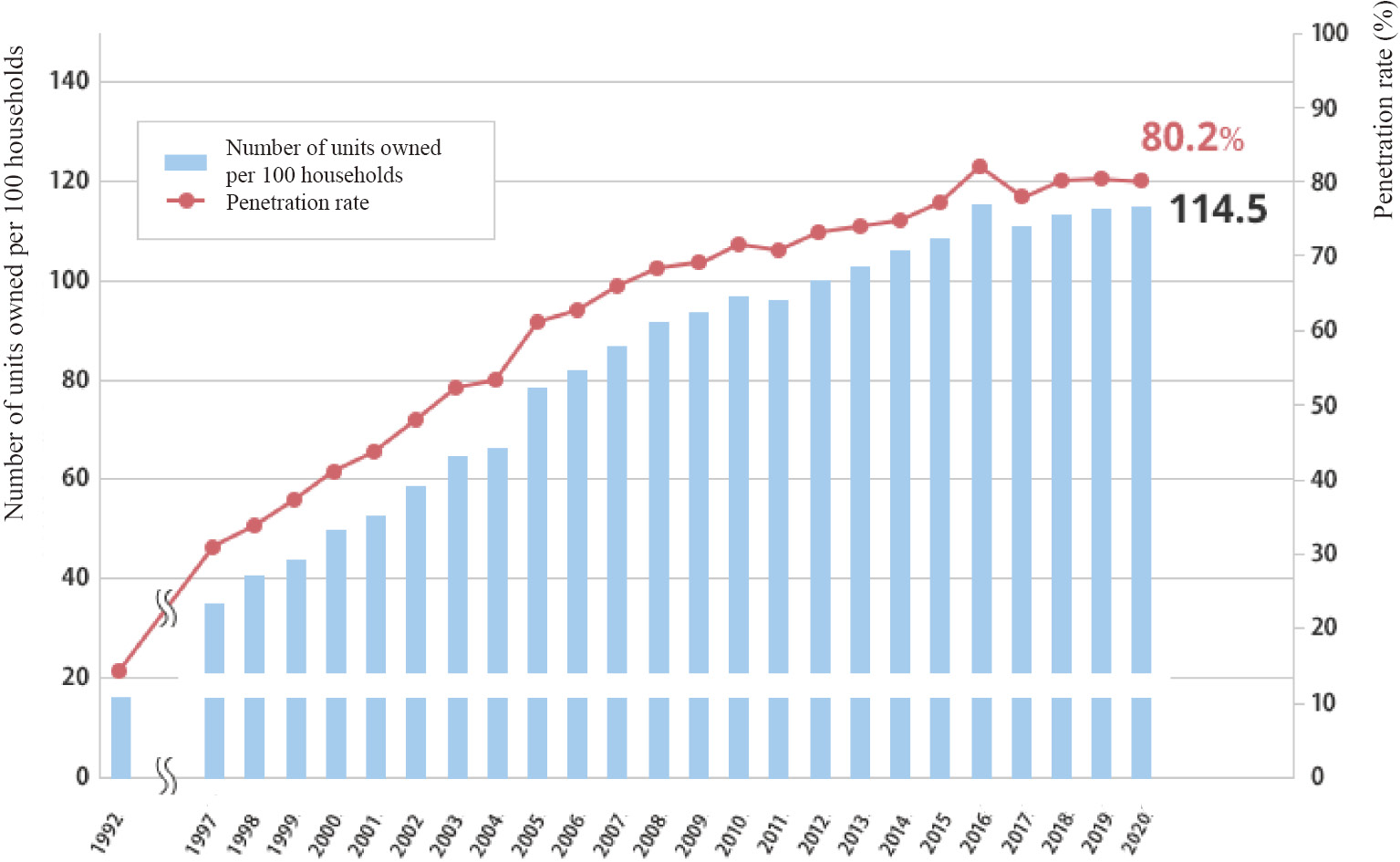
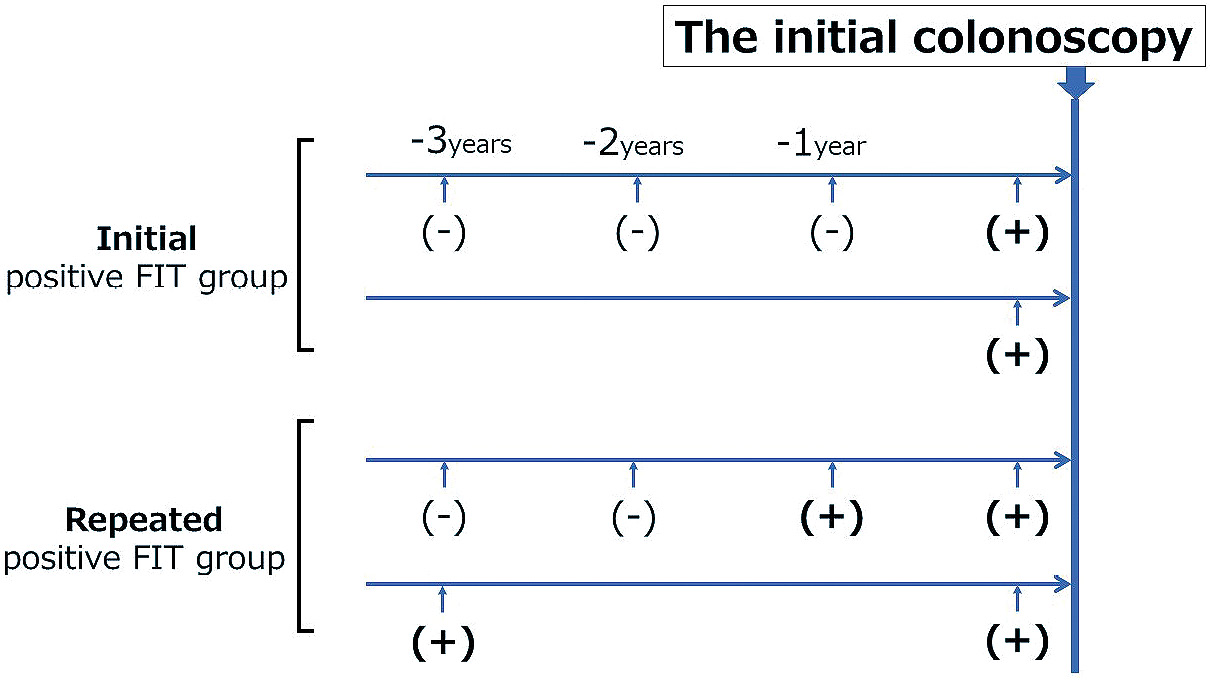
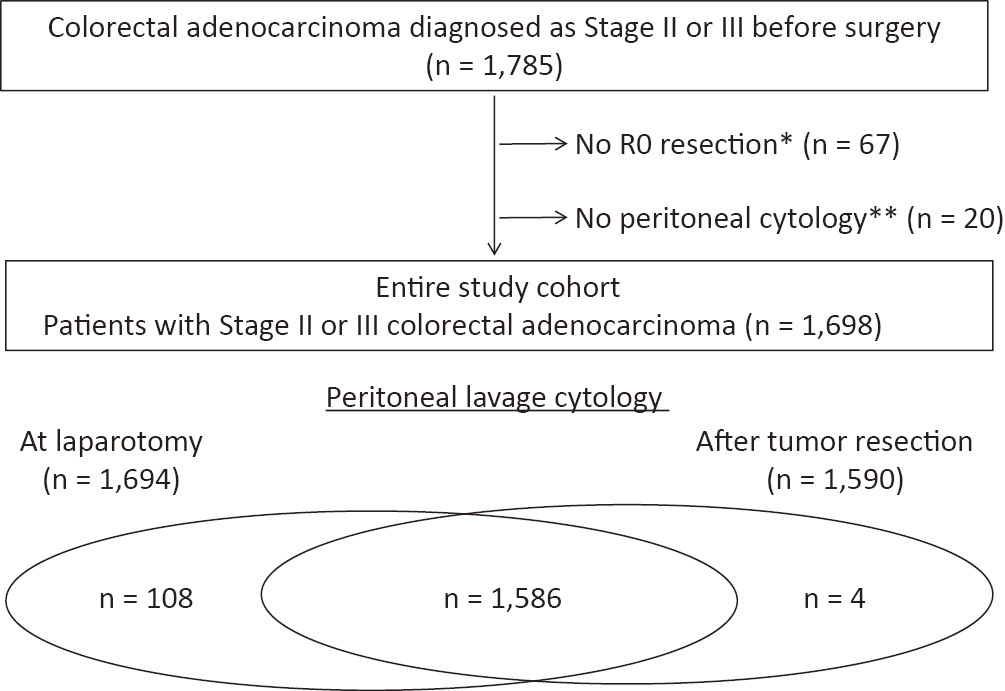
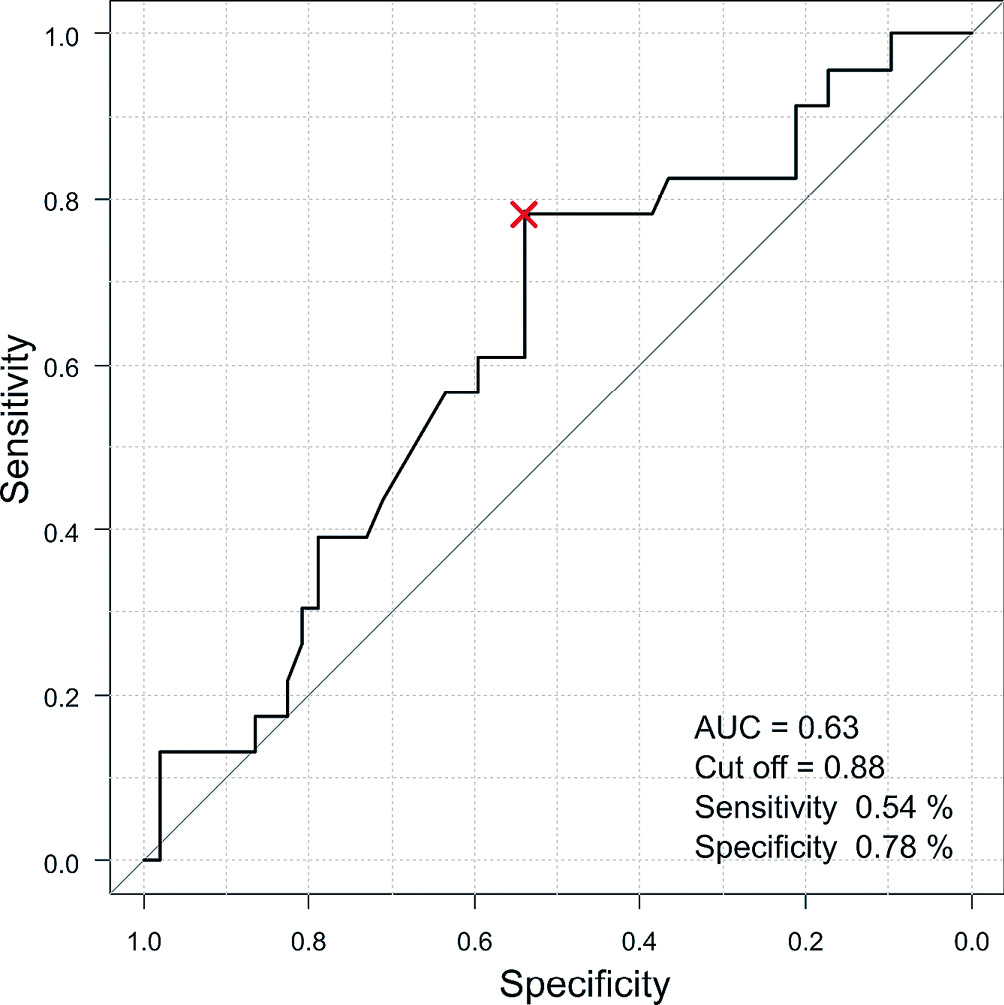
Volume 5, Issue 4
Displaying 1-14 of 14 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Review Article
-
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 335-339
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (251K)
Original Research Article
-
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 340-345
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (273K) -
Usefulness of a Precursory Small Epigastric Midline Incision during Laparoscopic Right Hemicolectomy2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 346-354
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (753K) -
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 355-365
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (179K) -
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 366-375
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (514K) -
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 376-385
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (339K) -
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 386-394
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (322K) -
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 395-404
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (182K) -
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 405-413
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (720K)
Trial Protocol
-
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 414-418
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (133K)
Clinical Research
-
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 419-425
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (151K) -
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 426-432
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (147K)
Case Report
-
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 433-438
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (914K)
Erratum
-
2021Volume 5Issue 4 Pages 439
Published: October 28, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2021
Download PDF (48K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|