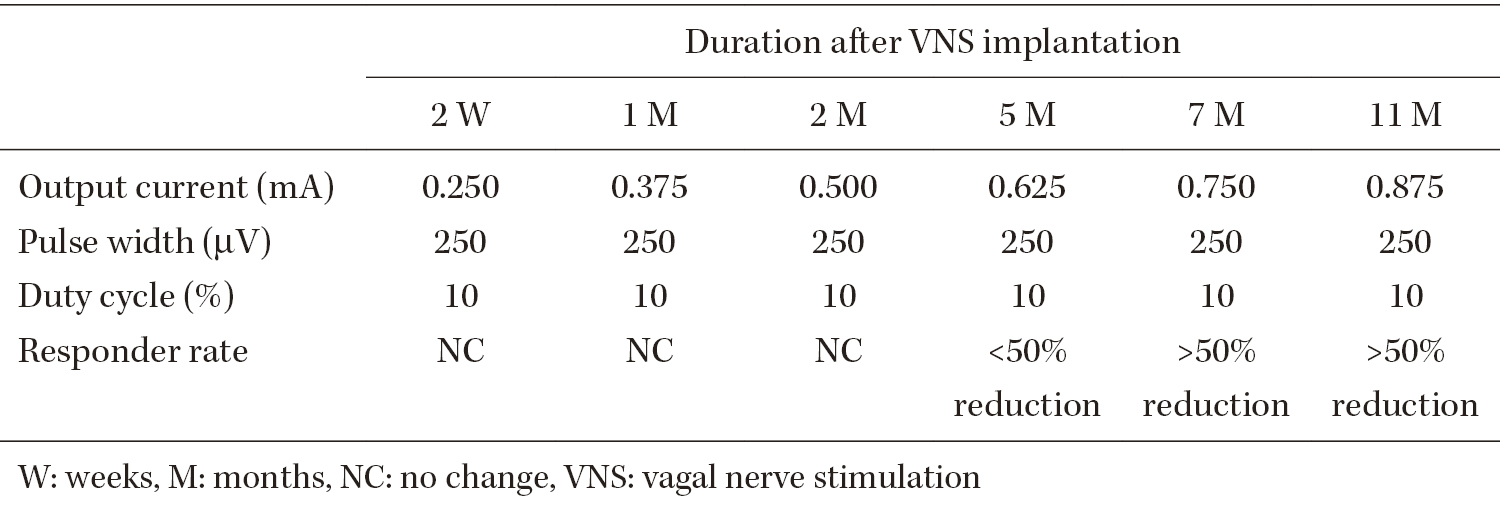
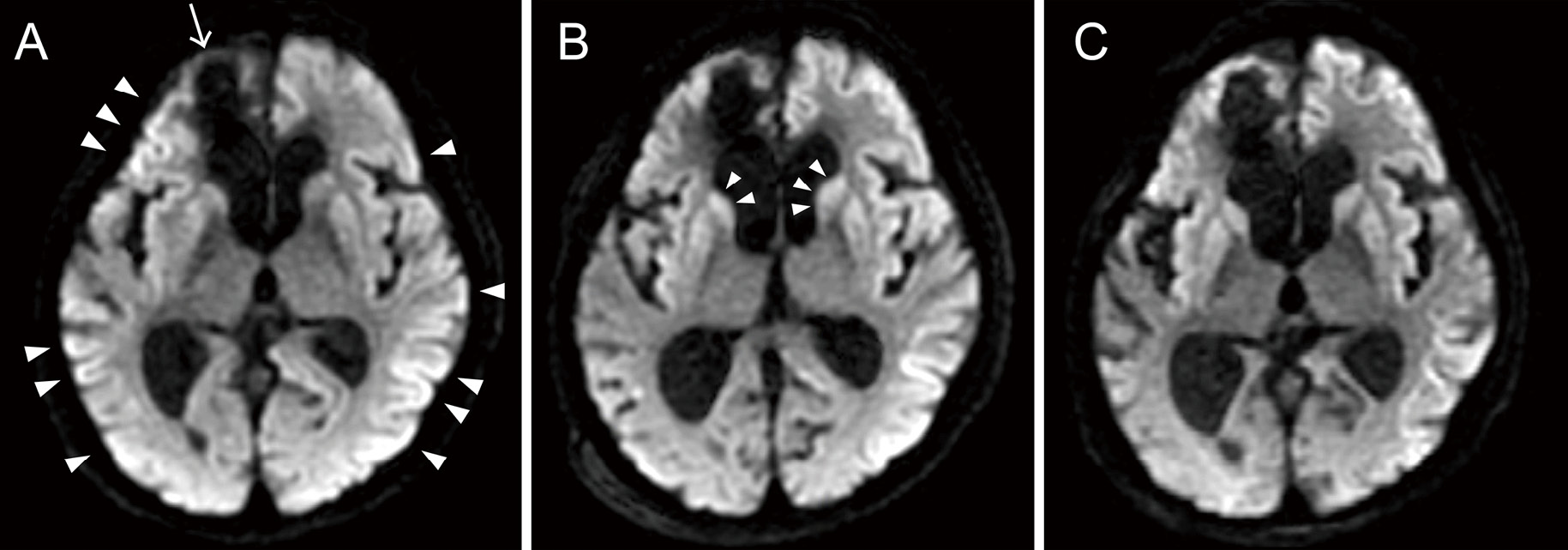
Volume 10
Displaying 51-57 of 57 articles from this issue
CASE REPORT
-
2023Volume 10 Pages 321-325
Published: December 31, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 11, 2023
Download PDF (137K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 10 Pages 327-330
Published: December 31, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 29, 2023
Download PDF (477K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 10 Pages 331-335
Published: December 31, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 29, 2023
Download PDF (843K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 10 Pages 337-342
Published: December 31, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 29, 2023
Download PDF (1184K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 10 Pages 343-348
Published: December 31, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2023
Download PDF (1318K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 10 Pages 349-354
Published: December 31, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2023
Download PDF (677K) Full view HTML
TECHNICAL NOTE
-
2023Volume 10 Pages 273-278
Published: December 31, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 14, 2023
Download PDF (722K) Full view HTML