Volume 87, Issue 2
Displaying 1-26 of 26 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Message From the Editor-in-Chief
-
Article type: MESSAGE FROM THE EDITOR-IN-CHIEF
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 237-239
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: January 20, 2023Download PDF (636K) Full view HTML
Focus on issue: Ischemic Heart Disease
Reviews
-
Article type: REVIEW
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 240-246
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: September 15, 2022Download PDF (1767K) Full view HTML
Original Articles
Coronary Intervention
-
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Coronary Intervention
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 247-255
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: August 27, 2022Download PDF (1862K) Full view HTML -
Article type: EDITORIAL
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 256-257
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: September 17, 2022Download PDF (1000K) Full view HTML -
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Coronary Intervention
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 258-265
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: October 26, 2022Download PDF (1332K) Full view HTML -
Article type: EDITORIAL
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 266-267
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: November 15, 2022Download PDF (337K) Full view HTML -
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Coronary Intervention
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 268-276
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: September 16, 2022Download PDF (1349K) Full view HTML -
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Coronary Intervention
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 277-286
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: November 08, 2022Download PDF (1265K) Full view HTML -
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Coronary Intervention
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 287-295
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: December 01, 2022Download PDF (1057K) Full view HTML -
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Coronary Intervention
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 296-305
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: October 19, 2022Download PDF (1203K) Full view HTML
Surgery
-
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Surgery
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 306-311
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: November 10, 2022Download PDF (1035K) Full view HTML -
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Surgery
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 312-319
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: December 06, 2022Download PDF (938K) Full view HTML
Imaging
-
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Imaging
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 320-328
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: September 14, 2022Download PDF (1366K) Full view HTML -
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Imaging
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 329-335
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: October 15, 2022Download PDF (1214K) Full view HTML
Population Science
-
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Population Science
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 336-344
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: October 07, 2022Download PDF (2803K) Full view HTML -
Article type: EDITORIAL
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 345-347
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: November 25, 2022Download PDF (2019K) Full view HTML -
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Population Science
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 348-359
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: August 25, 2022Download PDF (2254K) Full view HTML -
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Population Science
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 360-367
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: September 14, 2022Download PDF (3335K) Full view HTML -
Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subject area: Population Science
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 368-375
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: September 23, 2022Download PDF (2277K) Full view HTML
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine
-
Article type: IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 376-
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: October 29, 2022Download PDF (773K) Full view HTML -
Article type: IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 377-
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: November 11, 2022Download PDF (647K) Full view HTML -
Article type: IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 378-
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: November 11, 2022Download PDF (797K) Full view HTML -
Article type: IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 379-
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: December 01, 2022Download PDF (572K) Full view HTML -
Article type: IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages 380-
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Advance online publication: December 01, 2022Download PDF (679K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages Cover2-
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Download PDF (374K) -
2023 Volume 87 Issue 2 Pages Content2-
Published: January 25, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: January 25, 2023
Download PDF (766K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|

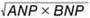 . MACE occurred in 73 patients (8.6%) during the follow-up period. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed the highest area under the curve for NPI (0.779) compared with ANP and BNP (0.773 and 0.755, respectively). A risk analysis of MACE occurrence adjusted for the multivariable model showed the highest hazard ratio (HR) for NPI (1.33; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.18–1.51; P<0.001) compared with ANP and BNP (HR 1.25 [95% CI 1.13–1.39] and 1.30 [95% CI 1.13–1.49], respectively; P<0.001). The NPI was a significant independent predictor of MACE, among other clinical parameters, in the multivariable analysis.
. MACE occurred in 73 patients (8.6%) during the follow-up period. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed the highest area under the curve for NPI (0.779) compared with ANP and BNP (0.773 and 0.755, respectively). A risk analysis of MACE occurrence adjusted for the multivariable model showed the highest hazard ratio (HR) for NPI (1.33; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.18–1.51; P<0.001) compared with ANP and BNP (HR 1.25 [95% CI 1.13–1.39] and 1.30 [95% CI 1.13–1.49], respectively; P<0.001). The NPI was a significant independent predictor of MACE, among other clinical parameters, in the multivariable analysis.