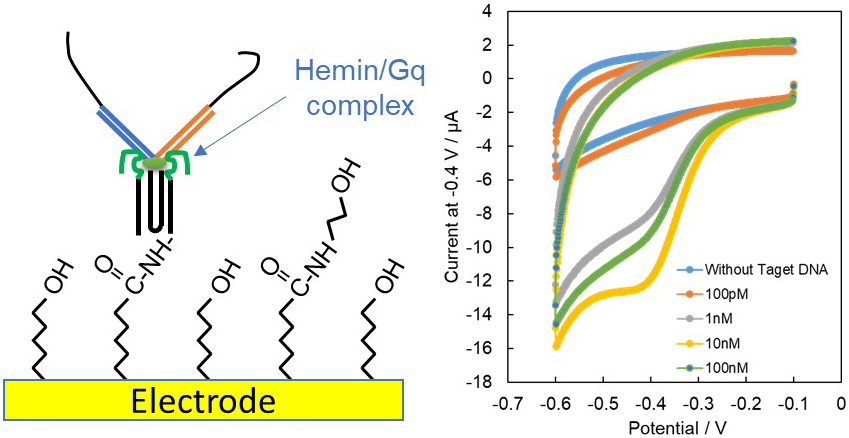
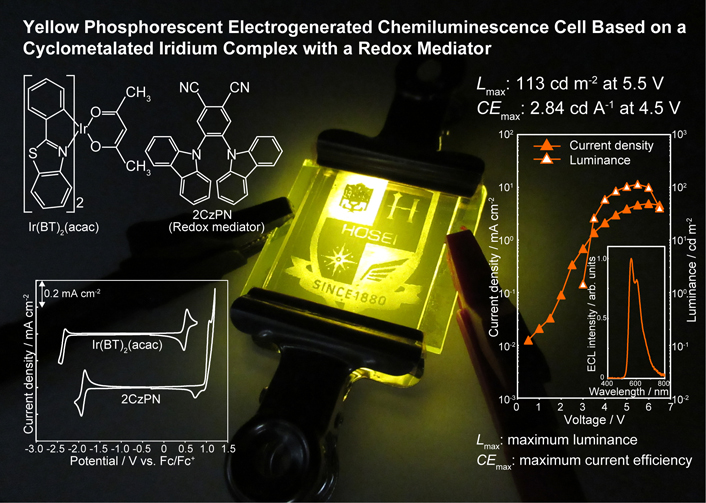
Virtual issue
Volume 92, Issue 2
Displaying 1-28 of 28 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
The 68th special feature “Electrochemistry to Understand Biological Functions”
Editorial
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022001
Published: February 27, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 27, 2024
Advance online publication: December 20, 2023Download PDF (477K) Full view HTML
Headline (Invited Paper)
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022002
Published: February 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 06, 2024
Advance online publication: November 14, 2023Download PDF (819K) Full view HTML
Reviews (Invited Paper)
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022003
Published: February 13, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 13, 2024
Advance online publication: January 11, 2024Download PDF (4057K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022004
Published: February 13, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 13, 2024
Advance online publication: January 12, 2024Download PDF (5190K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022005
Published: February 17, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 17, 2024
Advance online publication: January 24, 2024Download PDF (8246K) Full view HTML
Communication
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022006
Published: February 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 06, 2024
Advance online publication: November 07, 2023Download PDF (1534K) Full view HTML
Note
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022007
Published: February 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 06, 2024
Advance online publication: November 07, 2023Download PDF (2615K) Full view HTML
Articles
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022008
Published: February 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 06, 2024
Advance online publication: November 29, 2023Download PDF (2431K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022009
Published: February 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 06, 2024
Advance online publication: December 08, 2023Download PDF (2505K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022010
Published: February 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 06, 2024
Advance online publication: December 08, 2023Download PDF (1352K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022011
Published: February 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 06, 2024
Advance online publication: December 16, 2023Download PDF (2609K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022012
Published: February 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 06, 2024
Advance online publication: December 12, 2023Download PDF (2187K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022013
Published: February 09, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 09, 2024
Advance online publication: December 12, 2023Download PDF (6139K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022014
Published: February 15, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 15, 2024
Advance online publication: January 11, 2024Download PDF (2435K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022015
Published: February 15, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 15, 2024
Advance online publication: January 20, 2024Download PDF (1816K) Full view HTML
Note
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022016
Published: February 17, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 17, 2024
Advance online publication: January 13, 2024Download PDF (2114K) Full view HTML
Article
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022017
Published: February 20, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 20, 2024
Advance online publication: January 20, 2024Download PDF (4219K) Full view HTML
Communication
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022018
Published: February 29, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 29, 2024
Advance online publication: January 26, 2024Download PDF (2087K) Full view HTML
Article
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 022019
Published: February 29, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 29, 2024
Advance online publication: January 30, 2024Download PDF (2579K) Full view HTML
Regular Papers
Articles
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 027001
Published: February 09, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 09, 2024
Advance online publication: December 23, 2023Download PDF (2058K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 027002
Published: February 09, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 09, 2024
Advance online publication: December 16, 2023Download PDF (3532K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 027003
Published: February 15, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 15, 2024
Advance online publication: January 12, 2024Download PDF (3033K) Full view HTML
Communications
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 027004
Published: February 15, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 15, 2024
Advance online publication: January 13, 2024Download PDF (1382K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 027005
Published: February 15, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 15, 2024
Advance online publication: January 12, 2024Download PDF (1677K) Full view HTML
Articles
-
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 027006
Published: February 20, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 20, 2024
Advance online publication: January 27, 2024Download PDF (6861K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 027007
Published: February 20, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 20, 2024
Advance online publication: December 16, 2023Download PDF (7551K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 027008
Published: February 29, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 29, 2024
Advance online publication: January 12, 2024Download PDF (2673K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 92Issue 2 Pages 027009
Published: February 29, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 29, 2024
Advance online publication: January 13, 2024Download PDF (3320K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|