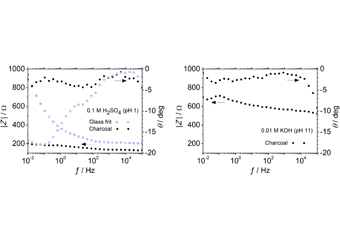
-
Yuya KADO, Yasushi SONEDA, Daisuke HORII, Kazuma OKURA, Shunzo SUEMATS ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
94-98
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: March 31, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
This study focused on the mechanochemical processing of natural graphite using a planetary ball mill under different atmospheres and analyzing their influence on the electrochemical behaviors of the processed graphite materials in electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs). Oxygen and/or nitrogen were incorporated in the carbon framework from the atmosphere used during milling. Specific surface areas of the pulverized graphite did not significantly depend on the employed atmosphere. These pulverized graphites processed under different atmospheres were evaluated as electrode materials for application in EDLCs with an organic electrolyte. All the pulverized graphites showed comparable capacitances independently of the used atmospheres. Considering the effect of post-thermal treatment of the pulverized graphite to remove oxygen surface functionalities, changes in the surface functionalities of pulverized graphites caused by ball milling did not significantly influence their applications as electrode materials in EDLCs.
View full abstract
-
Yoon-Yul PARK, Hiroshi TOMIYASU, Hiroshi ATARASHI, Yuji SUGIBAYASHI, M ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
99-106
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 07, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
An aqueous capacitor has been developed mainly for the purpose of recovering the regenerating energy for automobiles. A rapid charging within few seconds is required as well as the safety and the considerably large energy density. We have made two types of capacitors using a saturated sodium perchlorate aqueous solution (SSPAS) as an electrolyte, i.e., one consisted of a mixture of graphite and activated carbon, and the other mixtures of graphite and metal oxides. The former was an electric double layer type its energy density being 23 Wh/kg under the 70% of activated carbon and the applied voltage of 2.5 V. The generation of gases was not detected until the cut-off voltage 2.7 V using a SS444 foil as a current collector. Experiments using a titanium foil as a current collector revealed that the charge and discharge capacities were independent of temperatures from 0 to 60°C. In the applied electric current density of 20 mA/cm2, the capacity was determined to be 0.03 mAh/cm2 with the coulombic efficiency of 100% leading to the charging time of 5.4 s. The present result confirms a feasibility of recovering the regenerating energy for automobiles.
View full abstract
-
Ryota SAITO, Yusuke SATO, Daisuke TAKIMOTO, Sho HIDESHIMA, Wataru SUGI ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
107-111
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 10, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
MnO2 has been considered as a promising positive electrode material for aqueous electrochemical capacitors combined with activated carbon negative electrodes. Owing to the low electronic conductivity of MnO2, carbon is usually added in large quantities, in particular, for high power applications. In this study, we have pursued the possibility of using RuO2 nanosheets with high electronic conductivity and specific capacitance as a redox active binder. By adding only 20 mol% RuO2 nanosheets to MnO2, an increase in specific capacitance per total mass of composite electrode was observed. Notably, the enhancement effect was particularly pronounced at high scan rates with an increase in specific capacitance of 6.7 times at 50 mV s−1 by using RuO2 nanosheet binder, while at 2 mV s−1 the enhancement was 1.3 times. The cause of the enhancement in specific capacitance and rate performance is discussed based on RuO2 nanosheets acting as redox active conductive binder and MnO2 particles acting as spacers to suppress re-stacking of RuO2 nanosheets.
View full abstract
-
Yuuya HANZAWA, Sachio YOSHIHARA
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
112-118
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
The purpose of this study was to add the redox capacitance obtained by adding vanadium ions used in the vanadium redox flow battery to the electric double layer capacitance. CV measurement confirmed a square response characteristic of the electric double layer and a redox peak of vanadium. In EIS measurement, the characteristics as a capacitor when vanadium was added were investigated. The performance as a power storage device was measured during constant current charging and discharging, and it was found that a maximum improvement of 39% in discharge energy density was found compared to blank. However, it was confirmed that the redox capacitance addition in discharging was smaller in CV and CDC than that in charging. This irreversibility was attributed to the activated carbon fiber electrode. For comparison, ACF and CF with different internal and surface structures were compared to clarify the mechanism.
View full abstract
-
Hiroki WATANABE, Tomoki TSUMURA, Masahiro TOYODA
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
119-126
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 10, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
HPC is an ashless coal obtained via the thermal extraction of coal and is soluble in organic solvents. In this study, carbon powder was prepared from the HPC/pyridine solution via precipitation using water as a poor solvent and was subsequently carbonized via heat treatment at 900°C. The evaluation of the pore characteristics of the obtained carbon powder revealed that the carbon powders mainly contained micropores. The average pore diameter (Dave) of the micropores was 0.75 nm, suggesting that they are super-micropores or ultra-micropores. The applicability of the carbon powder was verified by examining the EDLC characteristics. The capacitance of the EDLC containing the aqueous solution of H2SO4 as the electrolyte was 170 F cm−3 (200–210 F g−1) at a current density of 50 mA g−1, denoting a capacitance similar to that of the activated carbon powder (YP-50F). The capacitance was 140 F cm−3 (170 F g−1) even when the current density increased from 50 to 5000 mA g−1, indicating a high retention rate of approximately 80%. Subsequently, the capacitance became 210 F cm−3 (260 F g−1) when the CO2 activation treatment was conducted for 60 or 90 min. Therefore, a high yield of carbon powders with extremely fine pores can be easily obtained via precipitation using HPC as the raw material.
View full abstract
-
Kanade HOKARI, Shinichiro SUZUKI, Naoki OKAMOTO, Takeyasu SAITO, Isamu ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
127-131
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 17, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Active carbon was prepared by treating carburized furfural resin particles (1 µm in diameter) with potassium hydroxide solution for 0–0.5 h at 700–800°C in flowing nitrogen gas. The pore structure of the active carbon was then evaluated by nitrogen adsorption experiments. The active carbon particles (1 µm in diameter) prepared at 750°C-0 h or 800°C-0 h had ca. 2.5-fold greater mesopore volume and 1.9-fold greater mesopore ratio than those prepared at 700°C-0.5 h. The surface chemical structure was evaluated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, while the fraction of organic functional groups in the pores was evaluated by Boehm titration. The carboxyl group fraction in the pores increased in the following order: 750°C-0 h (18.1%) < 800°C-0 h (23.0%) < 700°C-0.5 h (31.4%). The relationship between the pore size distribution, surface functional groups in the pores, and electric double-layer capacitor capacity was investigated for the specific surface area of 1200 ± 100 m2/g. The specific capacity increased in the following order: 700°C-0.5 h (66 F/g) < 800°C-0 h (111 F/g) < 750°C-0 h (148 F/g). This indicated that the amount of surface functional groups played a crucial role in the 6 M KOH electrolyte.
View full abstract
-
Mayuko OGINO, Ditpon KOTATHA, Yoshiki TORII, Keito SHINOMIYA, Satoshi ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
132-138
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 21, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
A novel gel polymer electrolyte based on chitosan with 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (EMImBF4) is prepared with a new procedure and applied to electric double layer capacitors (EDLCs). The chitosan-based gel polymer electrolyte causes less liquid leakage than the previous one. In this electrolyte system, EMImBF4 plays the roles of both a solvent for dissolving chitosan and a charge carrier ion for EDLC application. The present chitosan solution for gel polymer electrolytes shows acidity, and its acidity is raised by increasing the amount of EMImBF4 and the preparation temperature. The electrochemical stability of the electrolyte is decreased as the acidity of its chitosan solution increases. At 25°C, an EDLC cell with the electrolyte containing 70 wt.% EMImBF4 showed good charge-discharge performance and lower electrode/electrolyte interfacial resistance than those of a liquid-phase EMImBF4 system.
View full abstract
-
K. Kammer HANSEN
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
146-150
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 07, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Three ferrite based perovskites were investigated as cathodes for the electrochemical reduction of oxygen and nitric oxide, using cone-shaped electrodes and cyclic voltammetry. The ferrites investigated were LaFeO3, La0.85Sr0.15FeO3−δ and La0.5Sr0.5FeO3−δ. Especially the effect of anodic pre-treatment of the electrodes was investigated. It was shown that the ferrite based electrodes are better at reducing nitric oxide than oxygen in the temperature range 200 to 400°C. The ability of the ferrites to reduce oxygen depends mainly on the amount of Fe(III) and oxide anion vacancies, leading to the highest activity towards the reduction of oxygen for the intermediate compound La0.85Sr0.15FeO3−δ in the investigated temperature range. All the electrodes were either activated or de-activated when polarized at 0.4 vs. air, before recording the voltammograms, depending on temperature and gas atmosphere. This was attributed to annihilation of oxide ion vacancies, strontium segregation to the surface of the electrodes and perhaps formation of Fe(IV). The effect of water vapor was also studied. It had a slightly deactivating effect on the activity in the nitric oxide containing atmosphere, the effect being highest at the lowest temperatures.
View full abstract
-
Yusuke MORIKAWA, Yuki YAMADA, Kyosuke DOI, Shin-ichi NISHIMURA, Atsuo ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
151-156
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: February 21, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary material
Hard carbon is widely studied as a promising negative electrode in sodium-ion batteries. To achieve its stable charge-discharge reaction, a fluorine-rich passivation film arising from a fluorinated salt or solvent in an electrolyte was demonstrated to be effective, but its essential role remained unclear. Here, we report a sodium tetraphenylborate (NaBPh4)/1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME) electrolyte that is free from fluorine but enables the highly stable and high-rate charge-discharge cycling of hard carbon electrodes as compared to other combinations of Na salts and solvents. Surface analysis of the cycled electrode shows that the NaBPh4 is not decomposed during the cycle and that solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) is derived from DME. Hence, fluorine-based components are not indispensable to stabilize the hard carbon/electrolyte interface. The DME-derived SEI, though containing no F component, can highly stabilize the interface to enable the reversible and high-rate cycling of hard carbon.
View full abstract
-
Terumasa KUGE, Takanobu NISHIMOTO, Masayuki KUROHAGI, Kouji MAEDA, Shi ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
157-164
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: March 31, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
We have previously reported that the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in acidic water electrolysis shows a potential oscillation with amplitude of about 1 V. The oscillation, named HER oscillation, is accompanied with a periodic change in the evolution rate of hydrogen bubbles, i.e., hydrogen bubbles evolve more vigorously at low potentials than at high potentials, which has led us to propose a mechanism for HER oscillation (J. Electroanal. Chem., 713, 39 (2014)). In order to obtain a deeper insight into the mechanism of HER oscillation, this present work studies the effect of high pressure (e.g. 0.7 MPa) on the oscillation and current-potential curves. It reveals that any N-shaped negative differential resistance characteristics are not involved in HER oscillation unlike the majority of electrochemical oscillations. It also shows that a solution-stirring effect due to the hydrogen bubble evolution, which causes an enhancement of convection near the electrode surface, plays an essential role in HER oscillation. We thus conclude that the appearance of HER oscillation can be explained by considering that the enhancement occurs only at low potentials at which hydrogen bubbles evolve vigorously.
View full abstract
-
Shu JIANG, Wilfred V. ESPULGAR, Xi LUO, Masato SAITO, Hiroyuki YOSHIKA ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
165-173
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 07, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary material
Metallic nanostructures and their fabrication methods have been studied for over decades as they are crucial in developing plasmonic sensing platforms. In this work, a hierarchical nanopillar huddle structure fabricated by thermal nanoimprint lithography with anodic porous alumina as template is presented. By utilizing this scheme, nanopillars (branches) rooted on regularly deployed substructures (footings) can be easily produced/reproduced for large working area at low-cost with high-throughput. After metal deposition for plasmon activation, tiny nanogaps were generated within each single huddle. The as-fabricated substrates are also tunable by varying the anodizing conditions and metal deposition material/thickness. Substrates produced using this scheme were evaluated by absorption spectra measurements and SERS detection of series of adsorbed molecules. Finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulation was conducted to validate the promising feature of the higher electric field energy density stimulated at the tiny nanogaps which resulted in a regular distribution of “hot-spots”. Finally, biosensing potentials were demonstrated by conducting measurements of four different nucleotides (i.e. AMP, CMP, TMP, GMP at 10−2 M) using silver sputtered substrate without any modification. Its SERS performance in the micron level was also evaluated via line-scan in two orthogonal direction in 10−2 M AMP solution.
View full abstract
-
Mayeesha MARIUM, Kazuhide UENO, Kaoru DOKKO, Masayoshi WATANABE
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
174-177
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: March 31, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary material
Nanocomposite electrolytes comprising molten Li salt solvates (MLSs) and inorganic fillers provide liquid-like processing and reasonably high Li ion transport properties. Thus, they can be potentially used as thermally-stable and mechanically-robust electrolytes. In this study, nanocomposite electrolytes exhibiting two distinct non-Newtonian rheological responses, i.e., shear thinning and shear thickening behaviors, were prepared using glyme- and sulfolane-based molten Li salt solvates and hydrophilic fumed silica without any surface modification of the silica. The rheological responses strongly depended on the anionic structure of the MLSs. The MLS-silica composites containing bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide (TFSA) and BF4 anions formed a shear thinning gel and shear thickening fluid, respectively. The characteristic rheological properties (elastic modulus for the shear thinning gel and the maximum peak viscosity and critical shear rate for the shear thickening system) were extensively tailored by the silica content in addition to the chemical structure of the MLSs, while the changes in their ion transport properties were moderate even in the presence of silica fillers.
View full abstract
-
Yoshiharu MUKOUYAMA, Keisuke IIDA, Terumasa KUGE
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
178-184
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 03, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary material
It is well accepted that the electrooxidation of ethanol on Pt in aqueous solution proceeds via two parallel pathways: C1-pathway, which is the complete oxidation of ethanol to CO2 via COad intermediate, and C2-pathway, which produces acetaldehyde and also acetic acid with further oxidation. Water plays important roles for the oxidation, i.e., for the oxidative removal of COad in the C1-pathway and for the oxidation of acetaldehyde to acetic acid in the C2-pathway. In the present work, however, we show that the ethanol oxidation proceeds in the absence of water. Detailed study using surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy and high-performance liquid chromatography reveals that COad reacts with ethanol to form ethyl formate, which is designated as C3-pathway, and also that the ethanol oxidation produces ethyl acetate, which is designated as C4-pathway.
View full abstract
-
Taiki ADACHI, Yuki KITAZUMI, Osamu SHIRAI, Tenta KAWANO, Kunishige KAT ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
185-189
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 03, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary material
We investigated properties of direct electron transfer (DET)-type bioelectrocatalysis of recombinant native Copper efflux oxidase (rCueO) and its variants which lack α helices covering the electron-donating substrate-binding site (Δα5–7CueO, Δα5CueO, Δα6–7CueO, and Δα5–7+1/2α5CueO) at mesoporous carbon electrodes without pretreatment and modified with positively or negatively charged aromatic amines. Kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the electrode reaction were obtained by analysis of steady-state catalytic waves based on a random orientation model and examined the results on the basis of the structural information of the enzymes. The data suggested that the electron transfer pathway is different from that in solution; electrons are transferred from an electrode to the T1 Cu site through the negatively charged position near the T1 Cu site in rCueO without passing through the α helix region in DET-type bioelectrocatalysis. Positively charged electrode was a suitable scaffold for DET-type reaction of rCueO. The T1 Cu site in Δα5CueO became somewhat hydrophobic and hydrophobic electrode worked as a suitable scaffold for the variant. Negatively charged electrode seems to induce unfavorable attractive orientation for DET-type reaction between the electrode and positively charged region of the CueOs on the opposite side of the T1 Cu site.
View full abstract
-
Tatsuya SAKAKURA, Yoshiyuki TAKATSUJI, Masayuki MORIMOTO, Tetsuya HARU ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
190-194
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 10, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
In the plasma/liquid (P/L) interfacial reaction, nitrogen fixation is performed on a water phase surface. In the P/L reaction, discharged nitrogen gas reacts with water molecules at the interface between the plasma gas phase and the water phase, followed by either a reduction reaction, ammonia production or oxidation reaction, nitric acid production. The production of nitric acid in the P/L reaction is influenced by the concentration of oxygen present in each gas phase and water phase, and the atomic nitrogen contained in the nitrogen plasma. For the reduction reaction at the P/L reaction locus, the water phase was modulated in order to make ammonia production dominant in nitrogen fixation. Ammonia is released into the gas phase under conditions of high water temperature and high pH. To obtain only ammonia using this reaction, it is necessary to incorporate a process for raising the temperature of the water. In the P/L reaction, only the ammonia gas can be obtained in one-step by using the rise in water temperature due to the discharged heat plasma gas. A reaction system was developed to control the water and the gas phase to enable high purity ammonia trapping as released by the gas phase.
View full abstract
-
Yuya KAIDA, Yuya HIBINO, Yuki KITAZUMI, Osamu SHIRAI, Kenji KANO
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
195-199
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 10, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary material
d-Fructose dehydrogenase (FDH) gives a clear direct electron transfer (DET)-type bioelectrocatalytic wave even at planar gold (Au) electrodes. The recombinant (native) FDH (r_FDH) has three hemes c in subunit II (1c, 2c, and 3c from N-terminus). With a view to downsize the enzyme and shorten the distance between an electrode-active site and an electrode, we constructed a variant that lacked 143 amino acid residues involving the heme 1c moiety (Δ1cFDH) and a variant that lacked 199 amino acid residues involving the heme 1c and 2c moieties (Δ1c2cFDH). In order to shift the redox potential of heme 2c of Δ1cFDH to the negative direction, the M450 residue as the axial 6th ligand of heme 2c was also replaced with glutamine (M450QΔ1cFDH). The DET-type catalytic properties of r_FDH and the three variants at planar Au electrodes were compared with each other, and the steady-state waves were analyzed on a random orientation model. The orientation of the enzymes on the electrode was also discussed. In addition, in order to examine the electron transfer pathway in the DET-type reaction of Δ1c2cFDH, ESR measurements and inhibition of DET-type reaction by cyanide ion were performed.
View full abstract
-
Xiao-Ping ZHANG, Wei SUN, Shuo-Hui CAO, Wen-Long JIANG, Hao PENG, Shu- ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
200-204
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 17, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
In this paper, the electrochemical oxidation of dopamine was studied by using gold nanoparticles modified nano-polyaniline film as the catalyst. Electrochemistry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (EC–NMR) was used to investigate electro-catalytic mechanism and evaluate the electro-catalytic capacity. The influence of varied pH values and voltages in the electrocatalytic process was studied. The oxidation mechanism of dopamine can be proposed: (1) at pH 1 and 600 mV, the main oxidation product is dopamine quinone (DQ). Only a small amount of DQ occurs cyclization reaction to form quinone aminochrome (AC); (2) at pH 1 and 800 mV, the oxidation products are DQ and 5,6-dihydroxyindole (DHI). (3) With the pH value increases, the oxidation of dopamine steps over DQ and AC, and directly produces DHI. DHI is aggregated to form melanin sediment. Our results indicate that the gold nanoparticles modified electrode displays high catalytic performance toward dopamine electrochemical oxidation.
View full abstract
-
Seiya HIRANO, Junki SAITO, Tomoki YUKAWA, Daisuke SANO, Akihiro OKAMOT ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
205-209
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 14, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Electrochemical biosensors have attracted significant attention as a novel tool for the sensitive detection of pathogens and contaminants, with the potential capability of rapid, on-site diagnosis. In this study, we intended to improve the sensitivity of electrochemical biosensor using Fe(CN)63−/4− as redox marker, toward its application to norovirus aptasensors. Although many researchers have developed electrochemical aptasensors for various analytes using redox markers, the reported electrochemical conditions under which an aptasensor was examined varied across multiple studies. Here, we performed square-wave voltammetry (SWV) for electrodes modified with aptamer specific to murine norovirus and compared the reduction peak currents of Fe(CN)63− under various conditions. Effects of working electrode materials and NaCl and [Ru(NH3)6]Cl3 concentration in the electrolyte were examined. Among conditions we tested, the best sensitivity was obtained using a screen-printed gold electrode in an electrolyte containing 1 M NaCl with 4 mM K3[Fe(CN)6], in which the concentration of murine norovirus showed linearity with SWV peak current. This study provided useful information on the electrochemical measurement conditions regarding the development of electrochemical aptasensors.
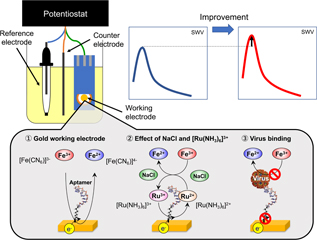
View full abstract
-
Keisuke OHKUBO, Hiroki TAKAHASHI, E. P. J. WATTERS, Masami TAGUCHI
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
210-217
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 14, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
The issue of excessive amounts of CO2 in the atmosphere has promoted the study of methods of removing it from the atmosphere. In the field of electrochemistry, electroreduction of CO2 has become an area of significant scientific interest. Our previous work has shown Pt oxide exhibits a higher CO2 electroreduction activity than Pt. In this study, the surface adsorption species on Pt and Pt oxide during electroreduction were investigated with SEIRAS to clarify the mechanisms of the superior electroreduction activity of Pt oxide. The main adsorption species during CO2 electroreduction were methanol and HCOO− on the Pt oxide, and methanol and linear-CO on the Pt. We confirmed that the CO2 electroreduction reaction proceeds via HCOO− on Pt oxide, and through CO on Pt. The CO2 electroreduction activity is significantly affected by the adsorption species because CO strongly adsorbs on the active site and inhibits subsequent reactions. The residual oxygen in the reduced Pt oxide electrode may cause the difference in adsorption species, controlling the reaction pathway. We conclude that the superior CO2 electroreduction activity of Pt oxide is due to the difference in the reaction pathway, possibly caused by residual oxygen and oxygen vacancies in the Pt oxide electrode.
View full abstract
-
Hidenori SAITO, Daisuke AOKI, Tomoyuki TOBE, Shinichi MAGAINO
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
218-223
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 21, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
A new algorithm for the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) method has been developed in order to determine the maximum power (Pmax) for slow-responding metastable PV devices such as perovskite solar cells (PSCs). It is well known that such devices often cause significant Pmax oscillation during a standard MPPT measurement. This oscillation was found to occur caused by difference in the current acquired after increasing the voltage and that acquired after decreasing the voltage. The new algorithm developed in this paper has eliminated such oscillation with comparison between the powers at different voltages after changing the voltage in the same direction. Pmax data determined by using this algorithm were found to be reliable by comparing with those determined by the dynamic I-V measurements.
View full abstract
-
Shu ZHANG, Waheed MIRAN, Divya NARADASU, Siyi GUO, Akihiro OKAMOTO
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
224-229
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
Advance online publication: April 21, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary material
Microbial extracellular electron transfer (EET) in diverse environments has gained increasing attention. However, the EET capability of oral pathogens and associated mechanisms has been scarcely studied. Here, our results suggest that the Capnocytophaga ochracea, an etiological human pathogen showed current production and demonstrated a rate enhancement of electron transport at a high cell-density. C. ochracea produced ∼10-fold more current at an OD600 of 0.5 associated with twice a higher glucose consumption rate per cell, compared to 0.1, measured in a three-electrode electrochemical system by single-potential amperometry at +0.2 V (vs Ag/AgCl [sat. KCl]). During current production, the accumulation of the redox molecules on the electrode was observed at high OD600 compared to low OD600. Apart from cell released redox active product, externally added redox active additives enhanced the electron transport, suggesting the EET capability of C. ochracea via electron mediator. A higher metabolic activity via single-cell assay (based on anabolic incorporation of 15NH4+) in cells that did not attach to the electrode strongly suggests the EET rate enhancement through an electron mediator. As bacterial populations play a role in the pathogenesis of human infections such as periodontitis, our results suggest that population-induced EET mechanisms may facilitate in-vivo colonization of C. ochracea.
View full abstract
-
Omar Samuel MENDOZA-HERNANDEZ, Eiji HOSONO, Daisuke ASAKURA, Hirofumi ...
2020 Volume 88 Issue 3 Pages
230-235
Published: May 05, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 05, 2020
JOURNAL
OPEN ACCESS
Commercially available 18650 Li-ion cells were exposed to charge-discharge cycling at 0°C using two different charging protocols: constant current-constant voltage (CC-CV) and constant current (CC). The effect of the charge process protocol on the Li-ion cell performance is shown and analyzed. After exposing the cells to low temperature charging, a high voltage plateau appeared at the beginning of the discharge. This high voltage plateau is related to the occurrence of lithium plating during the charging process. Interestingly, the intensity of the observed high voltage plateau decreased with cycling. In addition, the Li-ion cells that were charged using a CC protocol exhibited a larger capacity fade in comparison to those that were charged using a CC-CV protocol. Furthermore, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were carried out during cycling. It was shown that the internal impedance of the cells increased with charge-discharge cycling, indicating the formation of an interphase layer during low temperature cycling.
View full abstract