-
70 巻 (2022) 12 号 p. 885-891Natural Compounds with BMI1 Promoter Inhibitory Activity from Mammea siamensis and Andrographis paniculata もっと読む編集者のコメント
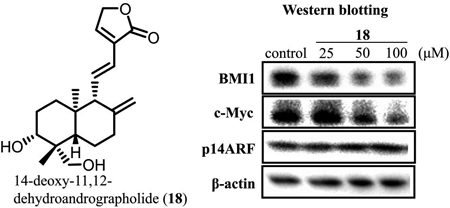
B cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion region 1 (BMI1) is known to be highly expressed in cancer stem cells that contribute to cancer recurrence and metastasis. The authors isolated a new coumarin derivative (1) and 30 known compounds from two plants (Mammea siamensis and Andrographis paniculata), guided by BMI1 promoter inhibitory activity. Among the isolated compounds, 15 compounds showed BMI1 promoter inhibitory activity, and five compounds were found to be cytotoxic against cancer cells. 14-Deoxy-11,12-dehydroandrographolide (18) was highly cytotoxic to DU145 cells. Western blotting analysis of compound 18 in DU145 cells suggested that compound 18 suppresses BMI1 expression.
-
70 巻 (2022) 12 号 p. 892-900Quantitative 31P-NMR for Purity Determination of Sofosbuvir and Method Validation もっと読む編集者のコメント
31P-qNMR in organic solvents was performed by using an organophosphorus compound, sofosbuvir (SOF) with phosphonoacetic acid (PAA) as the qNMR reference standard. In a protic solvent, methanol-d4, the purity of SOF determined by 31P-qNMR was 1.6% higher than that by 1H-qNMR. This difference most likely arose from the instability in the chemical shift due to the deuterium exchange of the acidic protons of PAA. In an aprotic solvent, DMSO-d6, the purity determined by 31P-qNMR agreed with the 1H-qNMR one, suggesting that an aprotic solvent is preferable for 31P-qNMR because it is unnecessary to consider the effect of deuterium exchange.
-
70 巻 (2022) 12 号 p. 901-906Omphalines A–E: ent-Rosane-Type Diterpenoids from the Madagascar Endemic Plant, Omphalea oppositifolia もっと読む編集者のコメント
Many species of flora and fauna in Madagascar were independently developed from other regions of the world. Thus, about 80% of 15,000 species of plants growing there is endemic and the editor very much appreciates that Omphalea oppositifolia (Euphorbiaceae) was collected by the authors’ own expedition to Madagascar. From the leaves and twigs of O. oppositifolia, one new ent-nor-rosane and four new ent-rosane-type diterpenoids were isolated. Rosane-type diterpenoids are rarely found in nature. Their structures were elucidated by the spectroscopic analyses and the absolute configuration was determined by the comparison of experimental and calculated ECD spectra.
-
編集者のコメント
The authors have established simple and accurate methods for quantifying sugars in herbal medicines, which have hitherto been difficult to quantify. The optimum conditions for separating nine sugars were determined by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and two types of columns with different chemical properties. One method enabled analysis within 10 min for galactose-free materials such as Japanese Angelica root, and the other enabled it within 16 min for materials containing both glucose and galactose, such as Rehmannia root. These methods can be widely used for sugar quantification in the quality evaluation of herbal medicines.
-
-
編集者のコメント
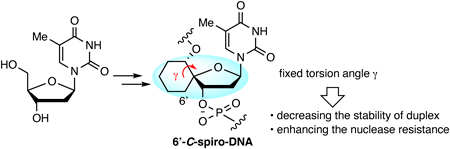
In recent years, research on antisense oligonucleotides and small interfering ribonucleic acids (siRNAs) has progressed rapidly. These oligonucleotide therapeutics have great potentials for the treatment of diseases that are difficult to approach with conventional drugs. To apply oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents, they are generally modified with artificial nucleic acids because natural DNA and RNA do not have sufficient duplex-forming ability or stability against nucleases. In this report, the authors designed and synthesized 6ʹ-C-spiro-thymidine with a fixed torsion angle γ as a novel material for oligonucleotide therapeutics.
-
70 巻 (2022) 10 号 p. 707-715Hydrazide-Mediated Solubilizing Strategy for Poorly Soluble Peptides Using a Dialkoxybenzaldehyde Linker もっと読む編集者のコメント
Chemically synthesized proteins are increasingly becoming a research tool for elucidating protein functions. Ligation technologies proceeding in aqueous conditions have accelerated chemical protein synthesis; however, poorly soluble characteristics of peptide intermediates often hamper the synthesis of proteins that researchers may need.
Kohei Sato and co-workers report late-stage solubilization of peptide hydrazides using hydrophilic tags possessing a dialkoxybenzaldehyde moiety. The inherent advantage of this approach is the superior property for easy attachment and detachment of the solubilizing tags, which is ideal for a broad substrate scope. Using this methodology, the researchers synthesized a ubiquitin dimer derivative successfully. -
編集者のコメント
The authors reported the computation-guided total synthesis of vitisinol G, a resveratrol dimer. Computational chemistry is useful in synthetic organic chemistry, as it can be used not only to analyze reaction mechanisms, but also to calculate biosynthetic pathways and to plan and evaluate strategies for total syntheses. They focused on the semi-pinacol rearrangement derived from calculations of the biosynthetic pathway of resveratrol dimers. DFT calculations were used to develop a synthetic strategy and the total synthesis of vitisinol G at 7.8% was achieved in 4 steps from resveratrol.
-
編集者のコメント
Molecular space chemistry is an important concept for the design of novel functional materials and catalysts. The research group “Molecular space chemistry for the chemical conversion” was established by the member who advocate that the organic integration of supramolecular chemistry and catalytic chemistry enables flexible chemical conversion in multi-component molecular ensembles. It is noteworthy that most of the member got a position of full professor (or similar position) in these few years. To this volume of Chem. Pharm. Bull., four of the members, who have deep connection with the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, contribute their cutting-edge results.
-
編集者のコメント
This report describes the synthesis of novel dual-purpose reagents, p-methoxybenzyl N-acetylcarbamate potassium salt (PM-BENAC-K) and 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl N-acetylcarbamate potassium salt (2,4-DM-BENAC-K). The BENAC-Ks were stable colorless powders synthesized via a simple three-step procedure without column chromatography, which can be easily scaled-up. The BENAC-Ks reacted with various alkyl halides and sulfonates to form substituted products that were converted to N-alkylacetamides via acid-mediated deprotection. Simultaneously, p-methoxybenzyl and 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl carbamates were obtained via base-mediated deacetylation. Thus, the BENAC-Ks are worth remembering as simple reagents for synthesis of acetamides and benzyl carbamates.
-
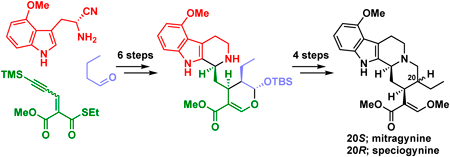
70 巻 (2022) 9 号 p. 662-668Asymmetric Total Syntheses of Mitragynine, Speciogynine, and 7-Hydroxymitragynine もっと読む編集者のコメント
Mitragyna speciosa, which belongs to the Rubiaceae family, contains several corynantheine-type monoterpenoid indole alkaloids that exhibit potent biological activity, including analgesic activity. In this article, the authors reported the asymmetric total syntheses of such Mitragyna alkaloids mitragynine, speciogynine, and 7-hydroxymitragynine. These syntheses were accomplished via asymmetric organocatalytic Michael reaction, diastereoselective Pictet-Spengler cyclization, and biogenetically inspired chemical transformations within 12 steps and in >11% overall yield from commercially available materials. These syntheses will strongly promote the structure-activity relationship study of Mitragyna alkaloids.
-
編集者のコメント
Biomembranes constitute the boundary between the living organism and the external environment, and their function is essential for maintaining biological activities. Quantitative understanding and precise control of the transport and conversion of various substances across biomembranes are important issues in biophysics and cell biology, but dealing with biomembranes, which are multi-component, heterogeneous, and complex systems, is not an easy task. In the Current Topics, investigators who are boldly tackling this area of research introduce recent advances in biophysical and molecular biological aspects and technology.
-
70 巻 (2022) 8 号 p. 540-543Site-Selective α-Alkylation of 1,3-Butanediol Using a Thiophosphoric Acid Hydrogen Atom Transfer Catalyst もっと読む編集者のコメント
The linear 1,3-diol structure is a common motif in biologically active molecules. C-H functionalization at an α-position of alcohols leads to efficient synthesis of sugars and polyols. However, regioselective conversions at the alcohol α-position of linear 1,3-diols have been limited. Nakao et al. developed secondary-alcohol-selective C-H alkylation of 1,3-butane diol by combining an acridinium photoredox catalyst and a thiophosphoric acid hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) catalyst. The use of DCM as a solvent with a relatively small dipole moment improved secondary α-alkoxy C-H selectivity by making the C-H abstraction process the rate-limiting step.
-
編集者のコメント
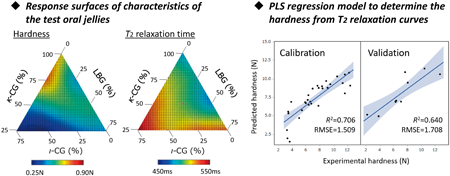
Hardness is a critical quality characteristic of pharmaceutical oral jelly. The purpose of this study is to determine the hardness using time-domain NMR (TD-NMR). After measurement of the T2 relaxation curves of the test jellies by TD-NMR, the acquired data were analyzed by partial least squares (PLS) regression analysis. Eventually, an accurate and reliable PLS model was created that enabled accurate assessment of the hardness of the test jellies. TD-NMR enables the measurement of samples nondestructively and rapidly with low cost, and so could be a promising method for evaluation of the hardness of pharmaceutical oral jellies.
-
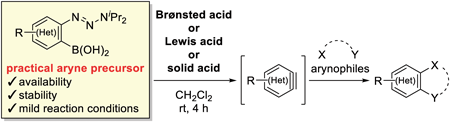
70 巻 (2022) 8 号 p. 566-572Aryne Generation from o-Triazenylarylboronic Acids Induced by Brønsted Acid もっと読む編集者のコメント
This paper describes acid-mediated aryne generation from o-triazenylarylboronic acids. The authors previously reported these practical aryne precursors generate arynes by the treatment with silica gel. In this paper, they reported acids including Brønsted acids, Lewis acids, and solid acids are also effective for aryne generation from the precursors. In particular, the use of camphorsulfonic acid provided high yields in reactions with a range of arynophiles, and enabled chemoselective reaction with a furan in the presence of an amine. Hammett plot analyses revealed that an aryne generation mechanism induced by the acid is distinct from the mechanism induced by silica gel.
-
70 巻 (2022) 7 号 p. 458-468Progress in Chiral Stationary Phases Based on Proteins and Glycoproteins もっと読む編集者のコメント
The ligand-binding sites of F1*S and A variants of human α-acid glycoprotein (hAGP), and chicken AGP were completely different. The former sites were located in lobs I-III including W122, while the later ones were located near W26. Both (R)- and (S)-benzoin were docked onto a cavity of the generated model structure of cAGP. In addition to hydrophobic interactions, some of hydrogen bonding interactions worked for chiral recognition of (R)- and (S)-benzoin. (R)-Benzoin bound to cAGP more tightly than (S)-benzoin. The elution order of benzoin enantiomers on chiral stationary phases based on cAGP in LC were consistent with the docking results.
-
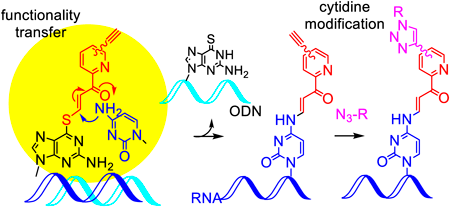
編集者のコメント
Due to the importance of chemical modification of RNA, methods for chemical modification at a predetermined site in an internal position of RNA have attracted much attention. The authors have developed an original method for the base- and sequence-specific modification by transferring the functional group of the oligonucleotides to RNA through the formation of hybrid complexes. To achieve further modification by copper-catalyzed alkyne-azide cycloadditions, the authors investigated transfer groups with the tri-, tetra- and pentaethylene glycol-linked alkynes. As a result, the transfer groups with tetra- and pentaethylene linkers were determined to be promising compounds to internally modify long RNA.
-
70 巻 (2022) 6 号 p. 420-426Enhancing Anticancer Potency of a 13-Substituted Berberine Derivative with Cationic Liposomes もっと読む編集者のコメント
This paper reports the successful use of a cationic liposomal-encapsulated novel 13-substituted berberine derivative for the targeted cell uptake and delivery to the cancer cell nucleus. Additionally the liposome also assists with stabilization of the selectively toxic anticancer berberine derivative with respect to oxidative cleavage in solution. Liposomes derived from a cholesterol-based lipid with a polar side chain which would become cationic after amine protonation, were of particular interest. Enhanced cancer cell toxicity was seen in vitro with the cationic liposomal formulation of the berberine derivative possibly via inhibitory interactions with the cell’s telomere/telomerase system.
-
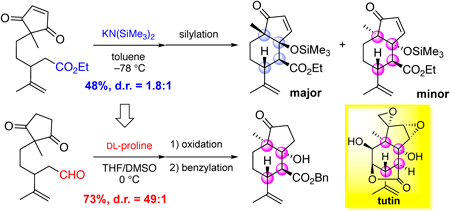
編集者のコメント
This paper describes a stereoselective synthesis of a cis-fused 5,6-ring skeleton in picrotoxane-type sesquiterpenes. This bicyclic skeleton is a synthetic challenging structure because of the presence of multiple consecutive stereocenters including two tetrasubstituted carbons at the angular positions. The authors developed a synthetic method of the core structure via DL-proline-mediated intramolecular aldol reaction accompanied with the desymmetrization of the 2-methyl-1,3-cyclopentanedione moiety and the construction of four contiguous stereocenters. This reaction can be also applied to the kinetic resolution using L-proline, implying that the established method would be useful for the synthesis of natural products classified as picrotoxane-type sesquiterpenes.
-
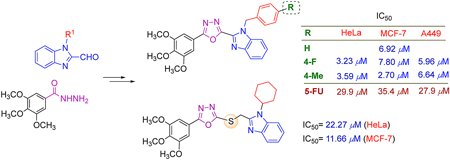
70 巻 (2022) 6 号 p. 448-453Design, Synthesis and Cytotoxicity Evalufation of Substituted Benzimidazole Conjugated 1,3,4-Oxadiazoles もっと読む編集者のコメント
Many drugs being used in chemotherapy of cancer has nitrogen-containing heterocyclic moieties as their basic structure, and the authors extensively focused on the 1,3,4-oxadiazole and benzimidazole scaffolds. In this article, two series of novel hybrids combining the 1,2-disubstituted benzimidazole and 1,3,4-oxadiazole or thioether linked 1,3,4-oxadiazole were designed and successfully synthesized. The in vitro cytotoxicity bioassays came up with the discovery of three lead compounds which displayed 4.5-13 fold increase in activity compared to 5-FU against the three human cancer cell lines (HeLa, MCF-7, A549), meriting further characterization and serving as promising scaffolds in the discovery of new potent anticancer agents.