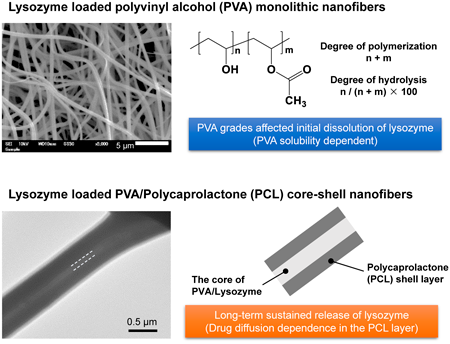
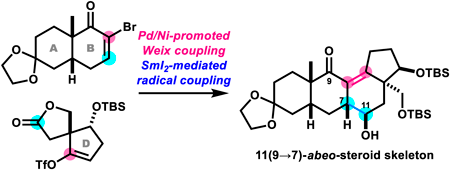
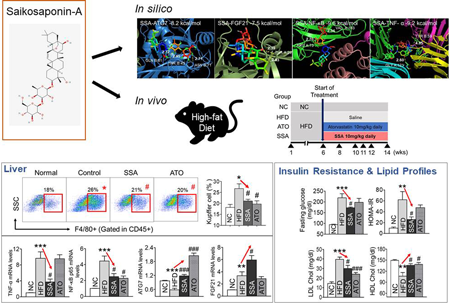
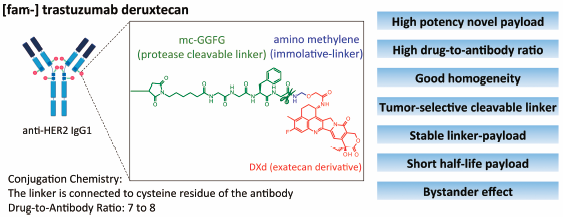
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin
The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, established in 1880, is one
of Japan’s oldest and most distinguished academic societies. The Society currently
has around 15,000 members. It publishes three monthly scientific journals. Chemical
and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (Chem.
Pharm. Bull.) began publication in 1953 as Pharmaceutical Bulletin. It
covers chemistry fields in the pharmaceutical and health sciences. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (Biol.
Pharm. Bull.)
began publication in 1978 as the Journal of Pharmacobio-Dynamics. It covers
various biological topics in the pharmaceutical and health sciences. A fourth Society
journal, the Journal of Health Science, was merged with Biol. Pharm. Bull. in 2012. Yakugaku
Zasshi (Japanese for “Pharmaceutical Science Journal”) has the longest
history, with publication beginning in 1881. Yakugaku Zasshi is
published mostly in Japanese, except for some articles related to clinical
pharmacy and pharmaceutical education, which are published in English.
The main aim of the Society’s journals is to advance the pharmaceutical sciences with research reports, information exchange, and high-quality discussion. The average review time for articles submitted to the journals is around one month for first decision. The complete texts of all of the Society’s journals can be freely accessed through J-STAGE. The Society’s editorial committee hopes that the content of its journals will be useful to your research, and also invites you to submit your own work to the journals.
Chairman of Committee
Sumio Ohtsuki
Faculty of Life Sciences, Kumamoto University
Read more
The main aim of the Society’s journals is to advance the pharmaceutical sciences with research reports, information exchange, and high-quality discussion. The average review time for articles submitted to the journals is around one month for first decision. The complete texts of all of the Society’s journals can be freely accessed through J-STAGE. The Society’s editorial committee hopes that the content of its journals will be useful to your research, and also invites you to submit your own work to the journals.
Chairman of Committee
Sumio Ohtsuki
Faculty of Life Sciences, Kumamoto University
Published by
The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
28,245 registered articles
(updated on April 25, 2024)
(updated on April 25, 2024)
Online ISSN : 1347-5223
Print ISSN : 0009-2363
ISSN-L : 0009-2363
Print ISSN : 0009-2363
ISSN-L : 0009-2363
1.7
2022 Journal Impact Factor (JIF)
2022 Journal Impact Factor (JIF)
JOURNAL
PEER REVIEWED
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
ADVANCE PUBLICATION
Scopus Pubmed
Scopus Pubmed