All issues

Volume 59 (2016)
- Issue 6 Pages 243-
- Issue 5 Pages 165-
- Issue 4 Pages 109-
- Issue 3 Pages 73-
- Issue 2 Pages 35-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
Volume 59, Issue 3
Displaying 1-5 of 5 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Review Paper
-
Tomoya TSUJI, Taka-aki HOSHINA, Toshihiko HIAKI, Naotsugu ITOHArticle type: Review Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 3 Pages 73-83
Published: May 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA hydrogen storage medium, using a dehydrogenation reaction of naphthene in a membrane reactor, is proposed for fuel cell systems. In this system, the permeation rate of hydrogen is not high so that the residual hydrogen, not passing through the membrane, must be recovered. A gas-liquid separator and an adsorption column were evaluated. For the design of the separator, the hydrogen solubility has been already reported for aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthenes, and equimolar mixtures. In this study, adsorption on activated carbon was measured in hydrogen flow saturated with pure benzene, cyclohexane, methycyclohexane, and toluene, and the equimolar mixtures, benzene + cyclohexane and methycyclohexane + toluene. The measurement was carried out by a new apparatus specially designed for this study, based on a flow type method, and equipped with gas chromatograph with both FID and TCD. In the measurement, the breakthrough curve and the specific mass adsorbed were measured at 347 kPa and 303.15 K. The adsorption mechanism was also discussed based on the breakthrough curves for the pure adsorbates and mixtures. Finally, the required mass of adsorbate, activated carbon, was estimated for the system by assuming the reaction rate and the hydrogen permeation ratio in the membrane reactor.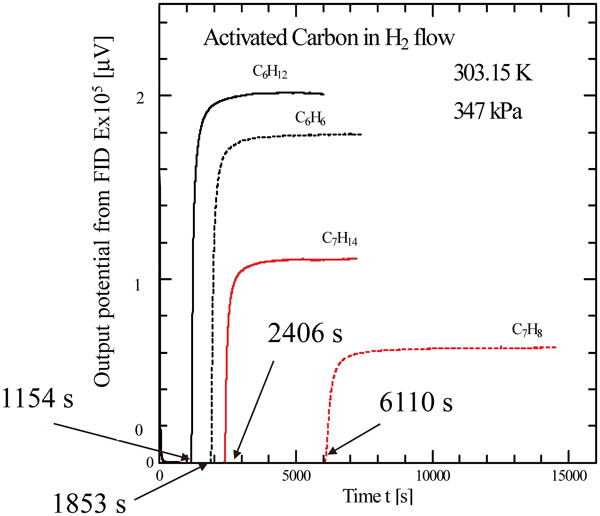 View full abstractDownload PDF (1632K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1632K) -
Tetsuaki FUJIHARA, Yasushi TSUJIArticle type: Review Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 3 Pages 84-92
Published: May 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCarbon dioxide (CO2) is a readily available carbon source, but the thermodynamic characteristics of CO2 limit its widespread use in chemical reactions. This review summarizes the transformation of CO2 via carbon–carbon bond-forming reactions. Ni complexes catalyzed the carboxylation of less reactive aryl chlorides and double carboxylation of internal alkynes in the presence of suitable reducing agents such as Mn or Zn powders under 1 atm of CO2. Using Cu complexes as catalysts under CO2 atmosphere, hydrocarboxylation and silacarboxylation of alkynes proceeded efficiently using hydrosilanes and silylboranes, respectively, as the reagents.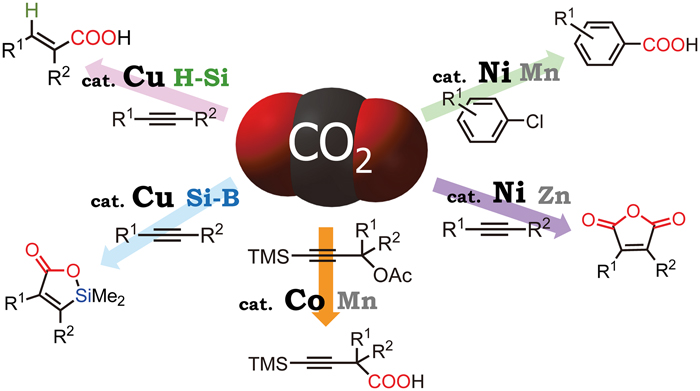 View full abstractDownload PDF (544K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (544K)
Regular Paper
-
Machi KANNA, Yumiko MATSUNAMI, Yukihiko MATSUMURAArticle type: Regular Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 3 Pages 93-96
Published: May 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLignocellulosic biomass is a highly promising source for the generation of sustainable energy. Bioethanol produced from lignocellulosic biomass can be used to fuel internal combustion engines that run on gasoline. To reduce the cost of ethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass, the simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) method is attractive, because it can be performed in a single reactor. We attempted to isolate thermotolerant and fermentation inhibitor-tolerant strains of yeast by altering the preculture conditions. Preculture at 35 °C increased SSF ethanol production in the presence of 5-HMF. This study demonstrated that yeast strains can adapt to higher preculture temperature for SSF. View full abstractDownload PDF (474K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (474K) -
Toshiaki HIRATO, Kenji HIMENO, Masato MURAYAMA, Shigeki TAKAHASHIArticle type: Regular Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 3 Pages 97-103
Published: May 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe rheological properties of asphalt are important in the characteristics of pavement used for long periods. The rheological properties of asphalt might be affected by repeat traffic loading or environmental factors such as ambient temperature, air, or UV radiation. This study investigated the effects of traffic and environmental factors on the aging of the asphalt and established an aging index based on the rheological properties of asphalt. Stiffness of asphalt was calculated with a nomograph and measured using a dynamic shear rheometer (DSR). The findings showed a very high correlation between stiffness calculated by nomograph and complex modulus measured by DSR regardless of the loading time and measurement temperature, as well as a very high correlation between complex modulus and loss modulus regardless of loading time, temperature, type of binder, field sample and accelerated aging sample. The relationship between damaged asphalt pavement and the rheological properties of asphalt is discussed. View full abstractDownload PDF (829K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (829K) -
Yuji SAKA, Norihito CHIYODA, Katsuya WATANABE, Satoshi INAGAKI, Yoshih ...Article type: Regular Paper
2016 Volume 59 Issue 3 Pages 104-108
Published: May 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHigher propylene production inside fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) units is strongly desired to satisfy the increasing demand for petrochemical feedstock in recent years. Although propylene production can be increased via physical mixing of a suitable catalyst containing ZSM-5 (commonly referred to as additive) with FCC catalyst, this technique is usually associated with increased amount of distillate containing heavy fuel oil such as slurry oil (SLO). In this study, the effect of aluminum phosphate ([Al–P]) as a new matrix component was investigated. The use of an additive with FCC catalyst containing [Al–P] successfully formed liquefied petroleum gas containing propylene in higher yield compared with conventional FCC catalyst containing rare-earth, and suppressed the undesirable increase in SLO yield. This catalytic system has high potential for use in FCC units. View full abstractDownload PDF (834K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (834K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|