-
野村 文夫, 朝長 毅, 清宮 正徳, 木村 明佐子, 曽川 一幸, 大石 正道, 小寺 義男, 前田 忠計
セッションID: S9-2
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Currently available serum markers are not satisfactory in terms of sensitivity and specificity for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Also, novel histochemical markers to ensure accurate pathological diagnosis are needed. Therefore, we conducted comprehensive proteome analyses to find novel biomarkers for HCC.
1) Search for novel serum markers
Three-step proteome analyses were carried out in a total of 22 serum samples obtained from 12 patients with HCC and 10 patients with liver cirrhosis (in collaboration with Prof. Yokosuka, Department of Medicine and Clinical Oncology, Chiba University). As a first step, serum samples were subjected to antibody-based immunoaffinity column system to remove abundant proteins. The concentrated flow-through was then fractionated using reversed-phase HPLC, followed by separation by SDS-PAGE.
A total of 83 protein bands were found to be up-regulated in HCC serum. We a are now in the process of identification of these bands.
2) Search for novel histochemical markers
Using agarose two-dimensional fluorescence difference gel electrophoresis, we analyzed HCC tissues obtained by tumor resection from 10 patients (in collaboration with Prof. Miyazaki, Department of General Surgery, Chiba University). The fluorescence volumes of 48 spots increased and 79 decreased in tumor tissues compared with adjacent non-tumor tissue; 83 proteins were identified by mass spectrometry. Immunohistochemistry confirmed that the expression of clathrin heavy chain (CHC) was significantly increased, while formiminotransferase cyclodeaminase (FTCD) significantly decreased in tumor. It was noteworthy that CHC and FTCD were useful to distinguish early HCC from benign tumors such as regenerative nodule or focal nodular hyperplasia (Hepatology 2008 in press).
抄録全体を表示
-
近藤 格
セッションID: S9-3
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Cancer is a diverse disease, and the present clinical and pathological diagnostic modalities have obvious limitation in the prediction of clinical outcome. The next level of predictive molecular diagnostics is expected to best-optimize the existing therapeutic strategy. We examined proteome contents in more than 1,000 tumor tissues using our original large format two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE) system. By integrating 2D-DIGE data with clinico-pathological parameters, we concluded that proteomics has a great potential to identify biomarker candidate proteins. For instance, 2D-DIGE experiments using clinical samples detected key proteins corresponding to the response to treatment in lung adenocarcinoma, osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma, the early recurrence in liver cancer, the lymph node metastasis of esophageal cancer, and the metastasis post surgery in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. The predictive performance of the identified protreins was successfully validated in more than 100 cases by immunohistochemistry. Such proteins should be strong candidates for biomarkers for personalized medicine. The clinical application of these research results is our next challenge. To facilitate the integrative and comprehensive omics study, we take a part of Genome Medicine Database of Japan. All proteome data by 2D-DIGE, protein annotations and clinico-pathologidal data are currently integrated into this database. We strongly believe that cancer proteomics is a powerful tool for biomarker development, and its practical utilities will be proven in the very near future.
References
1. T. Kondo and S. Hirohashi, Nat Protoc. 1, 2940-2956, 2006.
2. T. Okano and T. Kondo et al, Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 799-805, 2007.
3. Y. Suehara and T. Kondo et al, Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 1707-1717, 2008.
4. GeMDBJ Proteomics, https://gemdbj.nibio.go.jp/dgdb/DigeTop.do
抄録全体を表示
-
松原 淳一, 尾野 雅哉, 古瀬 純司, 上野 秀樹, 奥坂 拓志, 古田 耕, 杉山 永見子, 斎藤 嘉朗, 鹿庭 なほ子, 澤田 純一, ...
セッションID: S9-4
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
PURPOSE: Gemcitabine (GEM) monotherapy is considered to be a standard therapy for advanced pancreatic cancer (PC). To discover new significant biomarkers that can predict toxicities and outcomes of patients with PC treated with GEM alone, we performed exploratory evaluation of plasma proteomes. METHODS: From 176 patients with advanced PC treated with GEM alone as a first-line therapy, we retrospectively selected patients for comparison of their plasma proteomes as follows: adverse events (AE) groups, 25 patients with severe AE and 22 with no AE; survival groups, 31 patients surviving >400 days and 29 patients surviving <100 days; response groups, five patients with partial response and 24 with no response. All samples were obtained before chemotherapy. Plasma samples were pretreated with chicken IgY affinity microbeads, and partitioned flow-through samples were digested with trypsin. Each sample was randomly measured in triplicate using nanoLC-qTOF-MS, and the data were analyzed by 2DICAL (Ono M et al., Mol Cell Proteomics 2006), in which the peptide peaks of each sample with the same m/z were extracted every 1 m/z and aligned with the retention time of LC along the X-axis. RESULTS: There were 757 peaks whose intensity differed significantly between the AE groups (P<0.001, t-test) among a total of 60888 peptides. A peptide with the smallest P value (2.82x10
-5) was sequenced by MS/MS, and identification and differential expression of the protein were confirmed by immunoblotting. We detected 637 peaks as predictive of patient survival and 1225 as predictive of tumor response (P<0.001, t-test). We are currently identifying the proteins corresponding to these peaks by MS/MS. CONCLUSION: The plasma biomarker identified in this study may be useful for selection of PC patients who are likely to have undesirable outcomes of any GEM-containing treatments. We are planning to perform validation tests for each biomarker in another set of patients.
抄録全体を表示
-
西尾 和人
セッションID: S9-5
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
In the post-genomic era, great progress in research of cancer biology enables us to conduct of extensive biomarker research. Coincidentally, application of new proteomic and glycomics technologies to biomarker research yields discovery of molecular target drugs. Since proposal of Critical Path Initiative by FDA, it seems to be essential to utilize the biomarkers in drug discovery process. We have done some biomarker studies that identify the high risk group of adverse events induced by molecular target drugs using proteomics: biomarkers to predict the lung injury induced by tyrosine kinase inhibitors and other molecular target drugs in the clinical setting.
Another important approach is to identify the markers that predict the responders to molecular target drugs. We have tried to identify the novel glyco-markers to predict the responder to anti-Her2 antibody by comprehensive glycoprofiling. This approach allowed us to develop a new diagnostic blood test for pancreas cancer patients. At the same time, glycoprofiling of target proteins is attractive. In this symposium, we will discuss concrete proteomic and glycobiologic technologies and clinical goals with drug development process.
抄録全体を表示
-
増田 豪, 五十嵐 康之, 江角 浩安, 曽我 朋義, 冨田 勝, 石濱 泰
セッションID: S9-6
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Introduction; Protein phosphorylation is one of the key events in cancer signal transduction pathways. Therefore, it is of importance to compare the phosphorylation states of tumor tissues with those of normal tissues in addition to the relative quantitation of proteome between these tissues. Recent advances in MS-based proteomics in coupled with phosphopeptide enrichment methods allow the identification of thousands of phosphorylation sites of cellular proteins. Here, we applied shotgun proteomics-based and phosphoproteomics-based approaches to human colorectal adenocarcinoma tissues to estimate the difference in the protein expression and in the phosphorylation states.
Methods; Tumor and normal surgical tissues were obtained from the colorectal adenocarcinoma patients (N = 16). Phosphorylated peptides were enriched by aliphatic hydroxy acid-modified metal oxide chromatography. Protein abundances were estimated by an emPAI method. Cluster analysis was performed by the Cluster v3.0.
Results; From tumor and normal surgical tissues, 2941 proteins and 2604 phosphorylation sites were identified by shotogun proteome analysis and phosphoproteome analysis, respectively, and the overlap between the identified proteins and phosphoproteins was 193, containing 366 phosphorylation sites. Relative quantitation of phosphorylation states were estimated from the difference between the number of samples where the phosphorylation was identified. Protein abundance based on emPAI values and the phosphorylation difference were classified into eight groups by cluster analysis. In the groups of up-regulated phosphorylation in tumor tissues, 25 cancer-related proteins defined by UniProt disease description were observed, whereas less number of cancer-related proteins (13 proteins) were included in the groups of down-regulated phosphorylation in tumor tissues. Analyzing both the protein abundance and the phosphorylation status would be helpful for cancer biomarker discovery.
抄録全体を表示
-
後藤 祐児
セッションID: S10-1
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Protein folding diseases are caused by misfolding and aggregation of proteins. More than 20 serious amyloidoses, including Alzheimer's disease, prion disease, and dialysis-related amyloidosis, are important examples of folding diseases in which responsible proteins misfold to amyloid fibrils with a width of about 10 nm and rigid morphology, consisting predominantly of a cross-beta structure. Additionally, it has been shown that a variety of proteins and peptides are able to form amyloid fibrils or amyloid-like structures, implying that amyloid formation is a generic property of polypeptides. Clarifying the mechanism of amyloid fibril formation is essential not only for understanding the pathogenesis of amyloidosis but also for improving our understanding of the structure, folding and function of proteins. This symposium brings together several important topics of amyloidosis focusing on the structural properties of amyloid fibrils. These include (1) Historical background of protein folding and misfolding studies, (2) Molecular pathogenesis of amyloidosis, (3) Structural analysis of amyloid fibrils, (4) Infection of amyloidosis, and (5) Therapeutic strategies for treating prion disease. We hope that this symposium will be useful for addressing future directions of the study of protein folding diseases.
抄録全体を表示
-
内木 宏延
セッションID: S10-2
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
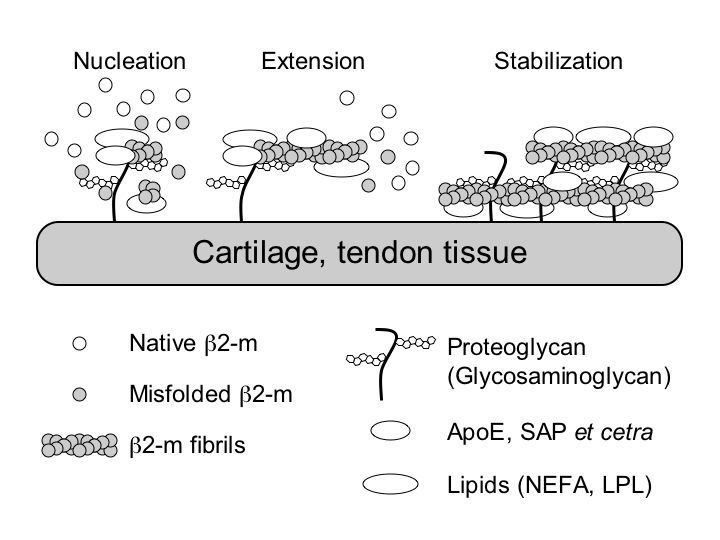
Beta2-microglobulin-related (Ab2M) amyloidosis is a common and serious complication in long-term hemodialysis patients. Intact beta2-microglobulin (b2-m) is a major structural component of amyloid fibrils deposited in the tissue, but the mechanism of the deposition of these amyloid fibrils is not fully understood. Based on a nucleation-dependent polymerization model and by using fluorescence spectroscopy with thioflavin T and electron microscopy, we systematically examined the effects of several classes of biological molecules on the formation and stabilization of Ab2M amyloid fibrils in vitro. Ab2M amyloid deposition takes place predominantly in the cartilaginous and tendinous tissues, suggesting that the specific interaction between b2-m and the extracellular matrix molecules in these tissues, such as type II collagen, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), and proteoglycans (PGs), causes Ab2M amyloid deposition. We first observed that various types of GAGs and PGs stabilize the Ab2M amyloid fibrils and inhibit their depolymerization at a neutral pH. We next reported that some GAGs, especially heparin, dose-dependently enhanced the 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol-induced fibril extension at a neutral pH. In the mechanism of amyloidogenesis of natively folded proteins such as b2-m and transthyretin, partial unfolding is believed to be prerequisite to its assembly into amyloid fibrils both in vitro and in vivo. We recently found that some non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAs) and lysophospholipids (LPLs) induced not only the extension of Ab2M amyloid fibrils but also the formation of Ab2M amyloid fibrils from the b2-m monomer at a neutral pH, by partially unfolding the compact structure of b2-m to an amyloidogenic conformer, as well as stabilizing the extended fibrils. Based on these observations, we propose a working model for the molecular mechanism of the deposition of Ab2M amyloid fibrils in vivo (Figure).
抄録全体を表示
-
茶谷 絵理, 小沼 剛, 大西 玲奈, 櫻井 一正, 内木 宏延, 後藤 祐児
セッションID: S10-3
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Protein misfolding frequently leads to the formation of supramolecular assemblies known as amyloid fibrils, the deposition of which is associated with over 20 degenerative diseases including dialysis-related amyloidosis, Alzheimer's disease, and prion disease. The amyloid fibril forms via a nucleation-dependent process in which precursor proteins associate slowly to form a nucleus, followed by an extension where the nucleus grows by the sequential incorporation of precursor molecules using the nucleus fibrils as a template. The template-dependent growth is a unique and essential character underlying the propagation of the original structure of fibrils, and consequently, of pathology of amyloidoses. Identifying the molecular mechanisms of the fibril growth is therefore an important challenge to design effective strategies for the inhibition and regulation of amyloidoses.
In this talk, we will present our recent attempts to monitor a monomer-fibril complex of beta
2-microglobulin formed transiently during the fibril growth. By using changes in tryptophan fluorescence spectrum, we analyzed kinetics of the seed-dependent reaction at different concentrations of seeds. While the reaction proceeded in a single-exponential manner at low concentrations of seeds, we observed the accumulation of the fibril-monomer complex in the early stage of the reaction at excessive concentrations of seeds. Mutational analysis suggested that the region around Trp60 is one of the possible interfaces with the fibril. Furthermore, we have developed hydrogen/deuterium (H/D) exchange of the fibril-monomer intermediate. Under the accumulating condition of the fibril-monomer complex, H/D exchange was performed by competitive exchange or by quenched-flow exchange, and proton occupancy of each residue was analyzed by
1H-
15N HSQC spectrum, which has provided detailed information about the intermediate structure.
抄録全体を表示
-
野田 勝紀, 内山 進, キャロル ロビンソン, 小林 祐次, 福井 希一
セッションID: S10-4
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Nucleosome assembly is essential for chromatin structure formation during transcription, translation and for the repair of genomic information. During these processes histones are delivered to naked DNA by proteins known as histone chaperones. NAP-1 (nucleosome assembly protein 1), one of the best characterized protein among 10 or more 15 known histone chaperones, is regarded as a multi-functional protein in interphase. During mitosis, NAP-1 is localized within the cytoplasm and segregated from histones required for the next cell cycle.
Previous reports on yeast nucleosome assembly protein 1 (yNAP-1) suggested that yNAP-1 forms dimers and higher oligomers, specifically, octamer, hexadecamer under the physiological salt concentrations (150 mM NaCl), while at higher ionic strength (>750 mM NaCl) only a homogeneous dimer was evident. However, association of the human NAP-1 is still unknown.
Here, we performed mass spectrometry (MS) analysis under the denaturing condition, and analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) to investigate association states of human NAP-1 in solution.
MS result clearly indicates that the primary assembly unit of hNAP-1 core is the dimer and that higher oligomers (tetramer, hexamer, octamer, decamer and dodecamer) are formed at physiological ionic strength. Sedimentation velocity measurement by AUC showed that they form a heterogeneous series of large oligomers at physiological ionic strength with their sedimentation coefficients ranging from 4 S to 22 S. At high ionic strength such as 750 mM sodium chloride, higher oligomers are disrupted. These results clearly shows hNAP-1 have different distribution pattern from that of yeast NAP-1 in solution.
We here demonstrate the combination of non-denaturing MS and AUC provides is powerful approach for the investigation of non-covalent protein-protein interactions in solution.
抄録全体を表示
-
樋口 京一
セッションID: S10-5
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Three major variants of apolipoprotein A-II (apoA-II), protein (types A, B and C) are present among in various inbred strains of mice. The variants are encoded by the Apoa2a, Apoa2b and Apoa2c alleles respectively. Type C apoA-II protein (APOAIIC) is found to be highly amyloidogenic, while the type B apoA-II protein (APOAIIB) is resistant to the amyloidosis development. Type A apoA-II protein (APOAIIA) is moderately amyloidogenic. In vitro fibrilization experiments found that the addition of pre-formed AApoAII amyloid fibrils can seeds and facilitate the formation of amyloid fibrils from apoA-II monomers. This finding suggested the possibility that the introduction of pre-formed fibrils into mice could accelerated fibril formation. We administered AApoAII fibrils via peripheral or intragastric injections into R1.P1-Apoa2c mice that carry the amyloidogenic Apoa2c allele and found that amyloid deposition was notably accelerated. The young mice were reared in cages with amyloid-deposited old R1.P1-Apoa2c mice. All of the young mice developed amyloid deposits after 3 months of co-rearing. Amyloid deposition was accelerated in the mice born from, and milked by, mothers with amyloidosis compared with mice born from to mothers without amyloidosis. We found amyloid fibrils were found in the both milk and fecal materials. The transmittablility of AApoAII amyloid fibrils was disappeared completely after treatment with 6 M guanidine hydrochloride, strong alkaline solution and formic acid. These results suggeste that the oral transmission of amyloid fibrils results in acceleration or induction of AApoAII amyloidosis in mice.
Accumulating observations of mouse AApoAII amyloidosis provide evidence for the hypothesis that amyloid fibrils transmit of non-prion amyloidosis such AApoAII and AA reactive amyloidosis.
抄録全体を表示
-
桑田 一夫
セッションID: S10-6
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Prion proteins are key molecules in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs). Although the precise mechanism of the conformational conversion process from the cellular form (PrPC) to the scrapie form (PrPSc) is still unknown, it may be generally composed of two stages, i.e. stage 1: unfolding of PrPC and stage 2: nucleation dependent folding to PrPSc. Regulation of the reaction process at stage 1 may be feasible by designing and administrating a small compound which can stabilize the PrPC conformation. Thus we aimed at developing a general strategy for designing a small compound, termed 'chemical chaperon', which can selectively stabilize the PrPC conformation thereby inhibiting its pathogenic conversion process.
We conducted in silico screening to find compounds that fitted into a 'pocket' created by residues undergoing the conformational rearrangements between the native- and the sparsely populated high energy states (PrP*) elucidated by Carr-Purcell Meiboom-Gill relaxation dispersion method (NMR), and directly bind to those residues. Hit compounds were tested by ex vivo and in vivo screening, and if effective, they were subjected to determination of the complex structure and further lead optimization processes.
More than hundred compounds were tested in a TSE-infected cell culture model, and more than twenty compounds efficiently reduced PrPSc. Subsequently, administration of GN8 was found to prolong the survival of TSE-infected mice. Heteronucler NMR and computer simulation showed that the specific binding sites are the A-S2 loop (N159) and the region from helix B (V189, T192 and K194) to B-C loop (E196), indicating that the intercalation of these distant regions termed 'Hot Spots' hampers the pathogenic conversion process.
Dynamics Based Drug Discovery (DBDD) strategy demonstrated here focusing on the hot spot of PrPc will open the way to the development of novel anti-prion drugs.
抄録全体を表示
-
山本 行男, 平松 恭子, 高橋 慶一, 山岡 和子, 秋田 朗子
セッションID: P-1
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
[Background] Assay of proteins in urine has been used for diagnosis and monitoring of various diseases. Urinary proteomics demonstrate potential for diagnostic, prognostic, and pathophysiologic discovery. To find biomarkers in colon cancer and to reach more reliable diagnosis, we analyzed proteins in urine. Here, we report on some characteristic proteins in the pathophysiologic state.
[Methods] First-morning mid-stream urine samples collected from healthy volunteers, and from patients with colon cancer undergoing surgery were filtered, centrifuged and acidic/acetone precipitated for desalting and concentrating. Proteins were assayed by isoelectric focusing (first dimension, Immobiline Drystrip, pH 3-10, 13 cm, Amersham Biosciences) and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (two-dimensional PAGE). Protein spots were analyzed and identified by tandem mass spectrometry for expression-changed spots.
[Results and Discussion] 1) Most of the several hundred spots detected were similar to some proteins from serum. 2) From filtering function of kidney, some characteristic spots with lower than 70 kDa MW and good resolution in gel were observed. We therefore focused on the protein range of 10~70 kDa MW. A comparison between spots from patients and controls revealed several expression-changed proteins. 3) Expressional changes during surgery were also detected. By mass spectrometry analysis, these were components which were related to regulation of inflammation. Validation of these changes, especially during surgery and in cancer, is now in progress.
抄録全体を表示
-
阿部 康人, 鍋田 基生, 木藤 克己, 香川 里沙, 植田 規史, 村瀬 隆一
セッションID: P-2
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
The purpose of this study is to establish a tumor marker that can be applied for the early detection and follow-up of oral cancer patients. Employing the proteomic approach using MALDI TOF-MS, 2-D gel electrophoresis, patient's sera and culturing cell lines, the serum autoantibodies (autoAbs) were screened and the serum levels were estimated by ELISA. Targeting the tumor cell invasion into the surrounding stromal tissues, MRC-5 human fibroblasts were employed as the target cells and a mitochondrial membrane protein, sideroflexin 3 (SFXN3), was identified. The serum anti-SFXN3-autoAb levels elevated in patients with the oral squamous cell carcinoma significantly: with 77% sensitivity and 89% specificity against control samples. The serum anti-SFXN3-autoAb levels were mildly correlated with the primary tumor sizes, however, the levels were slightly highly elevated in T1 early cancer. An immunohistochemical analysis revealed that the SFXN3 protein is expressed in the stromal fibroblasts between the caner nests and also in the basal layer of the squamous epithelium. Changes in the serum anti-SFXN3-autoAb levels after therapy correlated with the clinical tumor burden. These findings demonstrated that the serum anti-SFXN3-autoAb is worthy of clinical evaluation as a potentially of the novel tumor maker for the early detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma.
抄録全体を表示
-
渡辺 真, 竹政 伊知朗, 河口 直正, 西村 典子, 松原 稔哉, 松尾 英一, 関本 貢, 永井 克也, 松浦 成昭, 三宅 正和, 門 ...
セッションID: P-3
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
In the development of novel biomarkers, the proteomic approach is advantageous because it can directly identify cancer-associated proteins. We previously developed a 2-nitrobenzenesulfenyl (NBS) method to improve quantitative proteome analysis. Here, we applied this method to proteomic profiling of colorectal carcinoma (CRC) to identify novel proteins with altered expression in CRC. Each pair of tumor and normal tissue specimens from 12 CRC patients was analyzed, and approximately 5000 NBS-labeled paired peaks were quantified. Peaks with altered signal intensities (> 1.5-fold) and that occurred frequently in samples (> 70%) were selected, and 128 proteins were identified by MS/MS analyses as differentially expressed proteins in CRC tissues. Many proteins were newly revealed to be CRC-related; 30 were reported in earlier studies of CRC. Six proteins (ZYX, RAN, RCN1, AHCY, LGALS1, and VIM) that were up-regulated in CRC were further characterized and validated by western blot and immunohistochemistry. All six were found to be CRC-localized, either in cancer cells or in stroma cells near the cancer cells. These results indicate that the proteins identified in this study are novel candidates for CRC markers, and that the NBS method is useful in proteome mining to discover novel biomarkers.
抄録全体を表示
-
金子 直樹, 岡村 昇, 増田 太郎, 後藤 章暢, 白川 利朗, 寺尾 秀治, 渡辺 真, 松原 稔哉, 菅沼 一樹, 瀬戸 亮太, 松本 ...
セッションID: P-4
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is relatively resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Recent advances in drug development are providing novel agents for the treatment of RCC, but the effects are still minimal. In addition, there is an urgent need to identify diagnostic markers for RCC. In this report, to discover potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets, we subjected RCC samples to a quantitative proteomic analysis utilizing 2-nitrobenzenesulfenyl (NBS) reagent. Proteins were extracted from RCC and adjacent normal tissue, obtained surgically from patients, and labeled with NBS reagent containing six 12C or 13C. This was followed by trypsin digestion and the enrichment of labeled peptides. Samples were then subjected to analysis by MALDI-TOF MS. Peaks with altered signal intensities (> 2.0-fold) and that occurred frequently in samples (> 60%) were selected, and 92 proteins were identified by MS/MS analyses as differentially expressed proteins in RCC tissues. Thirty-four proteins were up-regulated in RCC samples of which some were previously known, and some were novel. The up-regulation of two proteins (Galectin-1, CNDP2) and their mRNA expression in RCC was confirmed by Western blotting and quantitative real time RT-PCR. The results suggest that NBS-based quantitative proteomic analysis is useful for discovering diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for RCC.
抄録全体を表示
-
岩瀬 怜, 上家 潤一, 大峰 健, 張替 秀郎, 大槻 純男, 寺崎 哲也
セッションID: P-5
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Acquisition of drug resistance is a critical issue in chemotherapy of leukemia, and transporters of anti-cancer drugs play important roles in the drug resistance. Comparing expression profiles of transporters at protein level between sensitive and resistance tumor cells could be a rational strategy to identify the transporters responsible for drug resistance. Recently we have developed a method to quantify multiple transporter proteins simultaneously by multi-channel MRM analysis using LC-MS/MS (1). The purpose of this study was to identify transporters involved in vincristine resistance in leukemia cells by comparison of quantitative protein expression profiles of transporters.
Crude membrane fraction was isolated from human myeloid leukemia cell line, K562 and K562/VCR (71-fold resistant to vincristine). Proteins were digested by trypsin and subjected to LC-MS/MS for simultaneous quantification of 34 ABC transporters, 5 SLC transporters and 2 membrane markers. Corresponding stable isotope labeled peptides were used as internal standard.
MDR1 protein, which mediates efflux transport of vincristine, was detected in K562/VCR cells (5.3 pmol/mg protein), but not in K562 cells (determination limit was 0.13 pmol/mg protein), indicating its induction by over 40-fold in K562/VCR cells. Protein expression of MRP1 was not significantly affected in K562/VCR cells, and MRP2, 3, and 7 were not detected in either cells, although these transporters have been reported to transport vincristine. MRP4 was decreased and ENT1 was increased significantly in K562/VCR cells, and these changes could not explain the drug resistance. The present result suggests that MDR1 is the most significant factor to acquire vincristine resistance in K562/VCR cells. A large scale quantitative profiling of transporter proteins using our technique could be a rational strategy to identify transporters responsible for a drug resistance.
(1) Kamiie et al, Pharm Res, E-pub ahead of print (2008)
抄録全体を表示
-
山岡 和子, 三島 一彦, 松谷 雅生, 西川 亮, 山本 行男, 廣井 隆親
セッションID: P-6
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Gliomas are the most common of the primary intracranial tumors. Using clinically and histologically assessed various grade of gliomas, we have studied their phosphoprotein profiles by a two-dimensional gel electrophoresis-mass spectrometry approach and identified differentially expressed phosphoproteins which may be useful molecular indicators to understand these progression. Examination of the phosphoprotein profiles of glioma samples of different grades from same patient or different grades from different patients revealed about 40 distinct, differentially expressed phosphoproteins during glioma progression. These phosphoproteins of interest were picked, in-gel digested and mass spectrometry fingerprinted. Some of them were identified successfully. These phosphoproteins belonging to various functional groups such as cytoskeleton and intermediate filament proteins, heat shock proteins, enzymes and regulatory proteins. Some were found to be differentially expressed in both Grade III and glioblastoma multiform (GBM) while others were associated with a particular grade. Several proteins had been reported previously as differentially expressed in human brain cancer in non-phosphorylated form. A notable observation was that prohibitin, a potential tumor suppressor protein, and HSPs as well as glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), major protein of the glial filaments were phosphorylated in both grade III and GBM tumors. We attempt to explain glioma malignancy and progression in terms of their combined role. Albumin, peroxiredoxin 1, aldolase C fructose-biphosphate, creatine kinase, hnRNPs, ATP-dependent DNA helicase were up regulated in GBM versus non-tumor tissues. These differentially expressed proteins provided novel information on the differences existing between normal brain and gliomas, and thus might prove to be useful molecular indicators of diagnostic or prognostic value.
抄録全体を表示
-
山中 秀徳, 堀内 雅史, 武吉 正博, 美濃部 安史
セッションID: P-7
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Blood immerses most tissues in the body and is therefore likely to contain cell-derived proteins and peptides that may provide information about various biological processes. Serum proteome and peptidome profiling—using mass spectrometry (MS) and two-dimensionalgel electrophoresis (2-DE), for example—may thus show a functional correlate of biological events and disorders. Although blood is a convenient source of biomarkers, any study of the serum proteome is confronted with the problems. First, serum is assumed to consist of minimally tens of thousands of different protein species that span a concentration range of an estimated 10 orders of magnitude. Second, the serum proteome is dominated by a few highly abundant proteins, i.e. the 22 most abundant human serum proteins combined constitute 99% of total protein mass. Indeed almost one-half of total serum protein mass is represented by just one protein, albumin.
To overcome these problems, the sample pretreatment, clean-up, enrichment, and LC-MS conditions were evaluated. At first, serum peptides were enriched by immuno-affinity column and MWCO spin-filter. Tthe depletion of abundant proteins such as albumin, IgG and transferrin was executed with immuno-affinity column and the molecular weight based fractionation was done with MWCO filter. Serum proteins of molecular weight in 5-30kDa were analyzed with 2D-DIGE and low molecular weight proteins and peptides under 5kDa were analyzed with LC-MS/MS.
抄録全体を表示
-
鍋田 基生, 阿部 康人, 香川 里沙, 木籐 克己, 草薙 康城, 横山 幹文, 植田 規史, 伊藤 昌春
セッションID: P-8
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Endometriosis, affecting women of reproductive ages, causes pelvic pain and is attributed as the cause of approximately 15% of infertility cases. The diagnosis of endometriosis is based on laparoscopic visualization, however, this method is worrisome and is not a trivial procedure. Less invasive methods for the diagnosis of endometriosis have been desired. The purpose of this study was to establish a new diagnostic marker for endometriosis that can be applied more easily on a clinical basis.
Material & methods: Experiments were carried out based on the proteomic approach using MALDI TOF-MS, 2-D gel electrophoresis, patients' sera and a human culturing cell line. All serum samples in this study were obtained with informed consent. The cells used were human malignant pleural mesothelioma cells. Sample protein was mixed with the sample loading buffer, then loaded onto the 2-D gel electrophoresis, followed by SDS-PAGE using 10% acrylamide gel. After electrophoresis, the proteins in the gel were transferred to a PVDF membrane. The membrane was incubated with the 1:1,000 diluted serum samples. In this study, sera from 3 endometriotic patients and 1 healthy volunteer were used. The membrane was incubated with anti-human IgG HRP conjugate. The membrane was developed using ECL solution and Hyper Film ECL. The 2-D gels were also stained directly with CBB. Spots were excised from the 2-D gel, treated with trypsin, and subjected to the MALDI TOF-MS analysis and the data were analyzed by the peptide mass fingerprinting method. Recombinant proteins were elaborated and ELISAs were developed for the estimation of serum autoAb.
Results: Four spots were identified as autoantigens specific to endometriosis, namely Protein A to D. None of these spots were reacted with the control serum. We analyzed these four protein by ELISA. Among these four proteins, Protein C was shown to be useful in the diagnosis of endometriosis. Now we are further investigating.
抄録全体を表示
-
曽川 一幸, 石井 知里, 佐藤 守, 小寺 義男, 朝長 毅, 野村 文夫
セッションID: P-9
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
We previously searched for a new serum markers for alcoholism using the ProteinChip® system, and found several novel markers ( Proteomics. 2004, 4:1187-95 ). Of these markers, a 5.9kDa degradation product of the fibrinogen Alpha E-chain was found to be useful for detection of gamma-glutamyltransferase non-responders in male subjects seeking for medical check-up ( Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007, 31:22S-26S ). In this study, we analyzed proteins with a molecular weight of 10kDa or more using a gel-based and three-step serum proteome analysis to identify new markers of for alcoholism.
Sixteen male patients with alcohol dependency according to the DSM IV criteria were included. Paired-serum samples were obtained on admission and at 90 days of abstinence from 16 alcoholic patients hospitalized for a rehabilitation program. As a first step, serum samples were subjected to antibody-based immunoaffinity column system that simultaneously removes six representative abundant serum proteins. The concentrated flow-through was then fractionated using reversed-phase HPLC. Proteins obtained in each fraction were separated by SDS-PAGE.
A total of 24 protein bands were found to be upregulated before abstinence and 3 were downregulated. At present, 24 upregulated bands have been identified, including Alpha2- HS glycoprotein and Apolipoprotein AI. Also, 3 downregulated bands have been identified, including Apolipoprotein CIII. Alterations of the expression levels of these 3 proteins were confirmed by the Western Blot analysis.
Clinical significance of the alteration of these proteins as compared with the conventional markers of heavy alcohol drinking remain to be investigated.
抄録全体を表示
-
吉田 豊, 山本 格
セッションID: P-10
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
HKUPP (Human Kidney and Urine Proteome Project) is an international collaborative research project for human kidney and urine proteomes, in which more than 150 participating colleagues collect and share proteomics data on the kidney and urine in order to understand functions of the kidney and mechanisms of disease progression, and finally to discover biomarkers and target molecules for new therapeutics of kidney diseases. The HKUPP has been recently approved as one of HUPO-sponsored scientific initiatives in October 2007. The data and information obtained in the project are open to the public through publications and the HKUPP website (http://hkupp.org) pertaining to the human kidney and urine proteomes.
Based on our continued discussion since HUPO 6th Annual World Congress on October 2007 and 40th ASN Renal Week on November 2007, we are planning to draft an initial HKUPP Standards and Guidelines for Urinary Proteome Analysis. These recommendations are really needed for current situation because rapidly increasing number of investigators are trying or applying urinary proteomics, particularly for biomarker discovery. In this presentation we will provide our initial draft of standards and guidelines for urinary proteomics. Our aim is neither to use these standards and guidelines as the "rules and regulations" for publication in a proteomic journal nor to discourage analysis of the archival urine samples. Our mission is to encourage investigators to pay more attention on sample collection and handling, storage and treatment, and to perform urinary proteome analysis in more standardized way.
抄録全体を表示
-
堀越 朋恵, 中山 孝, 大津 昌弘, 赤間 邦子, 中村 愛, 戸田 年総, 井上 順雄
セッションID: P-11
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Understanding neurogenesis is valuable for the treatment of nervous system disorders. To gain more insight into the induction from embryonic stem (ES) cells to neural cells, we sought to identify molecular events associated with the early transition from monkey ES cells to Neural Stem Spheres (NSSs). NSSs with a periphery of neural stem cells are formed from a colony of the ES cells by culture in astrocyte-conditioned medium under free-floating conditions. Protein extracts of the ES cells and the differentiating cells from ES cells into NSSs by culturing for four days were subjected to two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, and proteins showing the changes in their expression levels were detected. By MALDI-TOF MS, we identified protein disulfide-isomerase precursor, tumor rejection antigen (gp96) 1, tubulin alpha, translationally controlled tumor protein (TCTP) and some proteins that were up- or down-regulated. Phosphorylated TCTP was detected by ProQ Diamond staining. Furthermore mRNA levels of the identified proteins were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. These results suggest that significant changes of protein expression occur during the first stage of differentiation into neural stem cells.
抄録全体を表示
-
園 陽平, 池上 春香, 永井 宏平, 田口 善智, 細井 美彦, 佐伯 和弘, 入谷 明, 森本 康一, 松本 和也
セッションID: P-12
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Introduction: We observed that two-lines of transgenic mice ubiquitously expressing
Spinacia microsomal
fad2 gene for omega-6 desaturase were lean phenotype. These mice were shown to be resistant to obesity induced by high fat diet, indicating their basal metabolic rate is also elevated. Here, we investigated about differentially expressed proteins between two-lines of transgenic and wild-type mice.
Methods: Two mg of white adipose tissue and 1mg of skeletal muscle were homogenized and added 4uL of lysis buffer, containing 7M urea, 2M thiourea, 4% CHAPS, 0.5%IPG buffer pH 3-11 nonlinear,0.05%TBP and protease inhibitor cocktail. Proteins were separated by 2-DE and were visualized using SYPRO Ruby. The separated proteins were identified by MALDI-TOF/TOF and Mascot search (Matrix science). Expression levels of the separated proteins calculated with PG220 and TT900 software (Nonlinear dynamics). The statistical analysis of quantitative expression values of each protein was done between two lines of transgenic and wild type mice.
Result: In the white adipose tissue and skeletal muscle, 810 and 635 protein spots were commonly detected on 2-DE gels and 329 and 315 protein spots were identified by MALDI-TOF/TOF, respectively. When two lines of transgenic and wild-type mice were compared in the white adipose tissue, we observed that 38 protein spots were differentially expressed. These included glycolysis-related proteins. Moreover, 30 proteins spots were shown to be differential expressed in comparison between skeletal muscle from two lines of transgenic and wild-type mice. These proteins were involving in glycolysis and mitochondrial function. The current data suggest that up-regulated energy metabolism may induce lean phenotype in transgenic mice bearing
fad2 gene.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by grant from the Wakayama Prefecture Collaboration of Regional Entities for the Advancement of Technological Excellence of JST.
抄録全体を表示
-
黒川 真奈絵, 有戸 光美, 増子 佳世, 末松 直也, 岡本 一起, 鈴木 登, 加藤 智啓
セッションID: P-13
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
[Objective] Th1-skewed immune responses, mainly conducted by the T cells and monocytes/macrophages, play a pivotal role in the pathophysiology of Behcet's disease (BD). To analyze function of these cells more minutely, we comprehensively analyzed protein expression of peripheral blood mononucleocytes (PBMCs) from BD patients. [Methods] PBMCs were obtained from three complete type BD patients (CBD1-3), two BD patients with intestinal lesions (IBD1-2) and five healthy subjects (Healthy1-5) with their informed consent. Age and sex of Healthy 1-3 and Healthy 4-5 were matched with those of CBD1-3 and IBD 1-2, respectively. Proteins were extracted from the PBMCs and electrophoresed on 2-dimensional gels together with an internal control sample. [Results] Analysis of the three CBD patients and the corresponding three healthy subjects showed in total 1362 protein spots in the results of 2-dimensional electrophoresis. The expression levels were significantly increased to more than 2 folds in 43 spots and more than 3 folds in 17 spots in the CBD patients compared to those in the healthy subjects. In contrast, significantly decreased expression levels to less than 1/2 folds in 64 spots and less than 1/3 folds in 37 spots were found in the CBD patients in comparison with the healthy subjects. In analysis of the IBD patients, in total 2714 protein spots were obtained in the results of 2-dimensional electrophoresis. The expression levels were increased to more than 2 folds in 23 spots commonly in the IBD patients compared to those in the healthy subjects, whereas decreased expression levels to less than 1/2 folds in 75 spots and less than 1/3 folds in 23 spots were commonly found in the IBD patients in comparison with the healthy subjects. [Conclusion] The altered protein expression in PBMCs from CBD and IBD patients may be associated with the pathophysiology of BD and its intestinal lesions.
抄録全体を表示
-
金城 永幸, 岡本 一起, 有戸 光美, 黒川 真奈絵, 増子 佳世, 末松 直也, 木村 健二郎, 加藤 智啓
セッションID: P-14
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
[Introduction] IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is characterized by IgA deposition onto the mesangeal region of kidneys. Reportedly, repetition of tonsillitis often exacerbates IgAN and tonsillectomy often reduces the disease activity. Thus, tonsillar antigens would be deeply involved in the pathogenesis of IgAN. Thereby we here tried to identify the IgAN-associated antigens in tonsils by proteomic analysis. [Methods] Tonsils and sera were obtained from three IgAN patients with tonsillitis and from one patient with chronic tonsillitis. Proteins, extracted from the tonsils and separated by 2-DE, were transferred to a membrane. Western blot was performed with serum samples from the above IgAN patients and three healthy people, using anti-IgA second antibody. [Results] Mixed sera from the IgAN patients recognized 125 protein spots derived from the IgAN tonsils. On the other hand, mixed sera from the healthy people recognized 40 protein spots. The second antibody alone recognized 8 spots. Thus, 77 protein spots in the IgAN tonsils were specifically recognized by the IgAN sera. In contrast, sera from the IgAN and the healthy people recognized similar numbers protein spots in the chronic tonsillitis tonsil (61 and 63, respectively). [Conclusion] Proteins from the IgAN tonsils recognized specifically by the IgAN sera may be associated with the pathogenesis of IgAN. We are now promoting identification of these proteins.
抄録全体を表示
-
三城 恵美, 佐々木 一樹, 山口 秀樹, 里見 佳典, 石津 雄大, 熊谷 久美子, 高尾 敏文, 中里 雅光, 南野 直人
セッションID: P-15
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Neuroendocrine regulatory peptide (NERP) -1 and NERP-2 are novel amidated peptides identified by peptidomic analysis of culture supernatant of an endocrine-type tumor cells. NERPs are processed out from VGF, a polypeptide secreted through the regulated pathway from neurons and endocrine cells (J. Biol. Chem., 282, 26354-60, 2007). We have shown that NERPs dose-dependently suppress the arginine vasopressin (AVP) release induced by hypertonic NaCl or angiotensin II in vivo and in vitro in the rats.
The natural occurrence of NERPs was confirmed by studies using specific antibodies and radioimmunoassays (RIAs). Before investigating the biological function of NERPs, we here measured rat tissue levels of the NERPs by RIA. They were present in the gastrointestinal tract, adrenal gland, and thyroid gland, and particularly abundant in the brain and pituitary. Characterization of immunoreactive (ir-) materials in the brain with a conventional approach (liquid chromatography coupled with RIA) elucidated the endogenous presence of NERP-1, NERP-2 and big NERP-2 in rat brain extract. NERP-1 and NERP-2 were confirmed by mass analysis of the ir-materials on a surface-enhanced laser desorption ionization (SELDI) mass spectrometer as well. The molecular structure of big NERP-2 was deduced as NERP-1+NERP-2 including an intervening tri-peptide by SELDI analysis and immunological properties.
While peptidomics has largely relied on mass spectrometric techniques for endogenous peptide determination, larger peptides often escape mass spectrometry-based identification. In this study, we demonstrated the significance of determining endogenous peptide forms with conventional methods, following mass spectrometry studies. Especially, a specific antibody recognizing the identified peptide is a crucial tool for the follow-up analysis.
抄録全体を表示
-
中村 愛, 森澤 拓, 大海 忍, 高村 千鶴子, 福田 宏之, 戸田 年総
セッションID: P-16
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Oxidative stress is thought to be implicated in a number of age-associated disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. Dopamine neurons are known to be vulnerable to age-related disorders because of exposure to high level of oxidative stress by dopamine metabolism in neurons. Previously, we found that 6-hydroxydopamine-induced (6-OHDA, a dopaminergic neurotoxin) oxidative stress made changes in phosphorylation of nuclear lamin A/C, elongation factor 2, T-complex protein 1, and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H3 using human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y cells.
To understand the molecular basis of cellular response to oxidative stress, detailed information of protein-protein interaction under physiological (native) conditions is required. Here we further examined oxidative stress-related changes of SH-SY5Y cellular proteins by using blue-native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE), a powerful tool for the separation of protein complexes. BN-PAGE gel images showed successful separation of several complexes. Components of these complexes, separated by 2-D BN-PAGE in combination with SDS-PAGE, were identified by peptide mass fingerprinting on MALDI-TOF MS and MS/MS ion search on LC-MS/MS. TCP-1 complex, ATP synthase, and the complex of heat shock protein 90 and its client proteins such as pyruvate kinase were detected. Several proteins were shown to be changed by oxidative stress. Identification of these proteins is now in progress.
抄録全体を表示
-
宮崎 賢司, 田伏 洋, 寺本 礼仁, 藤田 真知子, 服部 渉, 川浦 久雄, 宗政 歓子, 松村 貴由, 相澤 健一, 永井 良三, 鈴 ...
セッションID: P-17
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which contains apoB100 as a major component, plays an important role in atherosclerosis. As oxidation of apoB100 occurs in several patterns in artificially oxidized LDL, detection and characterization of patterns of oxidation of apoB100 in serum is useful for diagnosis and evaluation of progression of atherosclerosis. However, intensive research for such modification in the serum protein using mass spectrometry has just begin on a global scale, and patterns of oxidation of apoB100, which play central roles in atherosclerosis, have been unclear.
To quickly analyze chemical modification patterns of proteins, we have developed a protein chip (a microfabricated device) on which peptides and proteins are separated in only a few minutes at a single run according to their iso-electric focusing points followed by MALDI-TOF MS analysis. Importantly, apart from sample preparation, the "2-DE" profile (pI and m/z) for the peptide mixtures is obtained in only 8 hours for 4 samples (on one chip) and the profile can be used for differential analysis between samples. Using this device, we investigated the patterns of oxidation of apoB100 in serum. Immunoprecipitation with anti-oxLDL antibody was carried out against a small amount of serum derived from both patients with atherosclerosis and healthy controls. Immunoprecipitated proteins were digested with trypsin and the digested products were diluted in electrophoresis buffer and then subjected to chip analysis. Obtained peptide profiles showed that several peptides were observed specifically in patients. Therefore, oxLDL is shown to be a candidate for a biomarker of atherosclerosis.
Collectively, here we show a novel device and detection method for screening a biomarker of atherosclerosis, which may be useful for screening and understanding the progression of atherosclerosis.
抄録全体を表示
-
鏑木 康志, 井狩 高平, 山下 亮, 郡司 眸, 浜田 圭子, 高橋 枝里, 安田 和基, 野田 光彦
セッションID: P-18
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Microalbuminuria is an established early marker of diabetic nephropathy, the leading cause of end-stage renal disease, and is used to classify the clinical stage of diabetic nephropathy. However, other urinary proteins including transferrin and type IV collagen have also been proposed as diagnostic markers of diabetic nephropathy, although their usefulness is yet to be established. In this study, we developed a two-dimensional gel-based method that enabled the analysis of approximately 2000 protein spots by combining ultrafiltration, immunoaffinity depletion of major urinary proteins, and 2D DIGE. Using this experimental system, we analyzed urine samples collected from diabetic patients with microalbuminuria, diabetic patients with normoalbuminuria, and healthy controls in order to search for early urinary diagnostic markers of diabetic nephropathy. In diabetic patients with microalbuminuria, 2D DIGE analysis identified 312 protein spots that were differentially expressed as compared with those in the healthy controls; from these spots, 33 unique proteins (24 upregulated and 9 downregulated) were identified. The upregulated proteins included several proteins previously reported to be elevated in the urine in the diabetic patients with microalbuminuria patients, such as ceruloplasmin, serotransferrin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein, haptoglobin, antithrombin-III, and leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein. We also detected a decrease in hemopexin in the urine samples obtained from diabetic patients with microalbuminuria, although most of the downregulated proteins detected in this study have never been reported to be decreased in the urine in diabetic nephropathy patients. These proteins may be potential biomarkers of early-stage diabetic nephropathy. Further studies in a large-scale cohort may confirm the utility of these proteins in diagnosing diabetic patients at a stage earlier than that detected using the urine albumin level.
抄録全体を表示
-
林原 加代子, 若松 秀和, 農 大輔, 小林 昇平, 内山 進, 松永 幸大, 福井 希一
セッションID: P-19
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
In higher eukaryotic cells, DNA presents as a chromatin fiber, a complex with various kinds of proteins, and chromatin fibers are highly condensed to form metaphase chromosomes during mitosis. Formation of metaphase chromosome structure is essential for equal segregation of replicated chromosomal DNA into the daughter cells. So far, information on the higher order structure of metaphase chromosome remains to be limited. Thus, we have carried out proteome analysis of isolated human metaphase chromosomes, provided proteinous view of the chromosomes (Uchiyama et al., J. Biol. Chem., 2005). In this study, in order to identify proteins involved in formation and/or maintenance of metaphase chromosome, the critical points of NaCl concentration of the solution at which the morphology of the isolated metaphase chromosomes dramatically changes has been determined and the proteins dissociated from the chromosomes at that points were identified. Under 0.4 M NaCl condition, the size of the chromosomes became significantly larger than those in the lower concentrations, with DNA haloes appearing around the chromosomes, and the separation of each sister chromatid at the arm region. The dissociated proteins were identified using ESI-LC MS/MS and MALDI-TOF MS, followed by classification into four groups based on their functional information and localization. Some of the identified proteins whose functions on mitotic chromosomes have not reported are now being analyzed for characterization.
抄録全体を表示
-
石田 洋一, 榊原 陽一, 須藤 正幸, 竹下 正彦, 宇都 浩文, 水光 正仁, 坪内 博仁, 片岡 寛章
セッションID: P-20
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is currently a very common malignancy and its incidence is increasing. Persistent infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a major risk factor for the development of HCC. A part of HCV carriers develops HCC about 30 years after the initial infection. Considering of the long period until the development, foods taken daily are important for the prevention of HCC.
We have been searching for functional foods effective for the prevention of HCC, and then investigating on the action mechanism of these ingredients using proteomic analysis. Recently, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), which is the ingredient of green tea, has been reported to have preventive effects on HCC
in vivo; however, the action mechanism of EGCG is not fully understood. In this study, we tried to identify new target protein(s) of EGCG using affinity chromatography and two-dimensional fluorescence difference gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE).
To identify EGCG-binding proteins, EGCG-immobilized sepharose beads were prepared using the epoxy activation method. To detect proteins that bind specifically to EGCG, catechin- and epicatechin-immobilized beads were used as control. Protein extract of HCV replicon cells, which are Huh7 human hepatoma cells stably transfected with subgenomic HCV constructs, was treated with EGCG-, catechin-, or epicatechin-imobilized beads. Then, Proteins that bound to the beads were eluted followed by 2D-DIGE. Fluorescent intensities of 13 spots in EGCG-binding proteins were significantly increased as compared with those in catechin-binding proteins and epicatechin-binding proteins (>1.5-fold change, P < 0.05). By peptide mass fingerprinting using MALDI-TOF/TOF MS, proteins related to lipid metabolism and redox-regulation were identified. These proteins have not been reported as EGCG-binding proteins. Several proteins are possibly new targets of EGCG. Further investigation is in progress.
抄録全体を表示
-
池上 春香, 園 陽平, 永井 宏平, 吉廣 卓哉, 井上 悦子, 小林 直彦, 松橋 珠子, 大谷 健, 中川 優, 森本 康一, 松本 ...
セッションID: P-21
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Introduction: In livestock researches, the proteomics has the potential to be a method for identification of biomarker related to carcass and meat quality traits. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) has been used in combination with MS identification of specific proteins as the proteomics tool. However, proteins that contribute to individual variations in carcass and meat quality traits are not fully understood. In order to discover protein biomarkers involved in carcass and meat quality traits in Japanese Black beef cattle, we have advanced large-scale proteomic analysis of bovine white adipose tissue (WAT), using 2-DE and mass spectrometry.
Methods:Proteins extracted from the WAT were separated by 2-DE and visualized using SYPRO Ruby. The separated proteins were identified by MALDI-TOF/TOF and Mascot search engine (Matrix science). Expression levels of the separated proteins were calculated with TT900 and Progenesis PG220 software (Nonlinear dynamics). Finally, correlation of protein expression and the carcass trait was examined by the statistical analysis using the quantitative expression values of each protein in the WAT from 133 animals.
Results:In our study, 879 protein spots were detected on the 2-DE gels. Of these, a total of 459 protein spots were extensively identified by MALDI-TOF/TOF. As a result of statistical analysis, it was shown that in higher carcass weight (CW) group, 95 protein spots were up-regulated and two protein spots were down-regulated compared with those in lower CW group. These proteins identified as biomarker candidates to the carcass weight in Japanese Black beef cattle are involved in a variety of functions, including energy metabolism, cell structure, cell defense, transport, and signal transduction.
Acknowledgement:This work was supported by a grant from the Wakayama Prefecture Collaboration of Regional Entities for the Advancement of Technological Excellence of JST.
抄録全体を表示
-
及川 伸二, 山田 智子, 小林 果, 古川 絢子, 及川(多田) 佐枝子, 平工 雄介, 村田 真理子, 山嶋 哲盛
セッションID: P-22
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Oxidative stress during ischemia-reperfusion is thought to be a major cause of brain injury. It has been reported that reactive oxygen species (ROS) causes extensive cell death in the cornu ammonis (CA) 1 region but not in the remaining CA2-4 region and dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus, which is known to be involved in learning and memory processes. In this study, to identify and characterize carbonyl-modified proteins, protein oxidation products, in hippocampal CA1 region isolated from Japanese monkeys after transient cerebral ischemia-reperfusion, we performed two-dimensional gel electrophoresis with immunochemical detection of protein carbonyls (2D Oxyblot) and two-dimensional differential in-gel electrophoretic analysis (2D DIGE). Using 2D Oxyblot analysis, we demonstrated for the first time that carbonyl modification of heat shock 70 kDa protein 1 (Hsp70-1), a member of Hsp70 family, in CA1 region was extensively increased prior to the neuronal cell death induced by ischemic-reperfusion insult. Hsp70 molecular chaperones are known to be induced by oxidative stress and have neuroprotective function. Therefore, we considered that ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative damage to Hsp70-1 in CA1 region may lead to loss of the neuroprotective function, which contributes to neuronal cell death.
抄録全体を表示
-
張 瑩, 吉田 豊, 許 波, 行田 正晃, 矢尾板 永信, 藤中 英彦, 山本 格
セッションID: P-23
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
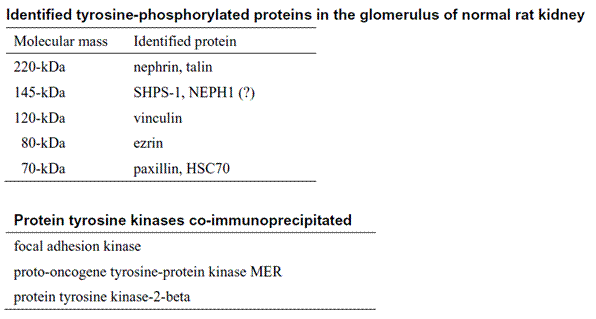
We have previously demonstrated the predominant localization of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins in podocytes in the glomerulus of normal rat kidney by immunoblotting and immunohistochemical analyses using anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies. The five major phosphoproteins (70-, 80-, 120-, 145- and 220-kDa), which were detected on 1-DE immunoblotting analysis, were spitted into multiple spots on 2-DE gels. A newly developed technique for precise matching of immunoreactive spots to corresponding spots on silver-stained 2-DE gel, in combination with a comprehensive analysis of immuno-affinity purified tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins, successfully identified 8 proteins including novel phosphoproteins and 3 co-immunoprecipitated tyrosine kinases as shown in Table. Based on these findings we speculate that tyrosine-phosphorylation of membrane cytoskeleton associated proteins and other signaling molecules play roles not only in maintain the unique cytoskeleton organization in the podocyte but also in signal transduction of the glomerulus.
抄録全体を表示
-
片野 雅淑, 松尾 光祐, 黒川 真奈絵, 有戸 光美, 増子 佳世, 末松 直也, 岡本 一起, 加藤 智啓
セッションID: P-24
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
[Objective] To explore disease-associated molecules in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), we analyzed phosphorylation of synovial proteins in RA in comparison with that in osteoarthritis (OA).
[Materials and Methods] Synoviocytes were obtained from three RA patients and three OA patients. Phosphoproteins purified from the synoviocytes were compared by 2D-DIGE between RA and OA. Protein spots with significantly different phosphorylation levels, were identified by mass spectrometry.
[Results] 22 spots showed more than 2-fold phosphorylation and one spot showed less than 1/2 fold phosphorylation in RA compared to OA. We identified 11 phosphoproteins out of the former 22 spots and the latter one spot. We specifically investigated roles of one of the identified proteins, Annexin A4. Interestingly, introduction of a recombinant Annexin A4 protein into OA synoviocytes reduced production of CXCL-1 and IL-8 brought by TNF alpha stimulation.
[Conclusion] We successfully identified multiple synovial phosphoproteins whose amounts were significantly increased in RA compared to OA. Severe synovial inflammation in RA may lead to the increased phosphorylation of Annexin A4, which decreases CXCL-1 and IL-8. Further phosphorylation of Annexin A4 may have therapeutic roles in RA treatment, by reducing chemotaxis of inflammatory cells into synovium.
抄録全体を表示
-
京野 完, 杉山 直幸, 冨田 勝, 石濱 泰
セッションID: P-25
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Recent advances in MS-based proteomics coupled with phosphopeptide enrichment methods allow the simultaneous identification of hundreds of phosphorylation sites. Previously, we reported a novel phosphopeptide enrichment method using aliphatic hydroxy acid-modified metal oxide chromatography (HAMMOC)
1), 2). This approach drastically reduces the binding of non-phosphorylated peptides to metal oxide and enriches phosphopeptides directly from crude biological samples such as cell lysates. In addition, we optimized elution conditions for phosphopeptides captured by HAMMOC to enlarge the phosphoproteome coverage. The optimized HAMMOC elution conditions provided a 1.6-fold increase in phosphopeptide number and a 1.9-fold increase in total peak area of phosphopeptides in comparison with the results obtained under the conventional conditions using ammonium hydroxide and phosphate buffers. By those improvements of phosphopeptide enrichment methods, over 3,000 non-redundant phosphopeptides could be identified from 100ug proteins from HeLa cell lysates at present. We also focused on the identification of multiply phosphorylated peptides, which are generally difficult to be identified by MS2 mode because the labile phosphate groups lead to the lack of b- and y-ion series. Neutral loss-triggered MS3 and multistage activation approaches have been used to generate more b- and y-ions. However, in our hand, these approaches did not show significant improvement because of the less number of the precursor ions selected for the fragmentation. On the other hand, alkaline treatments prior to LC-MS analysis, which generates dehydroalanine and dehydrobutyrine from pSer and pThr, respectively, improved to identify multiply phosphorylated peptides without using the multistage activation mode. This approach was also applied to HAMMOC to elute phosphopeptides.
1) N. Sugiyama et al., Mol. Cell. Proteomics, 6, 1103-1109(2007)
2) J. Rappsilber et al., Nat Protoc., 2, 1890-1906(2007)
抄録全体を表示
-
入江 厚, 原田 久美子, 荒木 令江, 西村 泰治
セッションID: P-26
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
We previously found that the nuclear phosphoprotein SET is a candidate substrate for protein kinase D2 (PKD2) in T cells. The SET is mainly localized in the nucleus and is an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), however, the relation between its functions and phosphorylation by PKD2 was not known. To clarify this issue, the amino acid residue of SET phosphorylated by PKD2, and the effects of phosphorylation on the cellular localization of SET and on PP2A phosphatase activity were investigated. In vitro kinase assay using various SET mutants revealed that the Ser171 was phosphorylated by PKD2. Ser171 is within the putative bipartite nuclear locarization signal of SET (168KRSSQTQNKASRKR181), however, both substitutions of S171 to Glu (S171E, phosphorylation-mimic) and to Ala (S171A, non-phosphorylation-mimic) had no effect on its nuclear locarization. Instead, S171E as well as wild-type SET treated with active PKD2 and ATP compromised its inhibitory effect on phosphatase activity of PP2A in vitro. Over-expression of S171E mutant of SET in Jurkat cells reduced the amount of phospho-ERKs induced by TCR-stimulation and this effect was canceled by the treatment with a PP2A inhibitor okadaic acid. These results suggest that phosphorylation at Ser171 of SET affects its inhibitory effect on PP2A and that PKD2 may regulate PP2A activity through the phoshorylation at Ser171 of SET protein.
抄録全体を表示
-
森川 崇, 坪田 誠之, 長山 慈, 小林 大樹, Anthony Wilson, Wilson森藤 政代, 中村 英夫, 倉津 純一, 森 ...
セッションID: P-27
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Loss of heterozygosity on chromosome arms 1p and 19q (LOH+) in anaplastic oligodendroglioma(AOG)/oligodendroastrocytoma(AOA) are frequently associated with chemotherapeutic response and overall survival of patients. To clarify the mechanism of the chemotherapy sensitivity of AOG/AOA, we analyzed tissue specific proteins which show the different expressions and phosphorylations in each tumor. The tumors collected after the surgical operation from the AOG/AOA patients, were analyzed pathological and genomic background, and divided into two groups according to their chemotherapy sensitivities. The proteins prepared from each tumor were subjected to 2-D DIGE, combined with ProQ diamond staining and iTRAQ. Recently, we identified 105 specific proteins expressed in LOH- compared with LOH+, including EGFR-MAPK and PI3K-AKT signal molecules, vascular PIFs, adhesion molecules, cell cycle regulator CDK families, and cytoskeletal organizing factors. Among them, we focused on vimentin that were highly expressed in LOH- samples with specific phosphorylated forms (at least 15 vimentin spots were identified). We confirmed increased expression of vimentin by immunohistochemistry and in 2D-western blotting in LOH- compared with LOH+. Interestingly, in addition to the specific phosphorylation, vimentin had some cleavage forms in LOH-. We classified the cleavage into 4 different MW groups, that is 53kDa(group1), 48kDa(group2), 45kDa(group3) and 42kDa(group4). By 2D-western blotting and MS analysis, we identified the spots of Group4 and acidic side of group1 were proteolytic forms and specific phosphorylation forms of the N-terminal vimentin, respectively. In addition, the proteins of group 1 and 4 of LOH- were much higher expression than those of LOH+. The specific structure and functional changes of vimentin and responsible enzymes regulated with the relation of the chemotherapy sensitivity will be analyzed and discussed in detail.
抄録全体を表示
-
高藤 和輝, パッタマー ウイリヤサムクン, 永森 收志, 金井 好克
セッションID: P-28
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Amino acids are important nutrients for living organisms and used as the substrate for a lot of biological reactions such as protein biosynthesis. Recently, it has been indicated that amino acids are not only substrates for protein biosynthesis, but also serve as signaling molecules controlling signal transduction pathways of protein biosynthesis. Especially, among all amino acids, it is reported that leucine stimulates protein biosynthesis remarkably.
Many evidences show that the stimulation with leucine is promoted by activation of mTOR signal transduction pathway. mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) is a huge serine/threonine kinase of molecular weight 280 kDa. It is also reported that the mTOR pathway is regulated by insulin or low energy hypoxia. This pathway is related to various biological phenomena of cell growth, cell cycle and autophagy inhibition besides the promotion of protein biosynthesis. Current studies suggest that the activation mechanism of the mTOR pathway by leucine is different from the activation mechanisms by insulin or low energy hypoxia. However, the activation mechanism by leucine is poorly understood.
Here we have examined the leucine-stimulation to the mTOR pathway using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis followed by staining with fluorescent phosphoprotein dyes as well as total protein staining. Cells were cultured in the absence of leucine and harvested after leucine-stimulation or no stimulation. Then, total proteins were subjected to the two-dimensional gel electrophoresis experiments. The results allow us to analyze expression and phosphorylation of proteins comprehensively. Finally, we have identified proteins which show significant different profiles of expression and/or phosphorylation in the absence or presence of leucine-stimulation by means of LC-MS.
抄録全体を表示
-
羽二生 久夫, 小山 省三, 金 隆岩, 林 卓哉, 竹内 健司, 遠藤 守信
セッションID: P-29
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
We have the alternation of protein expressions using human monoblastic leukemia cells (U937) exposed to multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) to explore the possibility of a new safety evaluation method using the proteomic approach. MWCNTs obtained by the catalytic chemical vapor deposition method were treated with four different temperatures to remove polyaromatic hydrocarbons and iron compounds as catalysts. The cells with MWCNTs were cultured for 4 days, counted, and analyzed by 2-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE). The protein spots with alteration of expression level were identified by matrix-associated laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. To the extent that the processing temperature of the MWCNTs was low, cell proliferation tended to be inhibited. But there were no significant differences in the proliferation of U937 cells which were exposed to MWCNTs treated with the highest temperature. On the other hand, when the MWCNTs were treated with low temperatures, the spots that showed changes in the protein expression levels increased. The intensity of 37 spots on 2-DE gels changed significantly (P < 0.05) on U937 cells exposed to MWCNTs treated with a lower temperature, while MWCNTs treated with the highest temperature changed 20 protein spots. Peptide mass fingerprinting identified 35 of 37 and 16 of 20 protein spots. Five spots were common among all grades of MWCNTs. Some stress-related proteins even changed in the cells exposed to MWCNTs treated with the highest temperature. In regard to safety risk, the proteomic approach could detect biological responses more sensitively than conventional evaluation methods
in vitro.
抄録全体を表示
-
坂口 菜央, 木下 英樹, 平塚 淳典, 丸尾 祐二, 坂入 幸司, 植山 公助, 鵜沼 豊, 横山 憲二
セッションID: P-30
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
(Summary)
Two dimensional electrophoresis (2DE) has widely been used to analyze proteins comprehensively. Both quantitative and post-translational modification analyses of proteins can be achieved in a single experiment. However, 2DE has several issues, such as time consuming separation protocol, poor reproducibility, and labor-intensive manners.
We have developed a fully automated 2DE system to solve those issues. The 2DE system achieved miniaturization of its size, improving reproducibility of spot position of the proteins. Sample introduction time was also minimized down to 5 minutes using 10 ul of small amount of solution, a miniaturized IPG gel strip (1.2 mm wide and 54 mm long) and a rehydration chamber (0.8 mm wide, 50 mm long and 0.52 mm deep). However, highly reproducible introduction of the sample volume was not achieved unless the entire region of the sample introduction chamber was spread with the sample solution.
In this study, we constructed a series of micro groove structures on the chamber in order to achieve the reproducible sample introduction to IPG without manual spreading the entire region of the chamber. Nine rectangular grooves (100 um wide, 54 mm long and 100 um deep) were fabricated on the bottom of the chamber. The newly constructed system can automatically introduce a sample solution to the entire region of the chamber by capillary action when 10 ul of the sample was only poured onto the center of the chamber. Reproducibility of the sample introduction is also improved.
抄録全体を表示
-
木下 英樹, 坂口 菜央, 平塚 淳典, 丸尾 祐二, 鵜沼 豊, 横山 憲二
セッションID: P-31
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
(Introduction)
A western blotting method is widely used to detect specific proteins in clinical and biochemical research areas. Proteins from living cells are separated using SDS-PAGE, followed by transfer from polyacrylamide gel to membrane, e.g. poly vinylidenefluoride (PVDF), on which protein blots are formed. Finally the blotted proteins are stained using immunoreaction. In this procedure, there are many steps such as soaking and stirring the blotted membrane. The immuno-staining reaction needs a long time and a large amount of antibodies to be reacted uniformly on the membrane. In addition, the membrane is thin and bendable, which causes difficulties of adaptation for automatic conveying system.
Recently, we are developing a fully automated immunoreaction system which is capable of uniform staining, a short staining time and a small amount of antibody. Here, we are reporting a mechanical structure of this system and experimental results of western blotting.
(Methods and results)
Figure shows a layout of the automated immunoreaction system. A platen-shaped structure folds the membrane and is conveyed using a bi-axial mechanical system. Immunoreactions are made using rotating the structure at a constant rate. The structure is conveyed into the reaction wells continuously.
Carbonic anhydrase protein (Sigma-Aldrich) was used as a model sample and immobilized on a membrane using screener-blotter (Sanplatec). An anti-carbonic anhydrase antibody and fluorescent labeled IgG antibody were used as the primary and secondary antibodies, respectively. In conventional method, immunoreactions were carried out in the plastic bag, and a blocking reaction and rinsing were made in the plastic container.
The results of western blotting showed that the lower detection limit of protein was the same level as the conventional method (approximately 100 fmole/ mm
2). Better uniformity of the fluorescent staining over the area of the membrane was achieved.
抄録全体を表示
-
佐々木 典子, 矢野 和義, 佐藤 淳, 木下 英樹, 坂口 菜央, 平塚 淳典, 鵜沼 豊, 丸尾 祐二, 緑川 宇一, 中村 眞, 坂入 ...
セッションID: P-32
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
For the personal diagnosis, we developed an easy, highly reproducible and fully automated two-dimensional (2D) gel electrophoresis system. Prior to using the clinical samples, the performance of this system was evaluated by using the samples prepared from mouse tissues. Also, a cell-based tumorigenesis model was constructed by treating the normal phenotype mouse fibroblast, NIH3T3, with a tumor promoter, TPA, which induces the tumor-like signals. The transition of cellular protein phosphorylation status by treatment with TPA was further investigated by phosphoprotein staining and western blotting using antibodies against some major proteins in cell growth signaling pathway.
Analyses of positions and shapes of some selected protein spots revealed that our 2D system had resolution comparable to commercial minigel systems. We also investigated the transition of the protein phosphorylation status by 2D-western blotting in NIH3T3 tumorigenesis model. Because p44 and p42 MAPK has two phosphorylation sites each, their spots are shifted to acidic side according to the number of phosphorylation. After treatment with TPA, the antibody against p44 and p42 MAPK detected 6 spots (3 spots each), while no treated samples showed only 2 spots (1 spot each). Furthermore, when the two images of western blots were overlapped, the spots located in alkaline side was shown to be also overlapped. Taken together, these data indicated that our 2D system had high reproducibility and resolution enough to separate one amino acid phosphorylation.
We further constructed a cell-based inflammatory response model. Differentiated human monocytic leukemia cell line, THP-1, was treated with LPS. We will present the investigation resluts concerning the transition of cellular protein status by western blotting using antibodies against proteins related to immune response.
抄録全体を表示
-
緑川 宇一, 木下 英樹, 平塚 淳典, 田中 毅, 松永 貴輝, 丸尾 祐二, 鵜沼 豊, 横山 憲二, 中村 眞
セッションID: P-33
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
The two-dimensional electrophoresis and Western blotting are widely used in comprehensive study of the proteome. In this system, proteins are separated by an isoelectric focusing and SDS-PAGE, and transferred to a membrane electrically, followed by the detection with immunoreactions. Generally both devices for electrophoresis and electroblotting are used independently. Researchers have to take out gel from the electrophoresis device, and set gel and membrane to electroblotter manually, and these procedures always lack reproducibility of the protein transfer efficiency and resolution, and also are complicated and time consuming.
To solve these problems, we are developing a fully automatic operation system of gel electrophoresis and Western blotting with higher reproducibility in a shorter time. This system will make it possible to perform all processes automatically; sample introduction, isoelectric focusing, SDS-PAGE, blotting, and immunoreactions. (Researchers only have to set a sample, a gel tip and buffer solution on this device.)
In this study, we developed an automated sequential system that makes possible to separate proteins in a gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), followed by a continual electroelution, and blotting to PVDF membrane. We optimized the system condition, such as the gel concentration of SDS–PAGE, current of electroblotting (20-25mA), velocity of PVDF membrane movement, and the constitution of the buffer solution on this device.
It was successful to obtain reproducible results on the transfer efficiency of proteins with a high resolution using this automated system, at the same level as a result obtained by the general manual protocol commonly used, and this system will be useful for the study of the proteins in biological materials.
抄録全体を表示
-
坪田 誠之, 森川 崇, 小林 大樹, 木下 英樹, 坂口 菜央, 平塚 淳典, 丸尾 祐二, 緑川 宇一, 鵜沼 豊, 佐々木 典子, 矢 ...
セッションID: P-34
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
We have developed a fully automated two-dimensional gel electrophoresis system (auto-2D system) which makes tissue/cellular protein analysis by 2D-PAGE and 2D-western blotting more simple, quick, sensitive, and reproducible with a small volume of sample within 2 hrs, thus, being expected as a convenient clinical analysis tool for the personal diagnosis. In this study, we utilized this system for the analysis of brain tumor specific proteins. Malignant gliomas are generally resistant to all standard therapies, however, patients with Anaplastic oligodendroglioma(AOG) or oligoastrocytoma(AOA) with loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 1p/19q (LOH+) frequently respond to chemotherapies. Information of the factors for these clinical findings has not been reported so fat. We have been studying specific proteins related to these findings by using newly established techniques of proteomics such as phospho-2D-DIGE and iTRAQ methods. Recently, we identified 105 specific proteins expressing in LOH- compared with LOH+AOG/AOA, which include EGFR-MAPK/PI3K-AKT signal molecules, vascular PIFs, adhesion molecules, cell cycle regulator CDK families, and cytoskeletal regulating proteins. Among them, we focused on vimentin, GFAP and CDK4 that were highly expressed with unique 17 phosphorylated/proteolysed forms in LOH- samples. Using a specific antibody cocktail to detect these proteins by the auto-2D-western blotting, we analyzed 30 samples of AOG/AOA and identified the specific pattern of LOH- tissue compared with LOH+ samples. The resolution, sensitivity and reproducibility for the analysis of this brain tissue specific spot pattern by the auto-2D method were significantly higher than those by the conventional methods. These results suggest that this auto-2D-western method will be useful to study the specific protein expression profiles not only for the brain tumors but also for variety of the biological specimens, and could be introduced as a new clinical laboratory technology.
抄録全体を表示
-
松山 由美子, 工藤 寿治, 韮澤 崇, Anja Resemann, Arndt Asperger, Katrin Sparbier, K ...
セッションID: P-35
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Glycosylation is the most abundant post translational modification of proteins. Analyses of glycopeptides of the N-liked type with MALD-TOF/TOF-MS provides for identification of the peptide as well as characterization of the glycan part and determination of glycosylation sites of glycoproteins.
2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) is the matrix of choice for carbohydrate and glycopeptide analysis. We developed a sample preparation providing homogeneous sample morphology with low propensity to from sweet spots combined with a precisely defined sample dimension and location well suited for the unattended acquisition of spectra from DHB.
Automated LC-MALDI analysis of tryptic digests of glycoproteins permitted sensitive MS/MS analyses of glycopeptides on MALDI-TOF/TOF instrumentation: dedicated software a) provided automatically the list of glycopeptides, b) allowed the direct peptide identification via Mascot, and c) provided the modification site in the peptide and first insights into the glycostructure.
抄録全体を表示
-
森澤 拓, 廣田 三佳子, 中村 愛, 戸田 年総
セッションID: P-36
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
The HUPO Proteomics Standards Initiative (PSI) defines community standards for proteomics research. The data format capturing peak list information of mass spectroscopy in them is mzDATA. Its phase is released before publish. Measuring instruments for mass spectroscopy and data mining software for the peak list are just corresponding to mzDATA. We use Mascot search engine (Ver 2.1.04) that accepts mass spectrometry data to identify proteins and Launchpad that supports the unique functionality of the mass spectroscopy, AXIMA-TOF2 in our institution. Mascot and Launchpad (Ver 2.7.0) are announced to correspond to mzDATA in HUPO PSI's homepage.
We investigate utilizations of mzDATA in our original laboratory information management system, LIMS for 2-D gel electrophoresis-based proteomics workflow. We have to accept that peak lists of mzDATA format saved from Launchpad differ from peak lists of manual setup in Launchpad measuring same sample by AXIMA-TOF2. If required, we should store the both peak lists in our LIMS. We have been studying requirements of them in our LIMS comparing the examinations of them by Mascot. And we would like to review all information of the mzDATA format in this presentation.
抄録全体を表示
-
細田 晴夫, 岩崎 了教, 瀬田 丈士
セッションID: P-37
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
We will describe a novel API-Qq-TOF mass spectrometer with ultra-high-resolution and ultra-high MS and MSMS mass accuracy at high scan speed. The resolution, speed and mass accuracy along with intra-spectra dynamic range of more than four orders of magnitude and preservation of isotopic patterns sets a new gold standard for one of the key challenges in the proteomic world – label free quantitation of complex biological samples.
The comprehensive quantification of specific changes in biological systems would use labelling with dyes or isotope enriched chemicals thus generating internal standards for quantification. Unfortunately, many labelling strategies are expensive, require large amounts of sample and can introduce significant quantitation errors due to extensive sample handling steps. The label-free approach aims to compare direct mass spectrometric signals across multiple LC runs. The main advantages for label free quantitation on our novel API-Qq-TOF are a rapid, inexpensive, robust and accurate method with the added advantage that less sample is required. Potential biomarkers can then be fragmented and confidently identified using MSMS mass accuracy in the region of 1ppm. Challenging large peptides and small proteins can additionally be identified using Electron Transfer Dissociation (ETD) fragmentation and Proton Transfer Reaction (PTR) on an ultra high speed High Capacity Trap.
We will demonstrate the successful application of label free quantitation on our novel API-Qq-TOF in a proteomics study of a cell culture model, Human lung carcinoma cell line A549. The treatment of these cells using TGF-beta is a model for lung fibrosis. We will compare the results between a 2D-DIGE study and our novel workflow for label free quantitation.
抄録全体を表示
-
西風 隆司, 天野 純子
セッションID: P-38
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
Glycosylation is one of the most important and ubiquitous posttranslational modifications. To date mass spectrometry (MS) is expected as a powerful tool for determination of these modifications. In particular, matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) has many advantages over other soft ionization methods due to its high sensitivity, simple spectrum, and rapid analysis. However, it is difficult to detect trace amounts of glycopeptides because they show inherent low ionization efficiency compared to unmodified peptides.
In order to overcome this problem, we have developed on-plate pyrene derivatization for highly sensitive and easy determination on MALDI-QIT-TOFMS and applied to glycopeptides. Interestingly, the ion yields of glycopeptides were enhanced by on-plate pyrene derivatization, whereas the peptide ion signals drastically decreased in both positive- and negative-ion mode. To elucidate the mechanism in this study, various kinds of peptides were measured after on-plate pyrene derivatization. As the result, generation of positive- and negative-ion from most of peptides used here was suppressed by on-plate pyrene derivatization. The extent of signal suppression seems to be dependent on physicochemical properties of peptides. Especially, more pyrene groups should be introduced to peptides rich in carboxyl groups and the ionization of them was more effectively suppressed even in positive-mode than other peptides. This suggests that the increasing number of pyrene in the peptide molecules have a negative effect on its ion yields. Although the detailed mechanism remains unclear, on-plate pyrene derivatization can selectively enhance ionization of glycopeptides but not peptides and is very useful for analysis of glycoprotains from biological samples.
This work was supported by Japan Science and Technology Agency, Development of Technology for Advanced Measurement and Analysis Program.
抄録全体を表示
-
大房 健, 一ノ瀬 修一, 大上 勝弘, 山縣 彰, 妙見 夕佳, 武田 善子
セッションID: P-39
発行日: 2008年
公開日: 2008/11/12
会議録・要旨集
フリー
We have announced in the previous a new concept flatbed fluorescent gel scanner at the 5th JHUPO Conference in last year.
Our previous model of the scanner was A4 (8 x 10 inch) size and had limited sensitivity. This time, we have improved the previous model, especially both in its size; A3 (12.2 x 16.5 inch), and its sensitivity for reducing durations of scan completion.
The new model is compatible with both Sypro Ruby (Invitorogen) and Flamingo (Bio-Rad) stained 1D/2D acrylamide gels up to A3 (12.2 x 16.5 inch) size.
抄録全体を表示