
- Issue 6 Pages 323-
- Issue 5 Pages 239-
- Issue 4 Pages 205-
- Issue 3 Pages 171-
- Issue 2 Pages 51-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Eri FumotoArticle type: Review Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 6 Pages 323-331
Published: November 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSteam has good potential as a hydrogen source for upgrading of heavy oil. Catalytic cracking of petroleum residual oil with steam was examined using iron oxide-based catalysts containing zirconium and aluminum. After the lattice oxygen of iron oxide reacted with the heavy fractions, oxygen species were supplied to the iron oxide lattice from steam and reacted with heavy oil to produce light oil, residue, and carbon dioxide. Hydrogen species were also generated from steam and supplied to form light oil, preventing alkene generation. Sulfur compounds in the residual oil were reacted with the hydrogen species to form hydrogen sulfide. The compositions of iron, zirconium, and aluminum were not homogeneous in the catalyst. No coke was deposited in regions where the main component was iron oxide. Oxidative cracking of heavy fractions effectively occurred around such regions. Iron oxide-based catalyst containing zirconium and aluminum showed durable activity for the cracking of residual oil under a steam atmosphere.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (777K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (777K) -
Takehisa MochizukiArticle type: Review Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 6 Pages 332-341
Published: November 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNovel preparation methods for Co/SiO2 Fischer-Tropsch synthesis (FTS) catalysts were developed based on the impregnation method using aqueous solutions containing various concentrations of Co nitrate and a chelating agent, either nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) or trans-1,2-diaminocyclohexane-N,N,N’,N’-tetraacetic acid (CyDTA). FTS activity of the Co/SiO2 catalysts with Co loadings of 5-20 wt% as metallic Co was improved by stepwise impregnation with the chelating agents. Catalysts prepared with CyDTA (Co loading = 20 wt%, Co2+/CyDTA = 4 mol mol−1) yielded 1500 g kg-cat−1 h−1 and 815 g kg-cat−1 h−1 of C5+ and C10-20 hydrocarbons, respectively, at 503 K and 1.1 MPa (H2/CO/Ar = 62/33/5). This activity significantly exceeded that of the catalysts prepared from aqueous solution containing Co nitrate and other chelating agents. The surface structures of the reduced and calcined catalysts were investigated using various characterization techniques. The results indicated that control of the interaction between Co2+, chelating agents and SiO2 surface was crucial for the preparation of Co/SiO2 catalysts with high FTS activity.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (291K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (291K)
-
Yutaka Onaka, Afshin Goharzadeh, Kozo SatoArticle type: Regular Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 6 Pages 342-349
Published: November 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSViscous flow in porous media with different surface wettabilities was experimentally studied to investigate the effect of liquid slip on the flow using the micro-particle image velocimetry (μ-PIV) technique. A transparent microchannel, made of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), with a depth of 100 μm was used for flow visualization. The micro porous medium was made of solid cylinders with a diameter of 180 μm. The cylinders were arranged in line inside the microchannel. The surface wettability of the microchannel was modified by O2 plasma treatments to prepare both water-wet and oil-wet conditions. Measured velocity profiles were compared with numerical simulations. Both experimental and numerical results showed that the difference in the velocity profiles with the wettabilities was under 2.4 % at the center of the throats. The ratio of absolute permeability under the oil-wet condition to the water-wet condition was calculated as 1.2. This study provides the criterion of the slip impacts on the velocity profiles and permeability of single-phase flow in porous media under the oil-wet condition. The results can be used for the verification of data when extending the investigation to two-phase flow for understanding oil displacement behavior.
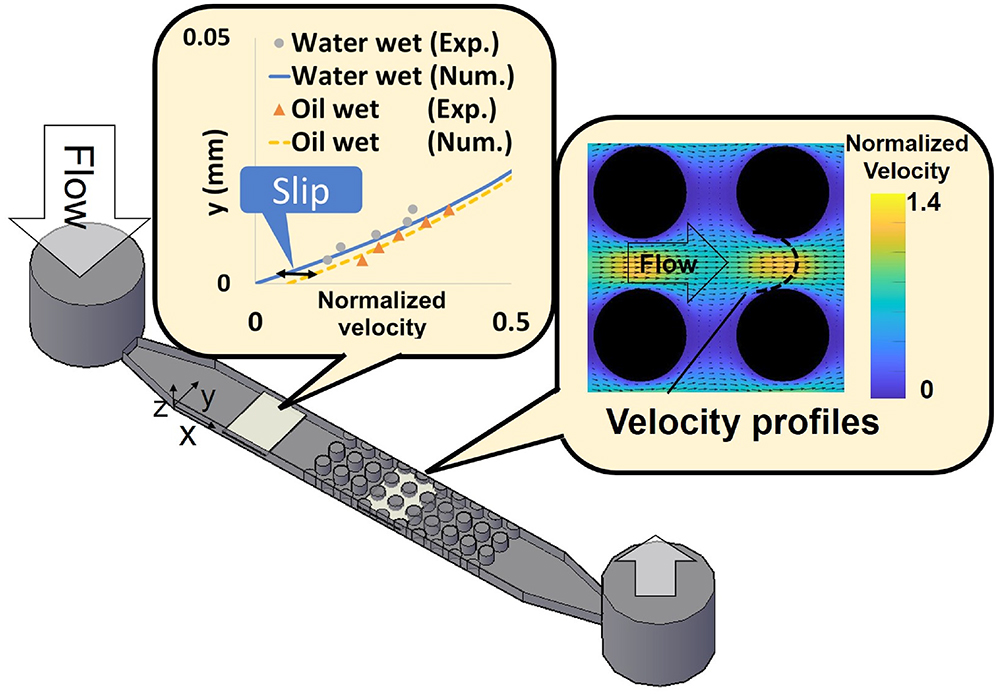 View full abstractDownload PDF (2978K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2978K) -
Kousuke Mori, Yasuharu Kanda, Yoshio UemichiArticle type: Regular Paper
2018 Volume 61 Issue 6 Pages 350-356
Published: November 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe catalytic performance of Pt supported on Al2O3, TiO2, SiO2 and activated carbon (AC) was investigated for the dehydrogenation of methylcyclohexane (MCH). The additive effects of Ce, Ga, Mn, Sn, and Zn on the Pt catalysts were also studied. Pt was highly dispersed on Al2O3 as an effective support, and was active for the dehydrogenation reaction. Sequential impregnation of Zn and Pt into Al2O3 in this order resulted in greatly increased MCH dehydrogenation activity and decreased methane selectivity, which were dependent on the amount of the loaded Zn. FT-IR of adsorbed CO, TEM, and XRD measurements revealed that dispersion of Pt on Al2O3 was little changed by loading Zn, and electron donation from Zn to Pt occurred. Therefore, the high dispersion and electron-donating ability of Pt in Zn–Pt/Al2O3 are responsible for the excellent catalytic performance. In contrast, addition of Zn to AC-supported Pt catalyst reduced the catalytic activity probably due to the formation of aggregated PtZn alloy particles on the support.
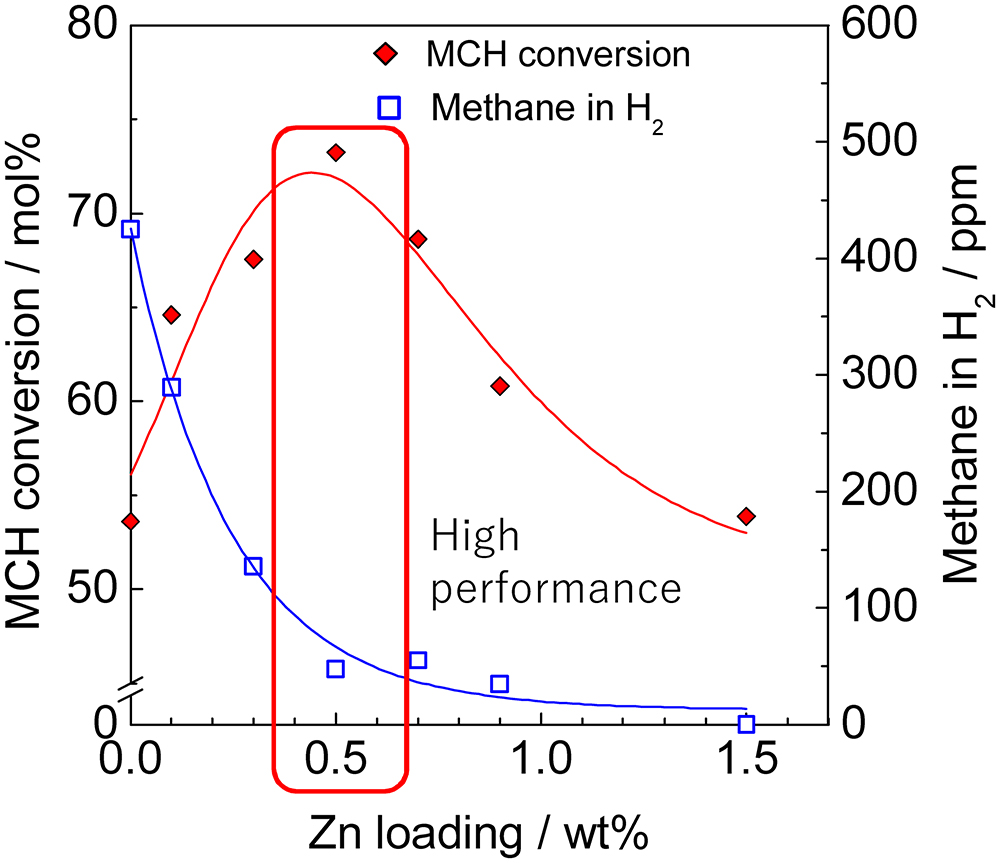 View full abstractDownload PDF (795K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (795K)
-
Yoshiki Ueno, Daisuke Taneda, Shohei Okino, Yoshihito ShiraiArticle type: Research Note
2018 Volume 61 Issue 6 Pages 357-360
Published: November 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSReduction in the cost of the cellulase used for saccharification of cellulose is essential to commercialize bioethanol and bio-chemicals derived from cellulosic biomass. Utilization of additives such as proteins and surfactants to prevent non-productive adsorption of cellulase on lignin can reduce the use of cellulase. However, the action of these additives is not sufficiently understood. This study investigated the effects of additives on cellulase adsorption on lignin using graphite as a hydrophobic substance to evaluate the hydrophobic interaction between cellulase and lignin. Inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis of filter paper was observed by addition of graphite, indicating hydrophobic interaction between cellulase and graphite. Addition of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and Tween80 enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis in the presence of graphite. In contrast, addition of polyethylene glycol (PEG) in the presence of graphite had no positive effect. The adsorption amounts of BSA and Tween80 were larger than that of PEG. Therefore, the effects of additives on cellulase adsorption mediated by hydrophobic interaction are considered to reflect the differences in adsorption amounts of additives on graphite.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (415K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (415K)
-
Mai Takase, Shingo Furukawa, Shun Matsuda, Kei-ichi Nishimori, Yasuhar ...Article type: Letter
2018 Volume 61 Issue 6 Pages 361-364
Published: November 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSH2S decomposition was examined in the gas and liquid phases over TiO2 photocatalyst. In the gas phase reaction, H2 was obtained using TiO2 as a photocatalyst. After the photocatalytic reaction, the color of TiO2 changed from white to yellow. SEM-EDS results revealed that sulfur was present on the TiO2 surface. H2 evolution rate was remarkably higher in the liquid phase reaction than in the gas phase reaction. Thus, liquid phase reaction is optimal to obtain H2 from the decomposition of H2S. Ethanolamine as a solvent of H2S underwent little photocatalytic decomposition. TiO2 photocatalyst has high potential for use in a new H2 recycling process in the petroleum industry.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (364K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (364K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|