
- Issue 5 Pages 057001-
- Issue 4 Pages 043001-
- Issue 3 Pages 037001-
- Issue 2 Pages 022001-
- Issue 1 Pages 017001-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Mitsuhiro KISHIMI, Masahito MORITA, Tatsumi HIRANO, Hisao KIUCHI, Kent ...2024 Volume 92 Issue 5 Pages 057001
Published: May 02, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 02, 2024
Advance online publication: April 04, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
J-STAGE DataThe effects of the current rate used during the first charging (pre-charging: so-called “formation”) on the cathodic deposition of metallic zinc (Zn) were analyzed for the high capacity (thick) zinc oxide (ZnO) electrode in rechargeable Zn-based batteries. Pre-charging at a lower current rate (1.875 mA cm−2) enabled greater electrode performances for the subsequent charge-discharge cycles. The Zn deposition profiles were investigated by conventional postmortem X-ray diffraction (XRD) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy using a scanning electron microscope, as well as in situ synchrotron XRD and ex situ synchrotron X-ray computed tomography. The results revealed significant differences in the deposition profiles of the metallic Zn depending on the current rates used during pre-charging. The higher rate (18.75 mA cm−2) resulted in an inhomogeneous deposition of Zn, whereas the lower rate yielded finer Zn particles dispersed homogeneously throughout the thick ZnO electrode. These morphological and spatial variations in the Zn deposition during pre-charging affected the subsequent cycling behavior of the thick ZnO electrode.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4436K) Full view HTML -
Peikun ZOU, Chunyu XIANG, Xuyang LI, Nayun ZHOU, Binbin FAN, Limin WAN ...2024 Volume 92 Issue 5 Pages 057002
Published: May 03, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 03, 2024
Advance online publication: April 17, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
J-STAGE DataA series of quaternary ammonium salts base on quinacridone aromatic ring were synthesized using 2,9-quinacridone as the parent material, and their leveling performance were evaluated using constant-current chronoamperometry addition curves. Additionally, the adsorption abilities of the leveler molecules on copper surfaces were investigated through quantum chemical calculations and molecular dynamics simulations, and their specific adsorption sites on the copper surface were investigated by XPS, then the effect of concentration on the leveling performance was probed by through-hole plating, and the copper surface was characterized by XRD and SEM. Among four quinacridone aryl quaternary ammonium salts, DCQA-C8-MI exhibits optimal leveling effects, serving as an excellent leveler with outstanding performance. This study expands the application scope of quinacridone aromatic heterocyclic quaternary ammonium salts and offers insights for exploring efficient organic additives for copper electrodeposition.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (7688K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (7688K) Full view HTML -
Hiroyasu NISHI, Taro TOJO, Tetsu TATSUMA2024 Volume 92 Issue 5 Pages 057003
Published: May 09, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 09, 2024
Advance online publication: April 11, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
J-STAGE DataChiral plasmonic nanostructures are of significant interest because of their strong chirality compared to typical chiral molecules and their potential for various applications such as enantioselective sensors and metamaterials. Although chemical or photochemical fabrication methods for chiral nanostructures have attracted attention because of their cost-effectiveness and large-area applicability, most of the chemically synthesized chiral nanostructures are two-dimensional ensembles or arrays of individual chiral nanoparticles. In the present study, more three-dimensional, densely interconnected chiral plasmonic nanoporous structures are fabricated via plasmon-induced dealloying of Au-Ag alloy under circularly polarized light (CPL). CPL is used as a sole chiral source and irradiated to a chemically treated Au-Ag alloy film showing absorption due to localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR). The resulting nanoporous structures exhibit chiroptical responses depending on the handedness CPL illuminated. The mechanism of chirality introduction is discussed on the basis of an electromagnetic simulation.
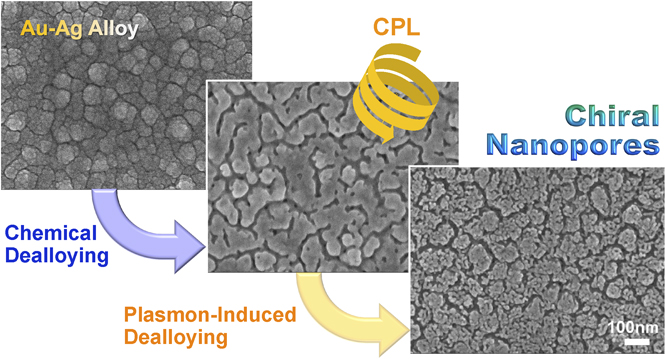 View full abstractDownload PDF (3700K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3700K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|