-
林 英子, 藏滿 保宏, 藤本 正憲, 張 秀蓮, 飯塚 徳男, 岡田 太, 小林 正伸, 上山 吉哉, 中村 和行
セッションID: 1P-1
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Tumor development and progression have a series of complex process involving multiple changes in gene expression. Progressive tumor cells acquire an invasive and metastatic phenotype that is the main cause of death for cancer patients. Therefore, for early diagnosis and effective therapeutic intervention, we need to detect the alterations associated with transition from benign to malignant tumor cells on a molecular basis. To unravel these alterations concerned with tumor progression, a proteome approach attracts great attention because it can identify of qualitative and quantitative changes in protein composition, including their post-translational modifications.
The progressive and regressive tumor models of murine fibrosarcoma cells (QR32 clone and QRsP clone) have been established by our group. The QR clones are weakly tumorigenic and non-metastatic. QR32 cells regress spontaneously after injection of up to 2 x 105 cells subcutaneously or 1 x 106 cells intravenously in normal syngeneic mice. The QRsP clones are more highly tumorigenic and metastatic malignant tumor cells derived from QR32 cells.
The aim of this study is to identify proteins expressed differently between these two clone cells, QR32 and QRsP11. The comparison of the differential expression of proteins between single-cell-originated benign tumor cells and its derived malignant tumor cells would be of benefit for detecting important factors on tumor progression because of their very close genetic backgrounds. In this study, we performed two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and identified some proteins that showed more highly overexpression in QRsP11 than in QR32 by mass spectrometry of LC/MS/MS. It was suggested that these proteins are associated with tumor progression.
抄録全体を表示
-
佐藤 守, 佐藤(春田) 恵里, 大森 彬, 大石 正道, 小寺 義男, 古舘 専一, 前田 忠計
セッションID: 1P-2
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
The
rdw rat has hereditary dwarfism and hypothyroidism, the primary cause of which is a mutation in thyroglobulin (Tg) gene. In spite of the Tg mutation the rat survives a shortage of the hormone, influences of which on pancreatic proteome were studied in this study. Two types of L-thyroxine (T4) supplementation to the rats were carried out: 1) once-a-day abdominal injection of T4 to the
rdw rats from 3 to 28 days after birth and 2) a thyroid graft to the four-week-old
rdw rats. Normal control and the
rdw rats without T4-medication were sacrificed at the age of 4 to 56 weeks old, and the T4 supplemented
rdw rats 12 weeks after birth. Pancreatic proteomes were analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) that uses agarose gels for the first dimensional isoelectric focusing (agarose 2-DE). At least four pancreatic protein contents in the untreated
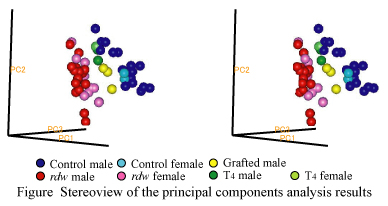
rdw rats were above, and four were below the normal level. Those eight proteins were more or less normalized in contents by the T4 supplementation. Cluster analyses of the representative eight proteins showed that the normal control and grafted
rdw rats were grouped into a same cluster, the untreated
rdw rats belonged to another one and the T4 medicated rats were in between the two. We drew a conclusion from the analyses that T4 treatment of the
rdw rats started at an immature stage was effective for normalizion of the pancreatic proteome of the
rdw rat but must be continued to keep the pancreatic proteome of the mature
rdw rats in the mitigated status.
抄録全体を表示
-
坂本 安, 廣澤 成美, 鈴木 悠子, 矢野 一行
セッションID: 1P-3
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Di-(2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate (DEHP) and Di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) possess great industrial value as plasticizing agents. They have become ubiquitous environmental contaminants and are considered to be endocrine disruptors. Exposure of rodents to phthalate esters is associated with developmental and reproductive anomalies, and there is concern that the chemicals may be causing adverse effects on human reproductive health. We examined the long-term exposure effects of the chemicals on female rats and measured organ weight. The pituitary, the ovary and the adrenal gland were shown to have altered weights, which seemed to imply that the phthalate esters were affecting these secretory organs, but we found no significant histological differences. Furthermore, significant decreases of sera estrogen levels were detected in the treated group. Therefore, proteome-based analyses of the pituitaries were performed to examine the endocrine disrupting properties of the plasticizer DEHP. As a result, two proteins from about ten altered protein spots that showed a remarkable reduction in level were identified as the valosin containing peptide/p97 (VCP/p97) and UMP-CMP kinase. VCP/p97 has been reported to play an important role in the fusion of Golgi apparatus with secretory vesicles, therefore the decrease in VCP/p97 seemed to cause incomplete hormonal priming by suppression of the fusion process. In addition, the reduction of UMP-CMP kinase appeared to cause a decline in mRNA synthesis. Thus the down-regulation of gonadotrophin secretion from the pituitary by the significant reduction of both proteins seemed to have additive effects to inhibit estradiol secretion from the ovary.
抄録全体を表示
-
及川 伸二, 古川 絢子, 及川(多田) 佐枝子, 川西 正祐
セッションID: 1P-4
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Bisphenol A (BPA), a monomer of polycarbonate and epoxy resins, has been detected in canned food and human saliva. BPA may be carcinogenic, taking into account of the report that dietary administration of BPA induced leukemias in rats. To clarify mechanisms of BPA-induced carcinogenesis, we examined DNA damage by its metabolite, 3-hydroxybisphenol A (3-OH-BPA), using
32P-5'-end-labeled DNA fragments obtained from the human cancer-related gene. Cell cycle phase distribution and the percentage of apoptotic cells in human acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60 treated with BPA were determined by flow cytometry. To identify proteins associated with apoptosis, a comparative proteome analysis was carried out using HL-60 cells treated with BPA.
3-OH-BPA induced extensive DNA damage in the presence of Cu(II) and NADH. 3-OH-BPA strongly damaged G and C of the ACG sequence complementary to codon 273, a mutational spot of the
p53 gene. Catalase and bathocuproine, a Cu(I) chelator, inhibited DNA damage, indicating the involvement of H
2O
2 and Cu(I). These results suggest that reactive species derived from the reaction of H
2O
2 with Cu(I) participate in 3-OH-BPA-induced DNA damage. Furthermore, flow cytometry revealed that HL-60 cells treated with BPA underwent apoptotic death. Protein profiles from HL-60 cells treated with BPA and control cells were analyzed by 2-D gel electrophoresis and stained with CBB. Four proteins were differentially expressed between control cells and cells treated with BPA. These proteins identified in our proteomic studies may be implicated in carcinogenesis and candidates as tumor biomarkers.
The study on DNA damage by 3-OH-BPA has been performed together with Dr. S. Yoshihara, Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hiroshima University.
抄録全体を表示
-
車 英俊, 頴川 晋, 大石 正道, 小寺 義男, 佐藤 守, 陳 偉強, 馬場 志郎, 前田 忠計
セッションID: 1P-5
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
We studied comprehensive protein expression in human prostate cancer cells, LNCaP, borne in male nude mice by using an agarose 2-DE method followed by LC-MS/MS. The agarose 2-DE being good at separating high molecular mass (HMM) proteins and alkaline ones, we successfully revealed differences between proteomes of androgen dependent and independent cancers especially in HMM regions larger than 80 kDa. About 500 of proteins separated by the 2-DE method were visualized in a Coomassie-stained 2-DE gel, and the staining intensities of respective protein spots enabled us to infer contents of the proteins in the tumors. We successfully identified 295 proteins (91.0%) out of 324 spots excised in total. Sixty-two among the 295 proteins being redundant, we obtained a non-redundant set of 233 proteins, among which eight were mouse proteins. Excluding these eight mouse-derived proteins, we considered remaining 225 proteins to be related to the cancer. We divided the 225 cancer-related proteins into HMM and LMM (low molecular mass) groups by their molecular mass above or below 80 kDa, the former group contained 84 HMM proteins and the latter 141 LMM ones. Functional classification of the proteins in these two groups showed clear differences between the two: More than half (54.8%) of the HMM proteins but less than one-third (29.1%) of the LMM ones were classified among transcription/translation related proteins. The biggest fraction (29.8%) of the LMM group was metabolism related proteins. Eighteen proteins changed in content when the tumor progressed from androgen dependent to independent states. Five of these proteins had a function to protect cells against oxidant stress induced apoptosis. In conclusion, HMM proteome of androgen independent prostate cancer provided critical information to understand its progression. Besides, some of identified proteins would be candidates for new biomarkers or therapeutic targets.
抄録全体を表示
-
許 波, 吉田 豊, 張 蛍, 矢尾板 永信, 大澤 哲雄, 山本 格
セッションID: 1P-6
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Large-scale protein expression analysis provides a discovery-driven approach in studying the detailed mechanism behind the pathogenesis of various diseases. We have intended in this study to classify proteins differentially expressed in the glomerulus, cortex and medulla of normal human kidney in an attempt to contribute to understanding the pathogenesis of renal diseases. Kidney tissues with normal appearance, far from the tumor mass, were obtained from patients under surgical nephrectomy due to renal cell carcinoma, and pieces of cortex and outer medulla were excised. Glomeruli were further purified from the cortices to an apparent homogeneity under a phase-contrast microscopy. The tissues were solubilized in a conventional extraction buffer (urea/NP-40/DTT), separated by 2-DE with 18 cm IPG strips of pH 3-10 range in the 1st dimension and 20 x 20 cm separation gels of 12.5 % in the 2nd dimension, and silver-stained. 2-DE gel images of the three tissues obtained from each of 4 subjects with no apparent pathologic manifestations were subjected to analysis by PDQuest, a 2-DE analysis software (Bio-Rad) to detect protein spots differentially expressed. We detected 1,810 valid spots in the glomerulus, 1,758 spots in the cortex, and 1,275 spots in medulla Statistical assessment of significance differences in expression among the three tissues was made by one-way ANOVE followed by Tukey's post-hoc test. Differences were considered significant at p<0.05. The statistical analyses revealed 204 protein spots abundantly expressed in the glomerulus, 138 protein spots in the cortex and 89 spots in the medulla. These spot proteins were now under identification by peptide mass fingerprinting with a MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer. These results were combined with the proteome database for the glomerulus of normal human kidney, which we have recently constructed and discussed in the view of physiological significance.
抄録全体を表示
-
西垣 竜一, 門田 満隆, 香月 康宏, 戸田 年総, Wang Chi Chiu, 白吉 安昭, 押村 光雄
セッションID: 1P-7
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Neuro-degeneration early in fetal development in the brains of Down syndrome (DS) patients is proposed to result in the apparent neuropathological abnormalities, and to contribute to the phenotypic character such as mental retardation and premature development of the pathologies of Alzheimer disease, those being the most common phenotype in DS. In order to dissect and identify the aberrant and specific genes manifested as developmentally associated in the early differentiating DS neurons, we have utilized an in vitro neuronal differentiation system of mouse ES cells containing a single human chromosome 21 [TT2F/hChr21] as a model of DS neuronal development, with TT2F parental ES cells as a control. This TT2F/hChr21 cells is observed higher apoptosis phenotype than normal controls in the early differentiation of neuronal stem cells.The paired protein extracts from TT2F and TT2F/hChr21 cells at several stages of neuronal differentiation were subjected to 2-DE protein separation followed by MALDI-TOF-MS to identify the proteins differentially expressed between TT2F and TT2F/hChr21 cells. We provide here a novel set of specific gene products altered in early differentiating DS neuronal cells, which is different from that identified in adult or fetal brain with DS. The aberrant protein expression in early differentiating neurons, due to the hChr21 gene dosage effects or chromosomal imbalance, may affect the neuronal outgrowth, proliferation and differentiation implying the developmental abnormalities in neural patterning eventually leading to formation of a suboptimal functioning neuronal network in early life.
抄録全体を表示
-
野田 徹二, 岩間 美奈子, 長谷川 亮, 平野 穣, 稲川 淳一, 石塚 雄一, 水本 清久
セッションID: 1P-8
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Virus infection has been studied with a variety of aspects in order to understand its mechanisms and how the cell reacts after the infection. After the infection, the cell undergoes morphological, biochemical and metabolic changes and start producing virus proteins. At later stage of the infection, the cells often show apoptosis and reaches to cell death. Many of genes and gene products have been found to play important roles during the infection. Often these genes and gene products show up- or down-regulation, thus differential analysis is a powerful method to detect such genes and gene products. In this presentation, cell lysate of a human cell line, HeLa cell infected with Sendai virus (SeV) were applied to fluorescent difference in-gel electrophoresis (DIGE) analysis in order to detect expressed viral proteins as differences of protein abundance from the mock-infected cultures. After DIGE analysis, these differentiated proteins were identified by PMF analysis with MALDI-ToF MS. SeV contains a monopertite negative strand RNA genome which consists of six genes encoding the viral proteins. Among these proteins, matrix protein (M), nucleocapsid protein (NP) and phosphoprotein (P) were identified by DIGE / MS analysis and followed by western blot analysis with anti-M, -NP and anti-P protein antibody. Furthermore, up/down-regulated cellular proteins in HeLa cells through the virus infection were identified using DIGE and MALDI-ToF MS with statistical confidence (>1.5-fold, seven proteins, <-1.5-fold, one protein, p < 0.01). These results suggest that DIGE / MS analysis will allow detecting not only induction of viral gene products, but effect of viral infection on protein profiling of host cells, simultaneously.
抄録全体を表示
-
海老澤 高憲, 久富 寿, 井坂 剛, 谷口 幹太, 戸田 年総, 笹野 公伸, 東條 克能, 田嶼 尚子
セッションID: 1P-9
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
The present case was a 39 year-old-female. Since 1999, gain of body weight and moon face appeared. Since 2002, further gain of body weight, headache, acne, and general fatigue have developed, and she was admitted to our hospital for evaluation. She was finally diagnosed as Cushing's syndrome due to right adrenal tumor.
131I-adosterol scintigraphy showed strong accumulation into right adrenal tumor and abdominal MRI showed 5cm heterogenous right adrenal tumor. Plasma ACTH levels was less than 5.0 pg/ml, serum cortisol level was 46.8μg/dl, and serum DHEAS level was 25600 ng/ml.
From these findings, together with rapidly progressive clinical symptoms, this tumor was strongly suspected to be adrenal cancer, and right adrenalectomy was performed. Unexpectedly, pathological diagnosis was benign adrenocortical adenoma.
Although cortisol producing adrenocortical adenoma (CPA) is major cause of Cushing's syndrome, the molecular events in the pathogenesis of the tumor have not been well characterized. In the present study, we performed two-dimensional (2-D) gel electrophoresis analysis and quantative image analysis using proteome analysis on typical CPA and the tumor tissue of this case. We isolated several proteins differentially regulated between typical CPA and the tumor tissue of this case by comparing expression profiles of proteins .
Our results might provide the basis for more detail studies on the regulation of adrenocortical tumors. Although further studies using the high-throughput MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry are necessary to clarify these issues, the identification of the proteins responsible for the development of adrenocortical tumor might contribute to many aspects of our understanding of adrenocortical tumorigenesis.
抄録全体を表示
-
山本 行男, 秋田 朗子, 田井 重行, 深作 進, 山口 照英, 押澤 正, 山岡 和子, 島村 眞里子, 羽里 忠彦
セッションID: 1P-10
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Spinorphin, an endogenous peptide derived from bovine spinal cord, plays a role in anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activity. It also inhibits the enzymatic activity of dipeptidyl peptidase III (DPPIII; EC 3.4.14.4), the physiological role of which is still unknown, but which may be related to bradykinin-induced peripheral pain. To clarify the roles of spinorphin and DPPIII in pain control, their level of activity was analyzed in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from patients who demonstrated chronic pain of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA). Changes in protein profiles of RA and OA samples by two dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE) were also analyzed. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was obtained from candidates for surgery under spinal anesthesia: 20 samples from patients with RA and 20 from patients with OA. Patients scheduled to undergo herniorrhaphy, ovariectomy or transurethral resection were designated as the control group.
The spinorphin level was significantly higher in the RA group than in the OA group (P<0.05), whereas DPPIII activity showed no significant difference between the two groups. 2-DE analysis showed that the more than 500 spots observed in CSF improved by the removal of albumin and immunoglobulin from CSF. Differential analysis by 2-D fluorescence in-gel electrophoresis (DiGE) showed that the expression level of many proteins in RA and OA samples changed as compared with the control group.
We are presently investigating whether changes in spinorphin, DPPIII and protein profiles reflect pathological states.
抄録全体を表示
-
三上 寿幸, 辻本 あかね, 佐藤 寛之, 樋口 千洋, 小島 深一, 柱本 満
セッションID: 1P-11
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Insulin stimulates glucose transport by promoting translocation of intracellular glucose transporter-4 (GLUT4)-containing vesicles to the cell surface of adipose cells. Although numerous studies have examined the insulin signaling mechanisms leading to translocation of GLUT4 vesicles to the plasma membrane, this process is still unclear. In this study, we used mass spectrometry in combination with subcellular fractionation to identify protein components of THE plasma membrane in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The cells were homogenized and subjected to a series of centrifugation procedure to prepare plasma membrane and low and high density microsome fractions. Proteins were identified by SDS-PAGE and in-gel digestion, followed by tandem mass spectrometry. All MS/MS spectra were searched using MASCOT program and the results were processed and verified by our originally developed software. Using this approach, we have identified about 500 proteins, 55% of which had transmembrane domains, and which contained high molecular weight proteins over 100kDa. In addition, we investigated plasma membrane proteins after insulin stimulation and compared with those from the basal condition. Insulin-responsive amino peptidase (IRAP), which is known as one of the resident proteins in GLUT4 vesicle, was used to evaluate mass spectrometric comparison. The peak intensity of tryptic fragments of IRAP increased after insulin stimulation in the plasma membrane, which was also confirmed by western blotting. We have found a novel protein, which increased in the plasma membrane fraction after insulin stimulation.
抄録全体を表示
-
加美野 宏樹, 平塚 正治, 戸田 年総, 西垣 竜一, 尾崎 充彦, 井藤 久雄, 押村 光雄
セッションID: 1P-12
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
It is known that replicative senescence of endothelium in vivo contributes at least partially to age-related vascular disorders such as arteriosclerosis. However, the genes involved in this process remain to be identified. In this study, we employed a proteomics-based approach to identify candidate genes using in vitro cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) as an experimental model for replicative senescence. By comparing protein spots from young and senescent HUVECs using two-dimensional electrophoresis, we identified three up-regulated proteins and five down-regulated proteins in senescent HUVECs as compared to young HUVECs, whose alteration was not observed during replicative senescence of primary human fibroblasts. Consistent results were obtained in Western blotting analysis using specific antibodies raised against some of these proteins, whereas there were no significant changes in the mRNA levels of these genes during senescence of HUVECs. Among them, cathepsin B, a protease participating in both intracellular proteolysis and extracellular matrix remodeling was observed to be dramatically up-regulated in senescent HUVECs and whose activity is known to be up-regulated in atherosclerotic lesions with senescence-associated phenotypes in vivo. Additional proteins, including cytoskeletal proteins and proteins involved in the processes of synthesis, turnover and modification of protein, were identified, whose function in endothelium was previously unsuspected. These proteins identified by a proteomics-based approach using cultured HUVECs may be involved not only in replicative senescence but also in functional alterations in vascular endothelial cells with senescence-associated phenotypes and may serve as molecular markers for these processes.
抄録全体を表示
-
香月 康宏, 西垣 竜一, 木村 元思, 甲斐 義輝, 阿部 智志, 沖田 千芽, 白吉 安昭, 花岡 和則, 富塚 一磨, 押村 光雄
セッションID: 1P-13
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is a major clinical manifestation of Down syndrome (DS). We recently showed that chimeric mice containing a human chromosome 21 (Chr 21) exhibited phenotypic traits of DS, including CHD. Our previous study showed that myosin light chain-2a (mlc2a) expression was reduced in the hearts of chimeric mice and DS patients. We found that phosphatidylethanolamine binding protein (PEBP) was also downregulated in Chr 21 chimeras in this study. As mlc2a is involved in heart morphogenesis, and PEBP controls the proliferation and differentiation of different cell types, these genes are candidates for involvement in DS-CHD. The DS-CHD candidate region has been suggested to span between PFKL and D21S3, which is the STS marker near the ETS2 loci. To identify gene(s) or a gene cluster on Chr 21 responsible for the downregulation of mlc2a and PEBP, we fragmented Chr 21 at the EST2 loci, by telomere-directed chromosome truncation in homologous recombination-proficient chicken DT40 cells. The modified Chr 21 was transferred to mouse ES cells by microcell-mediated chromosome transfer (MMCT), via CHO cells. We used ES cell lines retaining the Chr 21 truncated at the ETS2 locus (Chr 21E) to produce chimeric mice and compared overall protein expression patterns in hearts of the chimeras containing the intact and the fragmented Chr 21 by two dimensional electrophoresis. While mouse mlc2a and PEBP expression was downregulated in the chimeras containing the intact Chr 21, the expression was not affected in the Chr 21E chimeras. Therefore, we suggest that Chr 21 gene(s) distal from the ETS2 locus reduce mouse mlc2a and PEBP expression in DS model mice and DS. Thus, this chromosome engineering technology is a useful tool for identification or mapping of genes that contribute to the DS phenotypes.
抄録全体を表示
-
小林 道元, 平野 穣, 服部 成介
セッションID: 1P-14
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Lipid rafts are membrane microdomains enriched in sphingolipid and cholesterol, which regulate numerous cellular events including signal transduction, membrane traffic and viral entry. During T-cell activation, many signaling molecules are shown to be activated in lipid rafts, or to be associated to their components. Following TCR stimulation, Src family tyrosine kinases including Lck and Fyn are activated in lipid rafts, and some types of molecules such as Zap70, PKC-theta and PLC-gamma are recruited onto lipid rafts. To understand the signaling events taking place in lipid raft, alteration of protein constituents in lipid rafts were investigated using proteomic techniques. [Methods] Jurkat T-cells are stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies. Proteins of lipid rafts were isolated by sucrose density gradients using non-ionic detergents. To analyze the difference between the stimulated and unstimulated cells, we employed two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis (DIGE) system. In this system, the samples from stimulated and unstimulated cells were labeled with different CyDyes, mixed and subjected to 2D electrophoresis. The gel was scanned at the appropriate wavelength for the fluor, and the spot intensities were quantified using imaging analysis software. The protein spots were identified by combination of protease digestion and matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. [Results] Several protein spots were observed on 2D-gels, which increased or decreased upon stimulation. By mass-spectrometric analysis, we identified one of them as Lck, which is phosphorylated upon TCR stimulation and undergoes an electrophoretic and isoelectrophoretic mobility shift. Furthermore, several raft-associated proteins were also identified. These results demonstrate that the approach using a combination of DIGE system and mass-spectrometric analysis is a powerful tool for understanding the signaling events on lipid rafts.
抄録全体を表示
-
加藤 智啓, 唐澤 里恵, 大岡 正道, 関根 太一, 西村 裕之, 貫名 信行, 三井 健一, 尾崎 承一, 西岡 久寿樹
セッションID: 1P-15
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Objective To identify the target molecules of anti-endothelial cell antibodies (AECA), which are thought to be involved in pathophysiology of systemic vasculitis.
MethodsTo detect endothelial cell-specific autoantigens for AECA, we separated proteins extracted from human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and HeLa cells respectively by 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE) respectively. They were then transferred onto membranes. By western blotting using serum samples from patients with systemic vasculitis, we detected autoantigens that were positively reacted to the serum samples in the HUVEC samples but not in the Hela cell samples. Then we identified these detected HUVEC-specific autoantigens by mass-fingerprinting. Further, we prepared recombinant autoantigens, by which we confirmed their antigenecity.
ResultsWe found that 50 protein spots were positively reacted to the serum samples only in the HUVEC proteome, but not in the Hela proteome. These proteins would be candidate autoantigens for AECA. We have identified 6 proteins out of the 50 detected protein by mass fingerprinting so far. One of the proteins was found to be a peroxiredoxin 2, which was an anti-oxidative enzyme. ELISA using a recombinant peroxiredoxin 2revealed that autoantibodies to peroxiredoxin 2 were detected in about 70% of the patients with vasculitis but in very small population of vasculitis-negative autoimmune patients.
ConclusionProteomic surveillance is an effective way to identify the targets of AECA. One of the identified autoantibodies, the autoantibody to the peroxiredoxin-2 homologous protein, would have diagnostic and phatophysiolosical importance in the systemic vasculitis.
抄録全体を表示
-
中村 愛, 大澤 多加子, 森澤 拓, 櫻井 洋子, 戸田 年総
セッションID: 1P-16
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Oxidative stress is thought to be implicated in a number of age-associated disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and aging mechanism itself. Dopamine neurons are known to be vulnerable to age-related disorders because of exposure to high level of oxidative stress by dopamine metabolism in these neurons. Here we examined the overall protein alterations of human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y under oxidative stress induced by 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), a dopaminergic neurotoxin. After exposure to 6-OHDA, cell injury was evaluated by a colorimetric assay for mitochondrial function using the 4-[3-(4-iodophenyl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2H-5-tetrazolio]-1, 3-benzene disulfonate (WST-1) test and cellular proteins were analyzed by two-dimensional gel-electrophoresis in combination with MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. The phosphorylation state of entire proteomes was analysed by using Pro-Q Diamond dye. The levels of free ubiquitin and ubiquitin-conjugated proteins were examined by Western blot analysis using anti-ubiquitin antibody. Differential display of proteins using computer-aided image analysis revealed that several protein spots were shown to be varied both in quantity and in quality as the effect of oxidative stress. Identification of these protein spots and their oxidative stress-related modification is now in progress.
抄録全体を表示
-
植木 正彬, 山口 深雪
セッションID: 2P-1
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Mass spectrometry using modern soft-ionization techniques has some difficulty in analysis of sulfo-peptides. We established a new method of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI)- time of flight (TOF)-mass spectrometry (MS) for analyzing homooligomers of
O-sulfated tyrosine as their tetrabutylammonium (TBA) salts. In the negative ion spectra in the linear mode using alpha-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHCA) as matrix, they showed the molecular ions in the form of [M-TBA]
- and typical ladder fragmentation patterns consisting of desulfated ions corresponding to the numbers of the sulfate groups. So, the molecular weight and the number of sulfate groups could be easily determined. To make this method more general, conversion to the TBA salt during sample preparation was tried. As expected, measurements using a mixture of CHCA and its TBA salt (1:1) gave almost the same patterns as above. Then, the improved method was applied to phospho-peptides. As a sample of multiply phosphorylated peptides, Ac-pTyr-pTyr-pTyr-Ile-Glu-OH was prepared by the solid phase method. Though HPLC of the crude product showed contamination of only a small amount of an imcompletely deprotected product, MALDI-TOF-MS using CHCA as the matrix showed the latter as a major peak and the free phospho-peptide as a very weak peak. However, using the mixture of CHCA and its TBA salt as the matrix, intensity of the phospho-peptide was much increased and a new peak appeared. In the analysis of the purified peptide, the third peak appeared and these peaks were tentatively assigned as [M(monoTBA salt)-TBA]
-, [M(bisTBA salt)-TBA]
-, and [M(trisTBA salt)-TBA]
-. While more precise measurements are necessary for the final assignment, it may be said that determination of the number of phosphate groups was made possible by simple measurement.
抄録全体を表示
-
亀山 一央, Chernokalskaya Elena, Kavonian Mark, Glazebrook Heather, Gutier ...
セッションID: 2P-2
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Biological fluids such as blood and urine present a convenient screening and diagnostic media for clinical analysis. Serum peptides may serve as an indicator of organism progression from normal to diseased state. However, proteomic analysis of complex samples, such as serum or plasma is frequently influenced by the presence of high protein concentrations hindering peptide detection. These proteins suppress the ionization of native peptides during MALDI-TOF MS analysis. As a result, sample complexity reduction to lower the level of abundant proteins is rapidly becoming an essential first step of any peptide analysis scheme. Several pre-fractionation strategies using chromatographic absorbents have been employed to remove abundant proteins such as albumin. As an alternative to adsorption chromatography, we have treated mammalian (human, murine, & bovine) serum or plasma samples with ultrafiltration (UF) membranes to produce relatively protein free filtrates. The UF samples were then acidified and transferred to ZipPlateC18 for de-salting and additional purification and concentration of the peptide samples. The results demonstrated that the 10K MWCO membrane gave the optimal results based on significantly improved detection and resolution of serum peptides in the 800-4000m/z range. The sample complexity reduction technology described in this presentation has resulted in convenient and rapid protocols for the isolation and analysis of native low molecular weight peptides in biological fluids such as serum or plasma. The combination of these techniques for enhanced peptide analysis applications such as the elucidation of peptide patterns enables more rapid and efficient discovery and characterization of potential biomarkers.
抄録全体を表示
-
John A Chakel, Jose E Meza, Christine A Miller, Steven M. Fische
セッションID: 2P-3
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
A goal of many proteomics projects is to identify the maximum number of proteins with the most complete sequence coverage from complex protein samples. A factor in the identification of proteins from such samples is the efficiency with which proteins are digested prior to their analysis by mass spectrometry. In turn, the efficiency of digestion is dependent on the degree of denaturation of a protein prior to its digestion. For example, in its folded state myoglobin is virtually resistant to trypsin proteolysis unless it is denatured chemically (i.e. with urea) or thermally, at which point it is readily digested. Recently, Russell et al (Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 2682-85) reported an increase in the digestion efficiency and sequence coverage by mass spectrometry of various proteins digested in buffers containing organic solvents (i.e, acetone, acetonitrile, isopropanol, methanol). The reaction was rapid but incomplete, for several missed cleavage sites were identified within the resulting fragments even after prolonged (overnight) digestions. We have taken their study a step further and developed a protocol using TFE as the denaturing agent. Our current study illustrates both the efficiency and completeness of digestion of various proteins using the TFE protocol. Additionally, the tryptic digestion of complex protein samples in TFE resulted in better sequence coverage and protein identifications compared to digestions using more traditional denaturing agents such as urea.
抄録全体を表示
-
島田 希代, 長野 美穂子, 原 康洋, 甲賀 弘, 小原 収, 湯浅 茂樹, 長瀬 隆弘, 岡崎 規理子, 古閑 比佐志
セッションID: 2P-4
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
In mammals, large multi-domain proteins are assumed to form large protein complexes and subsequently play a role in high order cell functions. To clarify the functions of large proteins, we had initiated a human cDNA project to accumulate information regarding the protein-coding sequences (CDSs) of unidentified genes since 1994. We have already registered more than 2000 genes (KIAA genes) to the public database and the average length of the CDSs reaches 949 amino acid residues. During these 10 years more than 50 KIAA genes have been identified as disease genes, so far our focus to large proteins are thought to be a correct direction. However completion of genetic and proteomic resource are required for the further functional characterization of KIAA proteins. For this purpose we planned to prepare mouse cDNA (mKIAA) collection corresponding human KIAA genes that make overcome legally and ethically restriction to use human materials. Since antibody is useful tool to specifically capture certain protein both
in vitro and
in vivo, we therefore planned to produce a set of antibodies against mKIAA proteins. At present we have already cloned more than 1600 mKIAA cDNA and produced 600 antibodies. For the efficient production of large number of antibodies, we have established a system to generate recombinant antigens using
in vitro recombination-assisted method. We are also systemically evaluating the antibodies as follows: (1) ELISA; (2) western blotting; (3) immunohistochemical analysis; (4) LC-MS/MS analysis combined with immunoprecipitation. Sharing these data with research communities are also important to accelerate the studies in this field, thus we are now preparing new database about our mouse resource in which integration of genetic and proteomic analysis will be achieved. We will present the outline of our project and detail of each systematic approach. This study is supported by the CREATE Program from JST
抄録全体を表示
-
片山 博之, 齋藤 はる奈, 石濱 泰, 田畑 剛, 小田 吉哉, 佐藤 俊孝, 長洲 毅志
セッションID: 2P-5
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
In the field of drug discovery, proteomic approach can be a powerful procedure to explore the drug effect because in most cases, target molecules of drugs are protein. Typical flow of proteome study is well established in combination with mass spectrometry analysis and database searching followed by gel separation and in-gel digestion of proteins. In this flow, improving the in-gel digestion protocol is important to have advantage over identifying lower abundant protein because it is difficult to modify mass spectrometry hardware to improve the sensitivity of the system by ourselves. We previously suggest using thin-gel separation such as 0.5mm thickness, negative staining and addition of n-octylglucoside with trypsin treatment in order to improve the recovery of the digested peptide fragments. These combinations also worked fine in 96-well plate high throughput format since n-octylglucoside helped both enhancing digestion efficiency and prevent adsorption of the digested peptides to the plate wall. In this study, we further modified our protocols using shorter separation gel such as 4cm while length of typical gels are 8-10cm. The shorter gel separation helped to reduce the gel volume per a band, and it was expected to improve digestion efficiency as well as using thinner gel for a same reason. This strategy was applied to GeLC-MS which gel lane was divided into 4 pieces with ignoring the separation pattern of the protein, and analyzed by LC-MS after in-gel digestion. The number of identified peptides from shorter gel was much superior to that of typical gel, and in-gel digestion efficiency was apparently improved. We will further discuss the possibility using other detergent instead of n-octylglucoside in order to establish better system.
抄録全体を表示
-
野田 徹二, 石塚 雄一, 大島 典子, 窪田 雅之, 木全 順子, 平野 穣
セッションID: 2P-6
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Post translation modification (PTM) of proteins has been recognized as one of the most important subjects in the proteomic research. PTM is unique aspect of protein function and most of PTMs are not possible to study by genomic approaches. We focused on protein phosphorylation as a model of PTM.Protein phosphorylation was studied with BALB/c 3T3 cell line treated with a protein kinase C (PKC) activator, Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). Potential phosphorylation was detected by 2D PAGE as an acidic sift of protein spots and its relative changes of the proteins were quantified by 2D DIGE. These spots on the 2D gel were confirmed with a fluorescence reagent for phosphorylated protein detection. The spots were picked and followed by in-gel tryptic digest. The extracted peptides were analyzed by MALDI ToF MS and ESI-IT MS. Proteins were identified by peptide mass fingerprinting (PMF) analysis (MALDI ToF MS) and by MS/MS (ESI-IT MS) analysis. Lamin B, coronin 1B and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRPK) were phosphorylated by PMA treatment. 2D DIGE analysis suggests that lamin B and hnRPK seems to have different state of protein phosphorylation. Further MS/MS analysis revealed that BALB/c 3T3 cell line most likely express 1) two types of lamin B, annotated lamin B and lamin B1 in the database, and 2) two types of hnRPK, annotated splicing valiance in the database. We found that this approach is a powerful tool for proteomic analysis for protein phosphorylation with following advantages; 1) Separation and quantifications of phosphorylated protein by 2D DIGE, 2) Rapid screening of expression difference in PMA treatment by 2D DIGE and PMF (MALDI ToF MS), 3) Detailed analysis for protein spots of interest by MS/MS (ESI-IT MS). It is suggested that the principal of this approach could be effectively applied to variety of proteomic analysis for PTMs.
抄録全体を表示
-
上野 剛, 川島 祐介, 小寺 義男, 大石 正道, 前田 忠計
セッションID: 2P-7
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Oxidative modification of proteins by reactive oxygen species (ROS) is implicated in a variety of chronic and acute diseases. One of popular methods for detecting protein oxidation is hydrazone derivatization of protein carbonyls with appropriate hydrazine reagents. In order to study protein carbonyls, we developed a new proteomic method for detecting protein carbonyls using a Cy-dye labeled-hydrazide (CHz). Application of the present method to detecting protein carbonyls in a renal cortex of diabetes model OLETF rat is also reported.
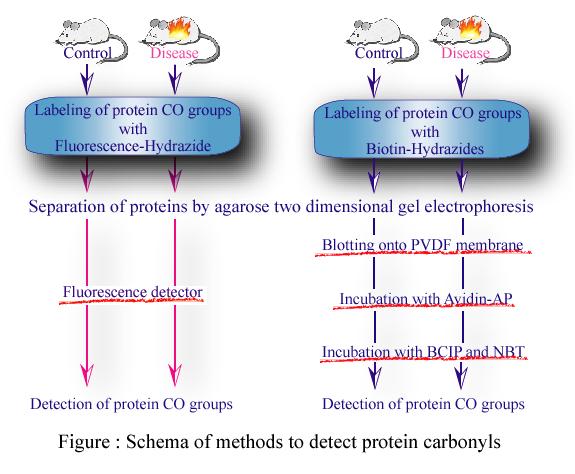
The use of CHz is an improvement of the previous method based on the use of biotin-hydrazide (BHz) (Oh-Ishi et al,
Free Radic Biol Med. 34, 11-22, 2003), which was not particularly good at quantifying the carbonyls because it relied on the use of Western blotting (Figure:Right) with avidin alkaline phosphatase after agarose two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE). The new method has advantages over the previous one by directly detecting protein carbonyls by fluorescence in 2-DE gels (Figure:Left). The present method is much easier and has greater potentialities than the previous one toward clarifying oxidative modifications of proteins.
抄録全体を表示
-
齋藤 はる奈, 片山 博之, 石濱 泰, 田畑 剛, 小田 吉哉, 佐藤 俊孝, 長洲 毅志
セッションID: 2P-8
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
In recent study of proteomics, mass spectrometry(MS) is an essential tool for rapid and high sensitivity protein analysis. To perform high quality analysis, it is important to understand the characteristics of various MS analyzers, because different combination of ionization procedure and MS detector shows different performances in terms of ionization efficiency, peak resolution and data acquisition efficiency depended on scan speed. Here we evaluated the characteristics of ESI-IT MS(LCQ, Thermo Electron), ESI-QTOF MS(QSTAR, Applied Biosystems), and MALDI-TOFTOF MS(4700, Applied Biosystems). For the preparation of test samples, soluble fraction of HCT116 cells were separated by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by negative staining. Some protein bands were excised, digested by trypsin, and the peptides were recovered for MS analysis. In case of ESI-IT and ESI-QTOF, peptide solution was injected to reversed phase LC-MS system while the solution was crystallized with alpha-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid for MALDI-TOFTOF. The database searching for protein identification was performed with Mascot(Matrix Science). When we focused on a unique protein obtained from a selected band, number of assigned MSMS spectra detected from ESI-IT, ESI-QTOF and MALDI-TOFTOF, were 34, 34, 3 respectively. The efficiency of MSMS analysis with MALDI-TOFTOF was very low in comparison with ESI-IT and ESI-QTOF. However, when we consider peptide mass fingerprinting method in MALDI-TOFTOF, 52 peptide peaks were assigned and sequence coverage was increased. The overlaping of assigned peptides among three instruments were low, because the molecular weight distribution of the peptides were different, for example, the average value of the molecular weight of parent ions obtained from ESI-QTOF, ESI-IT and MALDI-TOFTOF were 1280, 1860, 2040Da respectively. In the poster, we will show more data to understand the difference of the characteristics, and discuss how to show the best performance of those instruments.
抄録全体を表示
-
小寺 義男, 佐藤 守, 川島 祐介, 前田 忠計
セッションID: 2P-9
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Reactive oxygen species, ROS, causes oxidative damages on nucleic acids, fatty acids, carbohydrates, and proteins in vivo. Side chains of lysine, arginine, proline and threonine residues are susceptible to ROS damages to be carbonylated. It has been demonstrated that protein carbonyls correlates well with aging and many diseases including diabetes, degenerative brain diseases and chronic lung disease. However, the relationships between the carbonylated proteins and those diseases have not yet been clarified.
Here, we established a method to mass-spectrometrically study the relationships between disease and protein carbonyls using an affinity tag called TOP, tags for oxidized proteins. TOP consists of three functional elements: an affinity tag, an isotope-coded linker, and hydrazide to react with protein carbonyls. The tag enables us to enrich carbonylated proteins from crude cell extracts and to subsequently identify carbonylated sites. Furthermore, TOP lets us quantitatively and directly analyze the protein carbonyls using mass spectroscopy.
We applied the TOP to studying states of artificially oxidized peptides by LC-MS and succeeded in purifying the carbonylated peptides from variously oxidized ones. It was found that carbonylation of lysine occurred after oxidation of methionine. Furthermore, this tag was applied to studying an artificially oxidized protein.
抄録全体を表示
-
唐沢 毅, Chalk R, Hayn G, Schultheis L, Matter U, Alves S, Zenobi R
セッションID: 2P-10
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
A MALDI –ToF mass spectrometer has been designed for use with a superconducting tunneling junction (STJ) detector array. The STJ is maintained at its working temperature of 0.4 K by a closed-system He3 cryostat. The cryostat is designed for maintenance-free operation and regenerates automatically every 24 hours. STJs function by measuring ion kinetic energy deposited on their surface, an inherently 100 % efficient process. Since all intact ToF ions with the same charge have the same kinetic energy, the detection efficiency of STJs is independent of mass. There are 4 major consequences:
1. Cryodetector mass spectra represent the true ion yield, irrespective of mass, allowing quantitative assumptions to be made.
2. Detector performance does not deteriorate with increasing mass. At high mass, cryodetector mass spectrometers are orders of magnitude more sensitive than conventional ionizing detectors.
3. Since there is no theoretical mass limitation for ToF measurements, there is no theoretical mass limit for cryodetector ToFs.
4. Energy resolution in STJs allows direct measurement of ion charge state.
A 16 channel transient recorder generates a separate signal for each detector pixel. Specialized software and data processing are used to transform raw data (energy scatterplot) to a mass histogram. We illustrate the utility of this instrument by:
1. Protein detection at m/z = 2,200,000 Da.
2. UV laser nucleic acid analysis at m/z = 132,000 Da.
3. Quantitation of protein-protein and DNA-DNA interactions.
4. Determining the relative ionization efficiency for proteins in a mixture.
抄録全体を表示
-
鳥居 宏在, 宮崎 賢司, 上條 憲一, 次田 晧
セッションID: 2P-11
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
C-terminal sequence is important to consider the biological function of a protein. However, none of the conventional C-terminal sequencers is widely used relative to N-terminal sequencer. One of the reasons is the deficiency in the reliability of the sequencing results. Recently, Miyazaki
et.al. developed a new reaction of successive C-terminal amino acid truncation to overcome the limitation of the current technology. We investigated the mass spectra of the products of this new reaction in detail.
When the reaction progressed ideally, the mass spectrum was a clear one. Neighboring peaks with enough intensity indicated a truncation of one amino acid residue. Calculating the difference of the mass of these peaks, truncated amino acid residue was estimated. Putting the estimated amino acid residues together, the amino acid sequence of the C-terminus was determined. Sometimes complex spectrum was observed. Careful investigation of the peaks of the by-products suggested several by-reactions. The major by-reactions were acetylation of the hydroxyl group, perfluoroacylation of the amino group, and dehydration. The products of these by-reactions were observed as additional peaks shifted from the main peaks by the specific value of the mass. We found the rules about these by-reactions were helpful to interpret the complex mass spectrum. Taking the rules about the by-reactions into consideration, we have developed a comprehensive algorithm to analyze the mass spectrum for stable C-terminal sequencing.
抄録全体を表示
-
川村 猛, 石塚 雄一, 藤井 清永, 稲川 淳一, 吉川 正人, 野田 哲二, 平野 穣, 西村 俊秀
セッションID: 2P-12
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Two-dimensional electrophoresis followed by MALDI TOF MS analysis (2-DE MALDI-TOF-MS) and multi-dimensional liquid chromatography followed by ESI-IT MS/MS analysis (MuD LC ESI-IT-MS/MS) have been two major approaches for proteome analysis. Although both approaches are known to have advantage and disadvantage over the each other, many of comparative studies have not been performed.In the present study, we conducted a direct comparison between 2-DE MALDI and MuD LC-ESI-IT on plasma proteome analysis. A combination of Cibacron Blue and ProteinG columns was used for the removal of albumin and IgG from plasma, and the sample was further fractionated with ion exchange column. This prefractionation method enables us to explore lower abundant proteins in plasma. A schematic draw of this approach is shown in the figure. Currently we carry out protein identification by both methods. A comparative list of those proteins identified by 2-DE MALDI and MuD LC ESI-IT will be presented.Moreover, evaluation of an albumin and IgG removal method using anti human albumin and IgG antibodies will be also reported.
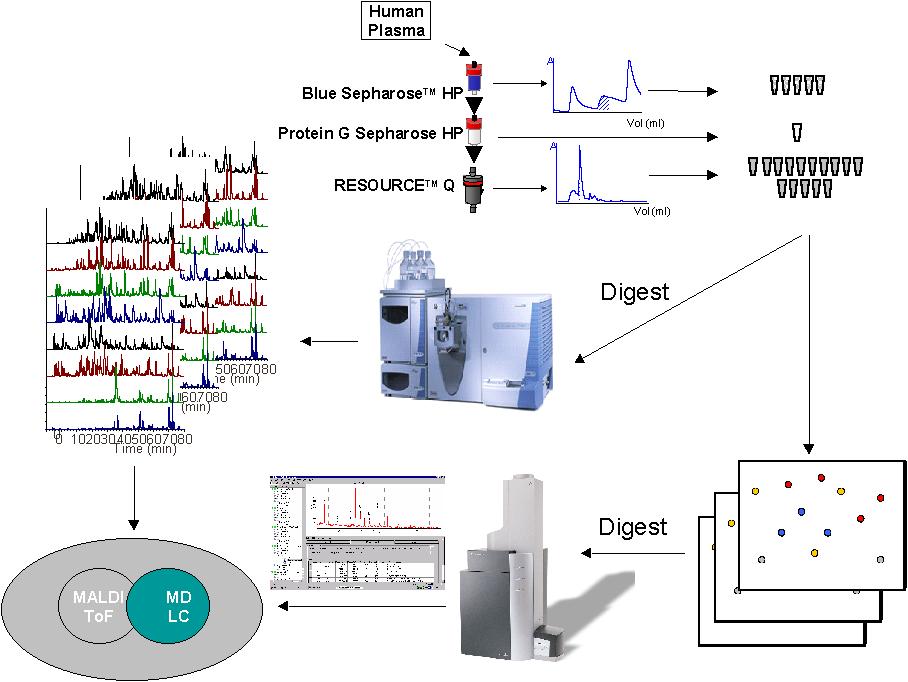
抄録全体を表示
-
町田 光世, 小迫 英尊, 牛山 正人, 稲川 淳一, 平野 穣, 西田 栄介, 服部 成介
セッションID: 2P-13
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Prefractionation procedure has been shown to be very effective in the proteome analysis to analyze proteins of low content such as signaling molecules. Phosphorylation is a fundamental reaction that regulates a variety of factors involved in the signal transduction pathways. We therefore tried to establish optimal conditions for the purification of phosphoproteins by using immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC), which has been used to purify phosphopeptides but rarely applied to phosphoproteins.We searched optimal conditions to purify phosphoproteins by varying pH and ionic strength. Under the optimized conditions, standard nonphosphorylated proteins, lysozyme and bovine serum albumin, did not absorb to the column, whereas phosphoproteins, alpha- and beta-casein, were efficiently recovered in the eluate. Phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and proteins phosphorylated by Akt were also purified with good recovery. Phosphoproteins were purified from ERK-stimulated and ERK-suppressed cells by IMAC, and purified samples were analyzed by a fluorescent two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis system (Ettan DIGE; AmershamBiosciences). This analysis exhibited many spots that were unique to ERK-stimulated cells, suggesting that phoshoprotein purification by IMAC may be effective in the identification of ERK substrates. We also observed that most of these spots could not be identified when whole cell lysates were employed, again suggesting the effectiveness of IMAC prefractionation. These results have shown that phosphorylated proteins can be purified by IMAC under established conditions and this method is useful to comprehensively analyze phosphoproteome.
抄録全体を表示
-
福冨 俊之, 小寺 義男, 古後 富久, 古舘 専一, 大森 彬, 前田 忠計
セッションID: 2P-14
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Proteome analysis is expected to be a new research tool in a post genome era and effective to studying such complicated multi-factor diseases as diabetes. Extension of proteomics to low-molecular-mass proteins or peptides (peptidomics) is to be desired, because peptides play crucial roles in many physiological processes. Application of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE), a popularly used tool in proteomics, to analyzing peptides smaller than 10 kDa in molecular mass is not so successful, and the use of Tricine-PAGE (PAGE for low molecules) is preferable in the peptidome analysis. The aim of the present work is to establish a method of disease peptidomics and to apply the method to the diabetes model mouse to find diabetes related peptides.
Our method of peptide extraction consists of two steps: The first step is precipitation of homogenized tissues in pure acetone at –40 C followed by centrifugation of the acetone-precipitated sample dissolved in 2 mM DTT, and the second Tricine PAGE of the supernatant. Peptide extraction from Tricine PAGE gels smaller than 10 kDa is comprehensive, efficient and reproducible. The extraction is hardly influenced by the presence of proteases and removal of high-molecular-mass proteins larger than 10 kDa is complete. Our method thereby enabled quantitative analysis of extracted peptides by two-dimensional HPLC and mass spectrometry and identification by peptide sequencing. Application of the method to analyzing peptides in extracts of the liver and kidney of a diabetes / obesity model mouse (
db/db mutant mouse) will be presented.
Contrary to popular beliefs that peptides are not abundant, we found plenty of peptides in body fluids and tissue extracts. We believe that our study will be a foundation of peptidomics useful for elucidating peptide functions as well as for developing medicines, diagnostic and therapeutic methods.
抄録全体を表示
-
Sani Salisu
セッションID: 2P-15
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
In the process of the production of photo sensitizer (bacteriophyrphyrin and its derivatives) by the conversation of the biomass Rhodobacter Capsulatus) , extracts of lipids mass amount up to 5 % of dry biomass.The process of production of porphyrinic bacteria from biomass of Rhodobacter Capsulatus also occurs simultaneous with the extraction of lipid components with the preservation of some of their natural native structures.The study of lipids waste has shown, Carotenoids and higher fatty acids as the most dominants components.(On the average 89.1 % of the lipid waste). The remaining components are tochopherol ,quinones and phetol. A double-stage processing of lipid waste was used for a well-directed extraction of the mixture of the components of fatty acids. Fraction of Carotenoid was gotten with the help of desorpting the polar solvents in a periodic process. Fatty acid was been identify on relative time of sustaining components of mixture in comparison to the standard method. The most dominant among Fatty acids based on the result provided by GLC are Oleinic acid (Ń18:1) 92.23%, also identified are fatty acid: C18:0 2.5%; C16:1 2.63 %; C16:0 1.25%; C14:0 1.38 %.
Thus, the product of the biomass from Rhodobacter Capsulatus can be as a source of biologically active substances from the class of lipid- Carotenoid and ethers of microbial fatty acids.
抄録全体を表示
-
Thomas Pohl
セッションID: 2P-16
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Whatever the wealth of information buried in the genome of organisms is converted to in order to create functional protein networks - the perfectly organized interaction of biologic macromolecules is of stunning complexity.
Several lines of development of protein analytical technology have evolved as todays tools towards dissecting functional interactions of proteins. Though mass spectrometry, liquid chromatography, protein chips and other techniques have gained widespread acceptance as powerful sources of information, 2DE-PAGE, the electrophoretic separation of complex protein mixtures in two different dimensions, retains its extraordinary position. The unequaled power of separation and the unique feature of simultaneous characterization of thousands of discrete protein entities underline the importance of this method. We have been specializing in the 2DE-PAGE variant acc. to Klose and Kobalz, called NEPHGE (non-equilibrium pH-gradient electrophoresis) for more than a decade. Ever since we work to improve and optimize this method. We have developed proprietary formulations of gel and sample preparation solutions as well as introducing newly designed equipment. With our current state of the art technology we prepare up to 40 by 30 cm giant gels with more than 10,000 resolved protein spots. In combination with NEPHGEs intrinsic advantages of high sample load capacity, the superior ability to resolve basic proteins and versatility in view of subsequent analytical and micro-preparative options, this platform is ideal for many of todays proteomics objectives. Embedded in a wide range of assistant protein analytical techniques, like adjunct electrophoretic methods, MALDI-MS as well as LC ESI-MS/MS characterization of proteins, automated Edman micro sequencing and reference peptide synthesis, we are well equipped to describe complicated biological situations and to answer protein analytical questions.
抄録全体を表示
-
久富 寿, 中村 愛, 桜井 洋子, 森澤 拓, 廣田 三佳子, 野村 晃司, 川野 克己, 戸田 年総
セッションID: 2P-17
発行日: 2004年
公開日: 2004/05/07
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Proteomics usually employs the separation of a protein mixture by two-dimensional (2-D) gel electrophoresis and identification of the separated proteins by mass spectrometry. However, the streaks that occure frequently on 2-D electrophoresis maps in alkaline region is a common problem. Extra spots on 2-D gels, caused by nonspecific oxidation of proteins, is another difficulty encountered when running gels contain basic regions. Thus both streaking and extra spots result in poor resolution and reduced reproducibility among gels. In this study, we developed a simple method for prevention of streaking which was caused by oxidation of proteins during first dimension isoelectric focusing (IEF).
Several electrophoresis parameters were monitored during the first dimension of 2-D electrophoresis to understand thier correlation upon the quality of protein separation patterns. Most effective step was alkylation step. We used the iodoacetamide for cysteine alkylation during performing the first dimentional electrophoresis. Brifely, extracted sample (10ug) was put on pre-cut wick piece (2 mm x 8 mm), its wick was placed in piles on wick (3 mm x 10 mm) into which 5 mM iodoacetamide (IAA) was infiltrated. Using this step, alkylation induced the prevention of streaking which was caused by the oxidation of proteins during the first-dimensional IEF. Some reagents for prevention of streaking (e.g. DeStreak
TM Rehydration solution, Amersham Bioscience; ReadyPrep
TM Reduction-Alkylation Kit, Bio-Rad) were commercially available, these reagent does not raise an adequate effect. And operation of these kits is complicated, and/or there is a use limit.
We have improved reproducibility and quality of 2-D gels by preventing streaking. And we have successfully eliminated extra spots to achieve well-resolved protein patterns.
抄録全体を表示