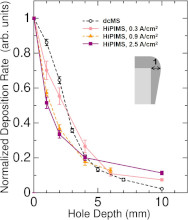
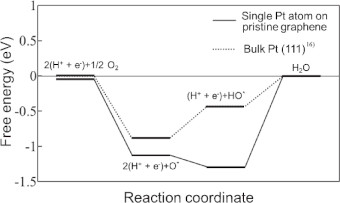
63 巻, 8 号
特集「2019年日本表面真空学会学術講演会特集号Ⅲ」
選択された号の論文の12件中1~12を表示しています
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
巻頭言
-
原稿種別: 巻頭言
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 397
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (336K)
瑞宝中綬章受章のお祝い
-
原稿種別: 瑞宝中綬章受章のお祝い
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 398
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (326K)
特集「2019年日本表面真空学会学術講演会特集号Ⅲ」
-
原稿種別: 解説
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 399-403
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (2135K) -
原稿種別: 論文
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 404-412
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (5838K) -
原稿種別: 論文
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 413-418
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (1917K) -
原稿種別: 論文
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 419-424
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (2811K) -
原稿種別: 研究紹介
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 425-430
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (5895K) -
 原稿種別: 研究紹介
原稿種別: 研究紹介
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 431-436
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
-
原稿種別: 研究紹介
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 437-440
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (1493K)
連載企画
オリンピック・パラリンピック
-
原稿種別: 連載企画
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 441-444
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (6974K)
談話室
海外研究体験記
-
原稿種別: 談話室
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 445-446
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (1894K)
先端追跡
-
原稿種別: 先端追跡
2020 年 63 巻 8 号 p. 447
発行日: 2020/08/10
公開日: 2020/08/10
PDF形式でダウンロード (329K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|