Volume 6, Issue 1
Displaying 1-10 of 10 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Review Article
-
2022Volume 6Issue 1 Pages 1-8
Published: January 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2022
Download PDF (519K) -
2022Volume 6Issue 1 Pages 9-15
Published: January 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2022
Download PDF (170K)
Original Research Article
-
2022Volume 6Issue 1 Pages 16-23
Published: January 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2022
Download PDF (314K) -
2022Volume 6Issue 1 Pages 24-31
Published: January 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2022
Download PDF (193K) -
2022Volume 6Issue 1 Pages 32-39
Published: January 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2022
Download PDF (216K) -
2022Volume 6Issue 1 Pages 40-51
Published: January 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2022
Download PDF (493K)
Trial Protocols
-
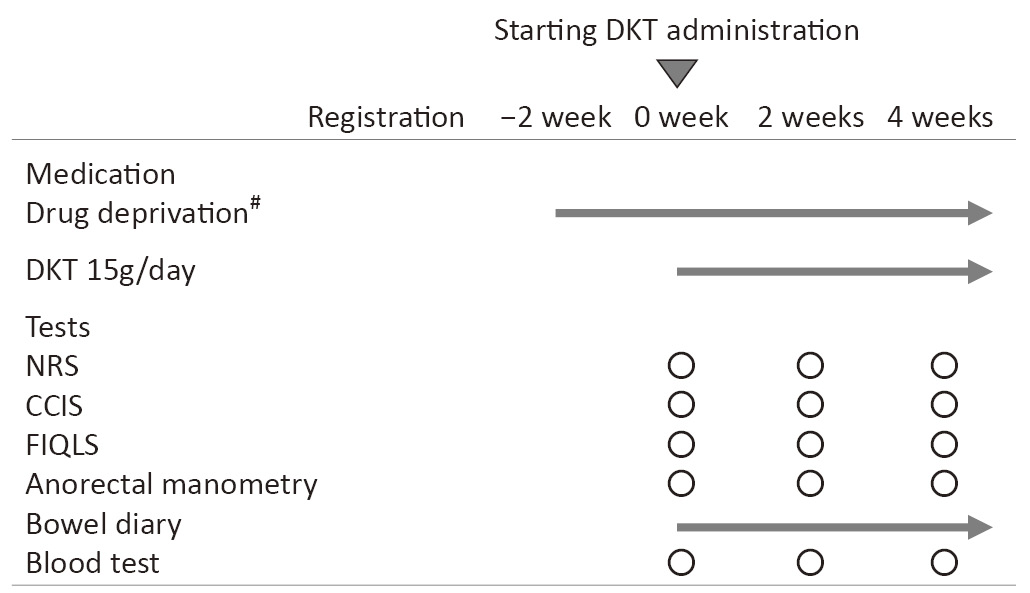
2022Volume 6Issue 1 Pages 52-57
Published: January 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2022
Download PDF (135K)
Practice Guidelines
-
2022Volume 6Issue 1 Pages 58-66
Published: January 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2022
Download PDF (1241K)
Case Report
-
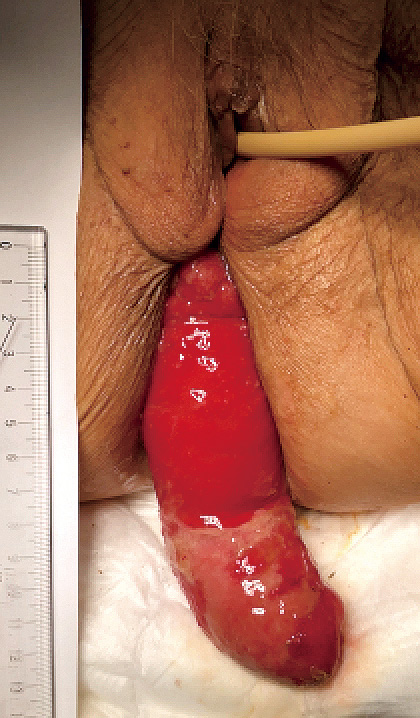
2022Volume 6Issue 1 Pages 67-71
Published: January 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2022
Download PDF (759K)
How I do it
-
2022Volume 6Issue 1 Pages 72-76
Published: January 28, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 28, 2022
Download PDF (745K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|