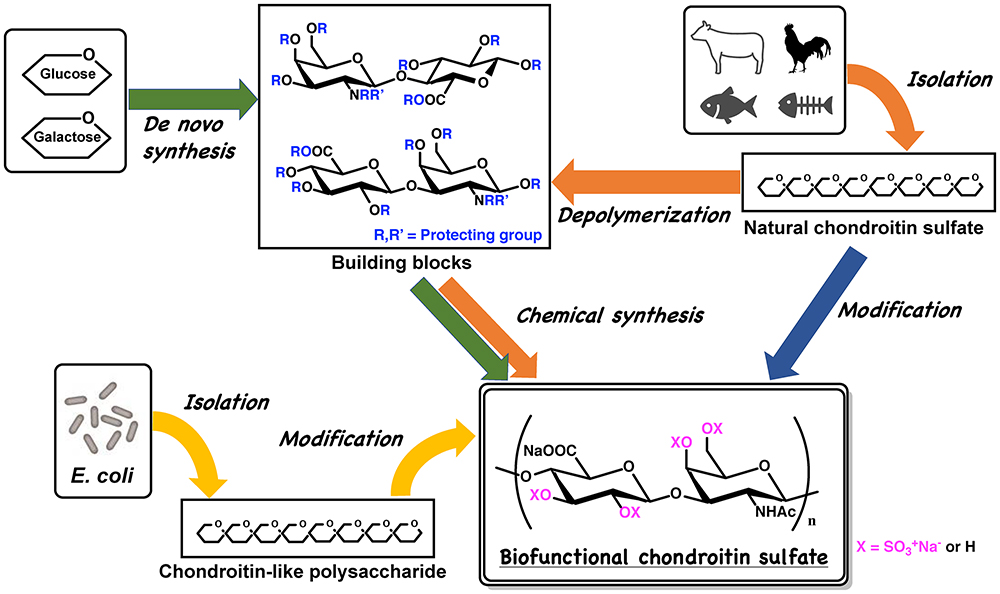
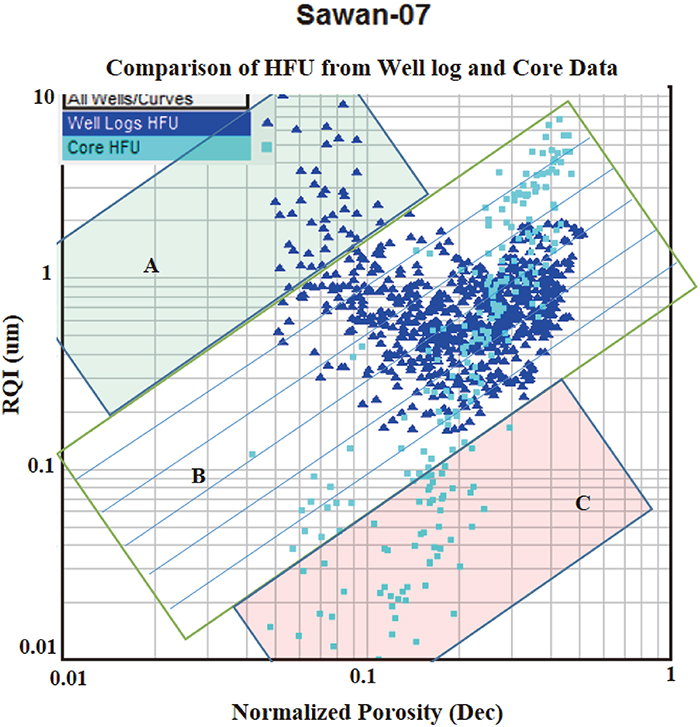
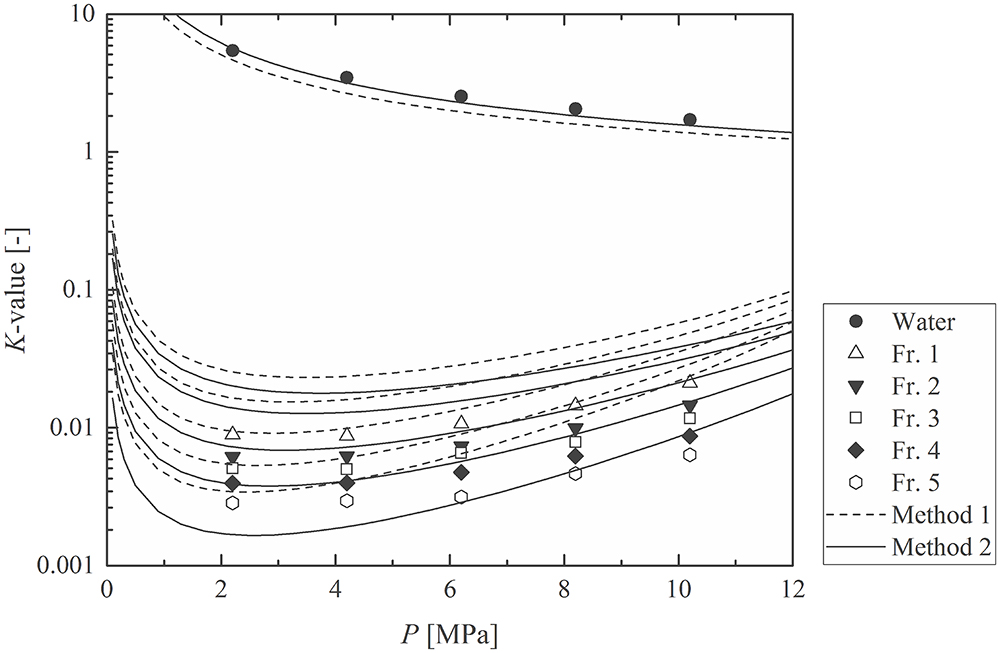
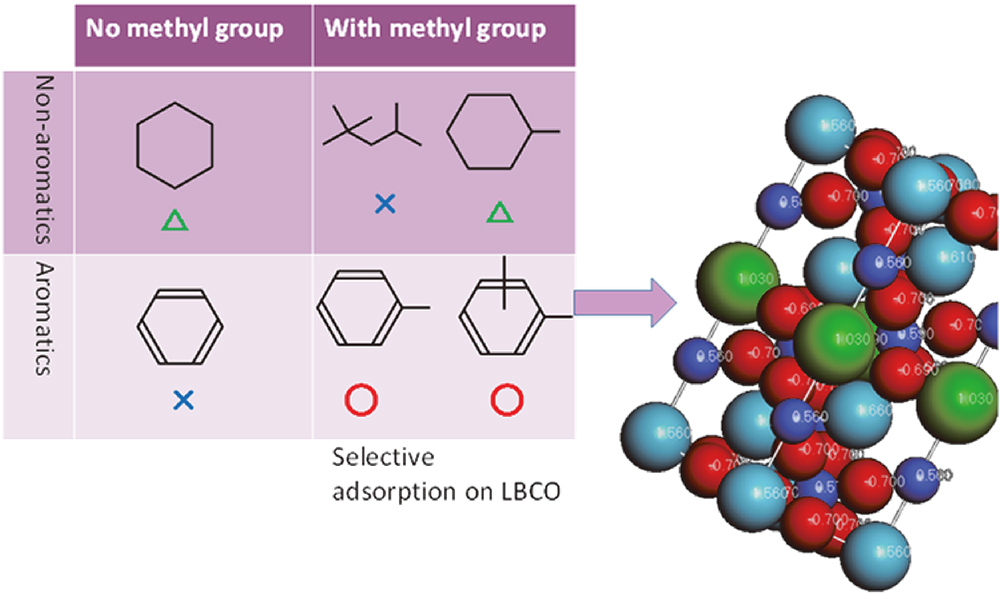
Volume 61, Issue 5
Displaying 1-11 of 11 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Review Paper
-
Article type: Review Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 239-245
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (2027K)
Regular Paper
-
Article type: Regular Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 246-255
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (7898K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 256-262
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (1187K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 263-271
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (4394K)
Regular Paper — Feature articles: Tottori Convention of the Jpn. Petrol. Inst. —
-
Article type: Regular Paper — Feature articles: Tottori Convention of the Jpn. Petrol. Inst. —
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 272-281
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (918K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 282-287
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (2677K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 288-293
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (2051K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 294-301
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (625K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 302-310
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (875K)
Research Note — Feature articles: Tottori Convention of the Jpn. Petrol. Inst. —
-
Article type: Research Note
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 311-315
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (369K) -
Article type: Research Note
2018 Volume 61 Issue 5 Pages 316-321
Published: September 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2018
Download PDF (1173K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|