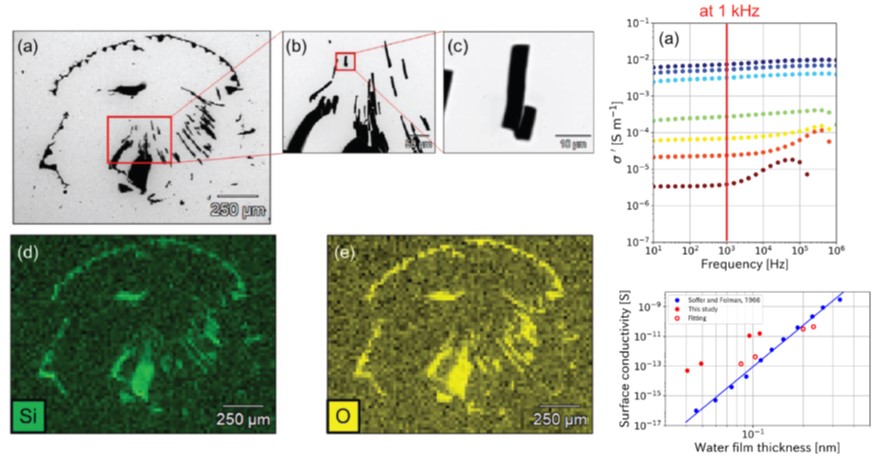
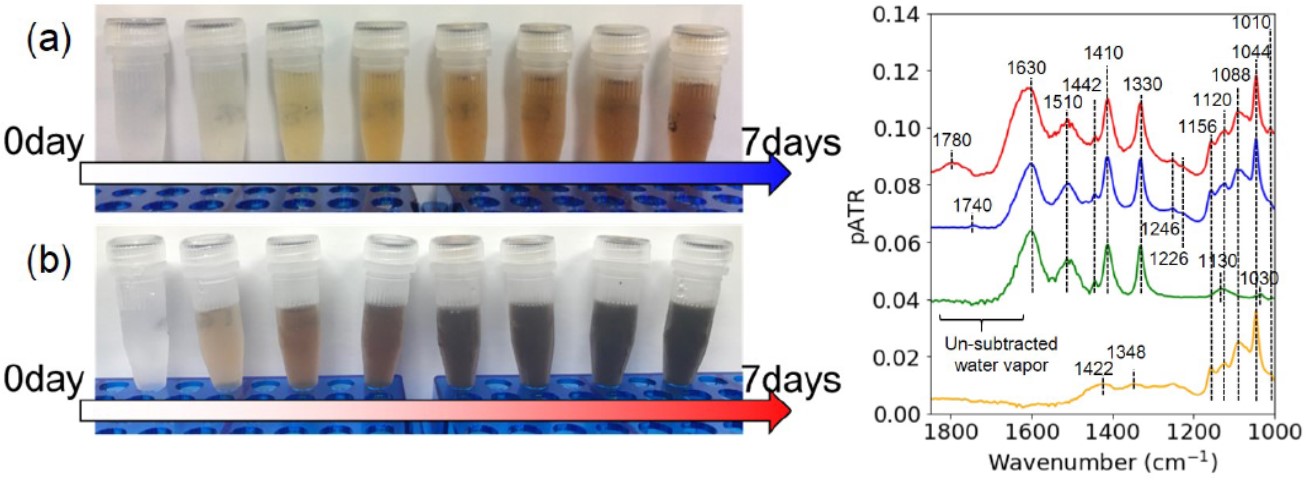
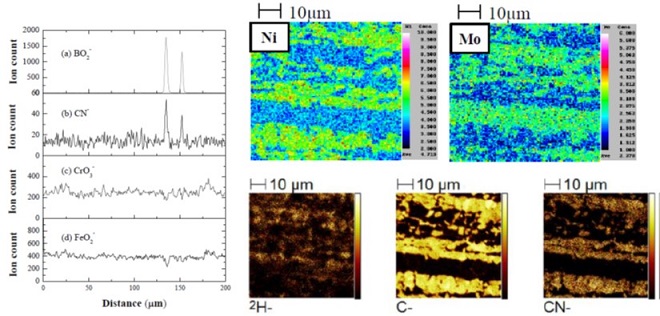
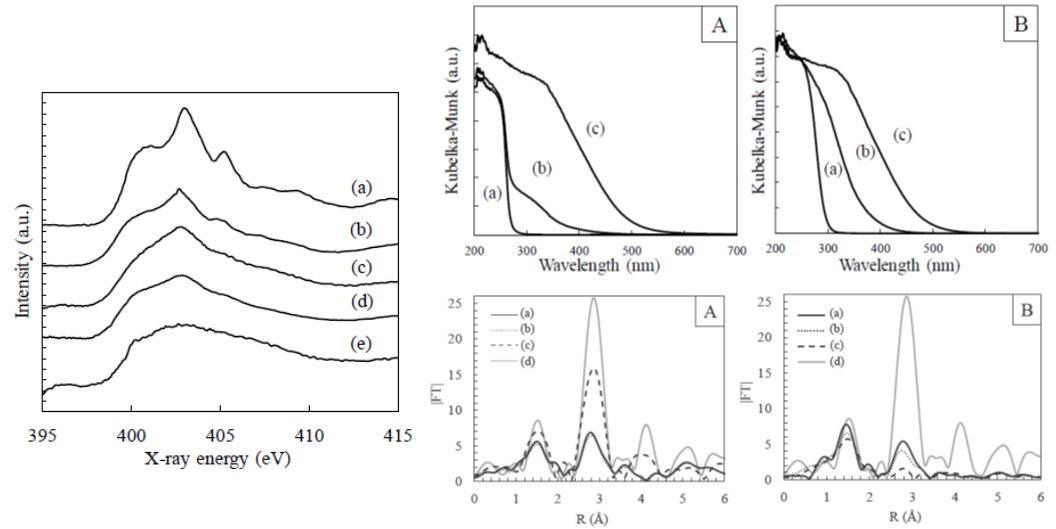
Volume 16
Displaying 51-87 of 87 articles from this issue
Conference -ISSS-8-
-
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Environmental and Energy Technology
2018 Volume 16 Pages 253-256
Published: June 09, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 09, 2018
Download PDF (645K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Micro- and Nano-Fabrication
2018 Volume 16 Pages 257-261
Published: June 09, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 09, 2018
Download PDF (1338K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Catalysis
2018 Volume 16 Pages 267-273
Published: June 14, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 14, 2018
Download PDF (718K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Nano-Materials
2018 Volume 16 Pages 279-282
Published: June 16, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 16, 2018
Download PDF (410K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Environmental and Energy Technology
2018 Volume 16 Pages 298-301
Published: June 21, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 21, 2018
Download PDF (250K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Thin Films
2018 Volume 16 Pages 302-305
Published: June 21, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 21, 2018
Download PDF (908K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Instrumentations and Techniques
2018 Volume 16 Pages 313-319
Published: June 30, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 30, 2018
Download PDF (600K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Thin Films
2018 Volume 16 Pages 320-323
Published: July 05, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 05, 2018
Download PDF (1099K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Instrumentations and Techniques
2018 Volume 16 Pages 339-342
Published: July 21, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 21, 2018
Download PDF (563K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Nano-Materials
2018 Volume 16 Pages 343-346
Published: July 28, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 28, 2018
Download PDF (1185K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Instrumentations and Techniques
2018 Volume 16 Pages 347-350
Published: July 28, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 28, 2018
Download PDF (253K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Vacuum
2018 Volume 16 Pages 356-359
Published: August 02, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: August 02, 2018
Download PDF (355K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Electronic Properties
2018 Volume 16 Pages 360-363
Published: August 04, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2018
Download PDF (361K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Devices and Sensors
2018 Volume 16 Pages 364-369
Published: August 09, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: August 09, 2018
Download PDF (488K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Reaction and Dynamics
2018 Volume 16 Pages 370-374
Published: August 11, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: August 11, 2018
Download PDF (1032K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Nano-Materials
2018 Volume 16 Pages 376-381
Published: August 30, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: August 30, 2018
Download PDF (627K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Nano-Materials
2018 Volume 16 Pages 382-386
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (483K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Thin Films
2018 Volume 16 Pages 396-399
Published: October 04, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 04, 2018
Download PDF (731K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Reaction and Dynamics
2018 Volume 16 Pages 411-418
Published: October 06, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 06, 2018
Download PDF (1093K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Thin Films
2018 Volume 16 Pages 427-430
Published: November 24, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 24, 2018
Download PDF (3452K) -
Article type: Conference -ISSS-8-
Subject area: Nano-Materials
2018 Volume 16 Pages 436-439
Published: December 22, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: December 22, 2018
Download PDF (264K)
Conference -ALC '17-
-
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Preface
2018 Volume 16 Pages A1-A2
Published: October 27, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 27, 2018
Download PDF (47K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Nano-Science and -Technology
2018 Volume 16 Pages 84-87
Published: April 14, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 14, 2018
Download PDF (664K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Nano-Science and -Technology
2018 Volume 16 Pages 93-96
Published: April 20, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 20, 2018
Download PDF (646K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Interdisciplinary
2018 Volume 16 Pages 150-155
Published: May 16, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 16, 2018
Download PDF (408K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Nano-Materials
2018 Volume 16 Pages 172-176
Published: May 19, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 19, 2018
Download PDF (364K) -
 Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Electronic Properties
2018 Volume 16 Pages 177-185
Published: May 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 25, 2018
-
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Instrumentations and Techniques
2018 Volume 16 Pages 247-252
Published: June 09, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 09, 2018
Download PDF (2425K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Structure
2018 Volume 16 Pages 262-266
Published: June 14, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 14, 2018
Download PDF (584K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Nano-Materials
2018 Volume 16 Pages 274-278
Published: June 14, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 14, 2018
Download PDF (478K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Electronic Properties
2018 Volume 16 Pages 283-285
Published: June 16, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 16, 2018
Download PDF (314K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Nano-Science and -Technology
2018 Volume 16 Pages 286-288
Published: June 16, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 16, 2018
Download PDF (891K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Instrumentations and Techniques
2018 Volume 16 Pages 294-297
Published: June 21, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 21, 2018
Download PDF (161K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Nano-Science and -Technology
2018 Volume 16 Pages 306-309
Published: June 21, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 21, 2018
Download PDF (221K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Nano-Science and -Technology
2018 Volume 16 Pages 324-328
Published: July 14, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 14, 2018
Download PDF (741K) -
Article type: Conference -ALC '17-
Subject area: Nano-Materials
2018 Volume 16 Pages 406-410
Published: October 04, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 04, 2018
Download PDF (466K)
Errata
-
Article type: Errata
Subject area: Micro- and Nano-Fabrication
2018 Volume 16 Pages 375
Published: August 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: August 25, 2018
Download PDF (41K)