
- Issue 6 Pages 245-
- Issue 5 Pages 199-
- Issue 4 Pages 141-
- Issue 3 Pages 87-
- Issue 2 Pages 53-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Takao MASUDAArticle type: Review Paper
2019Volume 62Issue 4 Pages 141-148
Published: July 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSOur recent studies of the application of iron-based oxide catalysts to upgrading of heavy oils under sub-/super-critical water conditions are reviewed. The effect of reaction parameters on the product yields were investigated for the reaction of bitumen over iron-based oxide catalyst. Reaction pressure greatly affected the product yield, indicating that formation of carbonaceous solid product, called coke, decreased with increase in pressure, and the yield of lighter component (Gas Oil and VGO) was the highest under sub-critical water conditions using both batch and flow type reactors. Kinetic analysis and reaction paths for the decomposition of bitumen were investigated. The decomposition reaction of VR (vacuum residual oil) in bitumen was assumed as second order kinetics, and the activation energy was calculated as 132 kJ/mol. Reaction kinetics were analyzed in details using the Lumping Model. The assigned reaction rate constant for each lump revealed that VR was consecutively converted into VGO, Gas Oil, and Gas, and coke formation was suppressed under sub-critical water conditions, as compared with the main reaction path. Therefore, the reaction process using iron-based oxide catalyst can be applied for the on-site upgrading of heavy oil including bitumen derived from the SAGD (Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage) method, in which bitumen is mined with water under high temperature and pressure.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1144K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1144K) -
Tomohisa MIYAZAWAArticle type: Review Paper
2019Volume 62Issue 4 Pages 149-156
Published: July 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSConversion of abundantly available, renewable and non-edible lignocellulosic biomass into usable energy, fuels and chemicals is important. However, lignocellulosic biomass has complex hierarchical structure and chemical resistance, so the conversion of non-edible lignocellulosic biomass is not easy. Therefore, many types of biomass conversion technologies were investigated both on the laboratory scale and bench scale. Development of the novel catalyst and reactor for woody biomass conversion at relatively low temperature, and the development of novel catalytic conversion of glycerol to propanediols were carried out on the laboratory scale. In addition, the bench-scale BTL (biomass to liquid fuel) plant for biomass conversion and liquid fuel production was developed and demonstrated. Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis diesel oil and dimethyl ether (DME) were produced from woody biomass by this bench-scale plant operation. Finally, continuous synthesis of DME over 600 h and recovery of approximately 1.1 kg of liquefied bio-DME were achieved. This bio-DME was used in the DME vehicle running test performed by the DME Vehicle Promotion Committee (DMEVPC).
 View full abstractDownload PDF (856K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (856K) -
Kiky Corneliasari SEMBIRING, Shiro SAKAArticle type: Review Paper
2019Volume 62Issue 4 Pages 157-172
Published: July 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe issues of global CO2 emissions and depletion of non-renewable energy resources associated with fossil fuels encourage the use of plant oils (both edible and non-edible) as biofuel sources. This review summarizes the literature on renewable hydrocarbon fuel production, including feedstock choice, oil extraction, and production processes. Plant oils can be upgraded into hydrocarbon biofuels by catalytic cracking or deoxygenation reactions, such as hydrodeoxygenation, decarboxylation and decarbonylation. This review also covers current progress in renewable hydrocarbon fuel blending with fossil diesel or gasoline to meet the requirements of product quality for engine fuel applications.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (381K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (381K)
-
Hideaki MIKIArticle type: Regular Paper
2019Volume 62Issue 4 Pages 173-180
Published: July 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCatalyst life was studied for developing a process for producing cyclopentyl methyl ether by continuous gas phase addition of cyclopentene and methanol using a strongly acidic ion exchange resin as a catalyst. Activity of the catalyst was found to decrease with time. C5 diolefins were indicated to form deactivation factor substances by analysis of substances deposited on the spent catalyst, analysis of behaviors of trace impurities before and after reaction, and other findings. Catalyst lifetime test using feedstock containing no C5 diolefins showed that deactivation of catalytic activity was greatly suppressed. The mechanism of catalyst deactivation is discussed based on the results of experiments reproducing tar formation, accelerated deactivation visualizing the inside of the reaction tube, and others.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1365K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1365K) -
Yuta SUGIMOTO, Yuki MATSUI, Ryosuke IWASAKI, Masaki OTA, Yoshiyuki SAT ...Article type: Regular Paper
2019Volume 62Issue 4 Pages 181-187
Published: July 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA predictive methodology for the interaction parameters of binary heavy oil fractions was developed by measuring and correlating the high temperature vapor-liquid equilibria (VLE) of hydrocarbon-atmospheric pressure residual oil (AR) systems. The VLE measurements were carried out at temperatures of 573-653 K using a flow type apparatus, using toluene as a typical hydrocarbon for aromatics, n-decane and n-hexadecane for paraffins, and decalin for naphthenes. The AR was divided into five fractions by boiling temperatures, and the fraction compositions were determined by GPC analyses. The vapor-liquid equilibrium data were correlated with the Peng-Robinson equation of state and the van der Waals one fluid model mixing rules. The determined values of the binary interaction parameter, kij, showed large temperature dependence and indicated that the values for the hexadecane-AR fraction were larger than for the other hydrocarbon-fraction pairs. A predictive equation for kij was proposed as a function of the critical temperature ratio between component i and component j.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (710K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (710K) -
Ichhuy NGO, Falan SRISURIYACHAI, Kyuro SASAKI, Yuichi SUGAI, Ronald NG ...Article type: Regular Paper
2019Volume 62Issue 4 Pages 188-198
Published: July 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2019
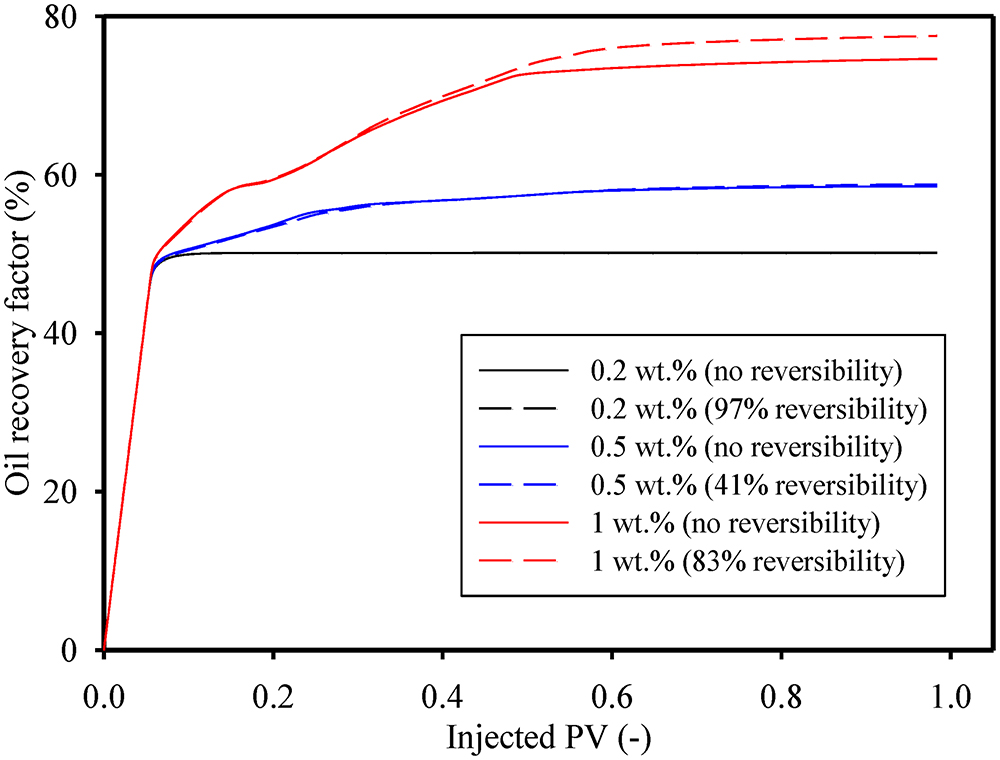
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSReduction of interfacial tension (IFT) between residual crude oil and formation fluids in oil reservoirs is the key to enhanced oil recovery (EOR) by surfactant flooding. However, adsorption of injected surfactant on minerals in the oil-bearing rock matrix reduces the effectiveness of this method. The present study investigated the effects of surfactant adsorption and desorption in the rock matrix on the oil recovery ratio achieved by surfactant-EOR. Sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS), a common surfactant in EOR, was used with Berea sandstone samples (rock particles and cores) as adsorbent. Adsorption of SDBS in the samples increased with concentration, and the static saturated amount was 0.9 mg-SDBS/g-rock for 1.0 wt% SDBS-water solution. If brine (1.0 wt% salinity) was injected after saturated adsorption of SDBS in the core, 83 % of adsorbed SDBS was desorbed into the brine (the reversibility effect). To clarify the reversibility effect in oil reservoirs, field scale numerical simulations were conducted for a typical 5 spot model (area: 180 m × 180 m, thickness: 60 m) using core-flooding data reported previously. By introducing the reversibility model into the simulations on of surfactant flooding injection of slugs of 0.1 PV and 0.3 PV into the initial reservoir, oil recovery factor showed differences of 2.3 % and 2.9 % compared to without the model, respectively. Injection of the surfactant solution after water-flooding caused a difference of only 0.4 %
 View full abstractDownload PDF (4574K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4574K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|