- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Yoshiyasu Nagashima, Ryota Tochinai, Shin-ichi Sekizawa, Daiki Kato, T ...2023Volume 36Issue 3 Pages 151-158
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Advance online publication: February 15, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSCombretastatin A4 disodium phosphate (CA4DP) is a prodrug of combretastatin A4 (CA4), a microtubule-disassembling agent that exhibits antitumor effects by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and inducing morphological changes and apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells in tumors. However, cardiotoxicity induced by ischemia and hypertension is a severe adverse event. In this study, we focused on the fact that phosphodiesterase (PDE) 5 inhibitors dilate the heart and peripheral blood vessels and aimed to investigate whether co-administration of tadalafil, a PDE5 inhibitor, can attenuate cardiotoxicity without altering the antitumor effect of CA4DP. To investigate cardiotoxicity, CA4DP and/or tadalafil were administered to rats, and blood pressure, echocardiography, histopathology, and cGMP concentration in the myocardium were examined. Administration of CA4DP increased systolic blood pressure, decreased cardiac function, lowered cGMP levels in the myocardium, and led to necrosis of myocardial cells. Co-administration of tadalafil attenuated these CA4DP-induced changes. To investigate the antitumor effect, canine mammary carcinoma cell lines (CHMp-13a) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells were cultured with CA4 and/or tadalafil, and cell proliferation and endothelial vascular tube disruption were examined. CHMp-13a cells were transplanted into nude mice and treated with CA4DP and/or tadalafil. CA4-induced inhibition of cell proliferation and disruption of the endothelial vascular tube were not affected by co-treatment with tadalafil, and the antitumor effects of CA4DP in xenograft mice were not reduced by co-administration of tadalafil. These results revealed that myocardial damage induced by CA4DP was attenuated by co-administration of tadalafil while maintaining antitumor efficacy.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4963K) -
Satoshi Furukawa, Naho Tsuji, Seigo Hayashi, Yusuke Kuroda, Masayuki K ...2023Volume 36Issue 3 Pages 159-169
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Advance online publication: March 24, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSWe examined the morphological effects of cyclophosphamide (CPA) on placental development in pregnant rats. CPA was administered as a single dose to pregnant rats intraperitoneally at 0 mg/kg (the control group), 25 mg/kg on gestation day (GD) 12 (the CPA GD 12-treated group), and 25 mg/kg on GD 14 (the CPA GD 14-treated group). The fetal and placental weight decreased in the CPA-treated groups, complete fetal resorption from GD 17 onwards in the CPA GD 12-treated group, and external malformations in the CPA GD 14-treated group. Histopathologically, CPA induced apoptosis and/or cell proliferation inhibition in each part of the placenta. In the labyrinth zone, syncytiotrophoblasts were selectively reduced, resulting in a small placenta. In the basal zone, the number of spongiotrophoblasts was reduced, resulting in hypoplasia of glycogen cell islands. In addition, a small number of interstitial trophoblasts invaded the metrial gland from the basal zone on GD 15. The severity of these lesions was higher in the CPA GD 12-treated group than in the CPA GD 14-treated group. In the metrial gland, although the number of uterine natural killer cells was reduced, metrial gland development was not affected.
View full abstractDownload PDF (8643K) -
Robert R. Maronpot, Michael Streicker, Debabrata Mahapatra, Rebecca Mo ...2023Volume 36Issue 3 Pages 171-179
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Advance online publication: April 04, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialToxicity assessment of the food colorant Gardenia jasminoides Ellis at dietary exposures of 0.0%, 0.1%, 0.5%, 1.5%, 3.0% and 5.0% included measures of T-cell- dependent antibody response, neurotoxicity, and clinical and anatomic pathology in Sprague Dawley rats during mating, gestation, lactation, postnatal development, and following weaning for up to 12 months including 3- and 6-month interim evaluations. Blue coloration of the gastrointestinal tract, mesenteric lymph nodes and kidneys was present in treated rats only at necropsy with minimal blue coloration at the lowest dose and without histopathological correlates in any of the tissues. There was good survival with no consistent treatment-related changes in hematology, clinical chemistry, enhanced evaluation of lymphoid tissues, or tissue histopathology at interim and final time points. T-cell dependent antibody response and neurotoxicity screening were negative in treated rats. The no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) was determined to be 5.0% gardenia blue (2,854.5 and 3,465.4 mg/kg/day in parental males and females, respectively, prior to mating; 3,113.5 and 4,049.6 mg/kg/day in male and female offspring, respectively, following up to 12 months of exposure.
View full abstractDownload PDF (817K)
-
Minto Nakagawa, Takeshi Izawa, Mitsuru Kuwamura, Jyoji Yamate2023Volume 36Issue 3 Pages 181-185
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
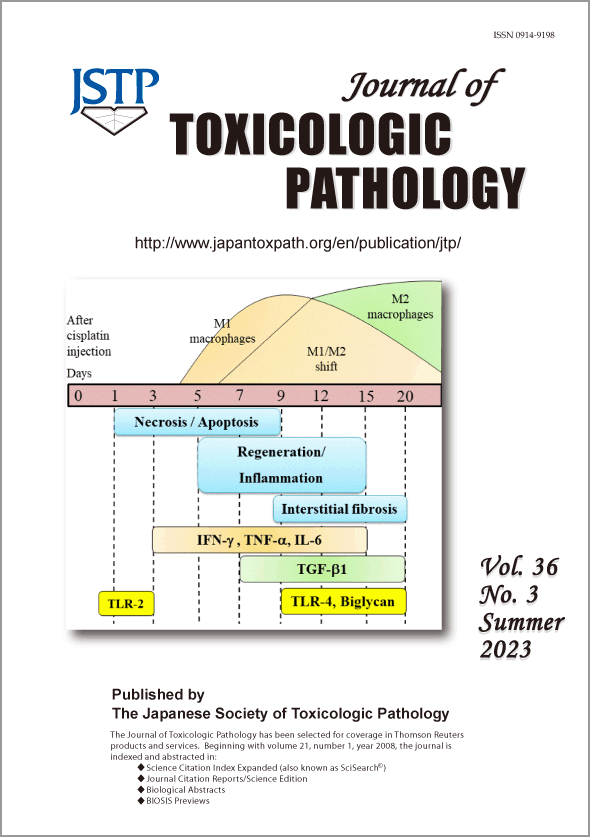
Advance online publication: March 22, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDamage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and their receptors (TLR-2 and -4) may play important roles in renal fibrosis, of which the pathogenesis is complicated. We used rat renal lesions induced by a single intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin at 6 mg/kg body weight; consisting of tissue damage of renal tubules on days 1 and 3, further damage and regeneration with inflammation mainly on days 5 and 7, and interstitial fibrosis on days 9, 12, 15, and 20. Microarray analyses on days 5 (the commencement of inflammation) and 9 (the commencement of interstitial fibrosis) showed that DAMPs increased by more than two-fold relative to control included common extra-cellular matrix (ECM) components such as laminin (Lamc2) and fibronectin, and heat shock protein family, as well as fibrinogen, although it was limited analysis; Lamc2, an element of basement membrane, may be regarded as an indicator for damaged renal tubules. In the real-time RT-PCR analyses, TLR-2 significantly increased transiently on day 1, whereas TLR-4 significantly increased on days 9 and 15, almost in agreement with the increased biglycan (a small leucine-rich proteoglycan as ubiquitous ECM component). As M1/M2 macrophages participated in renal lesions, such as inflammation and fibrosis, presumably, TLR-4, which may be expressed in immune cells, could play crucial roles in the formation of renal lesions in association with biglycan.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1446K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|