
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Mark Kevin P. Devanadera, Reuel M. Bennett, Kenshi Watanabe, Myla R. S ...2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1163-1174
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/11/15ジャーナル フリー
電子付録Marine oomycetes are ubiquitous, fungus-like eukaryotes known to produce fatty acids with potential anticancer activity. The long chain omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are currently popular and considered as safe when used as nutraceuticals in cancer treatment. In this study, crude fatty acids from three marine oomycetes, Halophytophthora spp. (T12GP1 and T12YBP2) and Salispina hoi (USTCMS 1611), were explored for their cytotoxic and apoptotic potentials against human breast adenocarcinoma cells (MCF7) and normal human dermal fibroblasts (HDFn). Extracts from mycelia mats consisted of diverse saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids such as linoleic, α-linolenic, γ-linolenic, eicosatrienoic and eicosapentaenoic acids. The crude fatty acids from all three oomycetes in in vitro assays for cytotoxicity showed no toxicity (30% toxicity values) on HDFn cells. On MCF7 cells, however, IC50 values of 23.44, 15.63, and 26.15 µg/mL were obtained with extracts from Halophytophthora T12GP1 and T12YBP2 and S. hoi, respectively. Treated MCF7 cells exhibited deformed cell membrane in MTT assay and also aggregation of DNA and disruption of nuclear membrane aggregation in nuclear staining; further, green signals indicative of apoptosis was recorded in caspase 3/7 assay.
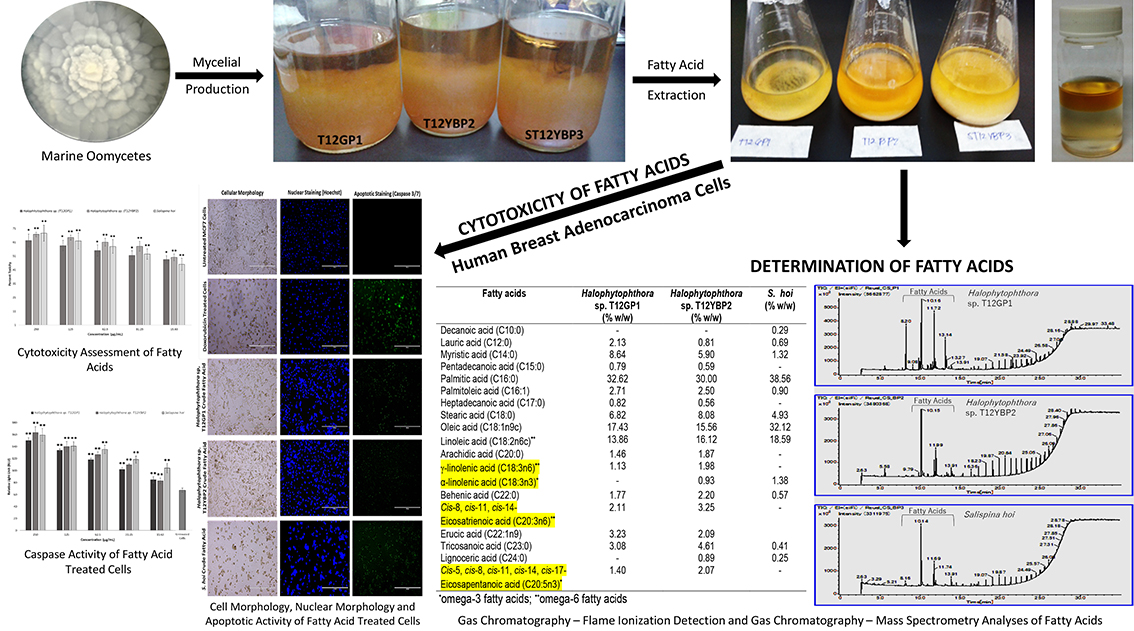 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2266K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2266K) -
Shaohua Liang, Xianzhi Wei, Man Zhang, Cong Sun2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1175-1185
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリーMedium chain triacylglycerols (MCTs) have gained wide attention due to its ability to induce the residual glyceride lipolysis and improve fat absorption. In this study, structured lipid enriched with MCTs was synthesized by chemical catalyzed acidolysis of coconut oil with the mixture of caprylic acid (Cy) and capric acid (Ca) in a solvent-free system. Three catalysts were compared for their efficiency in the production of MCTs yield. The results indicated that the highest yield of MCTs was achieved by H2SO4. Effects of reaction variables on the acidolysis reaction were optimized using response surface methodology, and the optimum conditions were as follows: molar ratio of Cy to Ca 1:1, reaction time 4 h, molar ratio of MCFAs to coconut oil 12:1, catalyst loading 12 wt%, reaction temperature 110℃. Under these conditions, the obtained structured lipid contained 89.5% of MCFAs and at least 82.0% of MCTs. This paper provides a simple and low-cost method for preparing structured lipid enriched with MCTs.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (764K) -
Yuanjiao Li, Peng Li, Guanghua Xia, Chuan Li, Xuanri Shen2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1187-1197
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/11/15ジャーナル フリーIn this study, we first isolate phospholipid (PL) from Golden pompano head (GPH), and elucidate its structure. Gas chromatography (GC) was used to assess the GPH-PL fatty acid composition, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and ultraviolet absorption spectrometry (UV) were used for the qualitative analysis of GPH-PL, and LC-MS analysis was used to determine the major PL species. The results show that the contents of the various molecular species of GPH-PL were generally in the order phosphatidylcholine (PC) > sphingomyelin (SM) > lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) > phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). The main molecular PC species are 16:0/18:2, 13:0/23:2, 27:2/9:0, 16:0/18:1, 12:0/22:2, 18:0/18:1, 18:0/24:1, and 18:1/24:0. The major SM species are 16:1/16:0, 16:0/18:1, 16:0/18:2, 16:0/26:2, and 18:1/24:1. The major LPC species are 18:1 and 16:0. The major PE species are 18:0/18:1 and 16:0/22:6. The total eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) contents in the GPH-PLs were 18.39%, and the content of DHA in the PL fraction was 16.47%. These results suggest that PLs from GPH is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), which have good activity in anti-inflammation, anti-tumor, anti-osteoporosis and other aspects, and have important development prospects in the future.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (403K) -
Hiroaki Saito, Hisashi Ioka2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1199-1213
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/11/15ジャーナル フリーThe lipid and fatty acid compositions of two species of gastropods, Aplysia kurodai and Aplysia juliana (collected from shallow sea water), were examined to assess their lipid profiles, health benefits, and the trophic relationships between herbivorous gastropods and their diets. The primary polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) found in the neutral lipids of all gastropod organs consisted of four shorter chain n-3 PUFAs: linolenic acid (LN, 18:3n-3), icosatetraenoic acid (ITA, 20:4n-3), icosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5n3), and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA, 22:5n-3). The PUFAs found in polar lipids were various n-3 and n-6 PUFAs: arachidonic acid (ARA, 20:4n-6), adrenic acid (docosatetraenoic acid, DTA, 22:4n-6), icosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5n-3), and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA, 22:5n-3) in addition to trace levels of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6n-3). Various n-3 and n-6 PUFAs (18:2n-6, 20:2n-6, 18:3n-6, 20:3n-6, 18:3n-3, 18:4n-3, 20:3n-3, n-3 ITA, and 22:3n-6,9,15) comprised the biosynthetic profiles of A. kurodai and A. juliana. Both Aplysia species have traditionally been eaten as local foods in Japan, and the high levels of n-3 (EPA and n-3 DPA) and n-6 (ARA and DTA) PUFAs indicate that they are a healthful addition to a human’s diet.
 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3879K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3879K) -
Yayoi Miyagawa, Shuji Adachi2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1215-1222
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリーCrystallization of vegetable oil affects the efficiency of the oil-refining process and the quality of foods containing the oil. However, the crystallization of the oil is a complicated phenomenon. The crystallization behavior of rapeseed oil was investigated using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) at a cooling rate of 0.5–10°C/min. It was found that multiple crystal structures with a metastable crystal formed at high cooling rates. A deconvolution technique was applied to analyze kinetically the DSC curves with some peaks. Each DSC curve was separated into 3–5 peaks fitted with an asymmetric double sigmoid function and a Lorentz one. Each peak was normalized by its integrated value, and the crystallinity was calculated. Using the crystallinity values, Avrami, Ozawa, and Friedman plots were obtained. The cooling rate was found to affect the crystallization mechanism and triacylglycerol (TAG) composition of the crystal in the separated peak. Even if the peak numbers are the same, the TAG composition of the crystals might be different depending on the cooling rate. Judging from the peak top temperature and area of the separated peaks, trioleoyl glycerol and 1,2-dilinolenyl-3-linoleyl glycerol would be included in crystals in the peaks with the largest and lowest peak top temperatures, respectively. The relationship between the peak top temperature and cooling rate was unique. This suggests that the crystallization behavior during isothermal storage was different from that in a nonisothermal process.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (597K)
-
Toshiaki Taira, Yuki Ishizaki, Shusei Yamamoto, Kenichi Sakai, Hideki ...2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1223-1230
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/11/15ジャーナル フリー
電子付録We report the synthesis of amphiphilic dodecenyl phosphonic acid PC12 from vinylphosphonic acid, a reactive phosphonic acid intermediate. The trans-P-C=C moiety enabled PC12 to disperse well in water. Surface tension and dynamic light scattering measurements revealed that PC12 exhibited high surface activity and reduced the surface tension of water from 72.0 to 23.6 mN/m, thereby resulting in the spontaneous formation of aggregates even in a dilute aqueous solution (critical aggregation concentration (CAC) = 4.8 × 10–4 M). In contrast to modern lipids with double-tailed structures, the PC12 of simple singletailed structure spontaneously formed bilayered vesicles, without an external energy supply. Compared with the strength of hydrogen bonds formed by the long, saturated alkyl chain of dodecyl phosphonic acid (DPA), the strength of PC12 intermolecular hydrogen bonds was weaker. The melting point of PC12 was approximately 20°C lower than that of DPA. These results indicate that the trans-P-C=C moiety was considerably important for spontaneous vesicle formation in water. Preliminary modeling of the morphological transitions of the closed bilayer structures in the vesicles was then conducted, by varying the pH and adding an α-helical peptide scaffold.
 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1084K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1084K) -
Malik Abdul Rub, Dileep Kumar2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1231-1240
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/11/15ジャーナル フリーPaper analyses the influence of cationic cetyltrimethylammonium bromide on rate of Zn(II)-histidine and ninhydrin. UV-visible spectroscopy was applied to note absorbance of Zn(II)-histidine complex with ninhydrin at the end of reaction in the two systems. Rate constant, kobs, (in aqueous) and rate constant, kψ, (in cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, CTAB) were determined by computer software. Reactions depict first-order in Zn(II)-histidine concentration and fractional-order in ninhydrin concentration in aqueous and micellar media. The results achieved indicate that the reactions take place principally by the same reaction mechanism in both the media. Critical micelle concentration of CTAB surfactant was calculated by recording the conductivity as a function of surfactant concentrations. Influence of various amounts of surfactant on Zn(II)-histidine complex and ninhydrin reaction was performed under different reaction conditions. Reaction was catalyzed and accelerated efficiently by surfactant medium compared to aqueous medium. The observed influence of surfactant on rate has been mentioned in details and their quantitative treatment of kinetic results have been deduced by the means of Menger and Portnoy model for micellar catalysis.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (624K)
-
Wanida Sukketsiri, Kiyoto Hoshino, Hirona Kugo, Tomomi Nakamura, Tsuka ...2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1241-1249
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/11/15ジャーナル フリーNicotine has been linked to the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Isoflavones, a group of polyphenolic compounds, reportedly exhibit antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and facilitate cardiovascular protection. However, the effects of isoflavone on nicotine-induced abdominal aortic aneurysms have not yet been elucidated. The objective of the current study was to evaluate the inhibitory effect of isoflavone on nicotine-induced weakening of the aortic wall in mouse models. Nicotine reportedly increases the occurrence of abdominal aortic aneurysms by activating endothelin-1 (ET-1), angiotensinogen and the angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor, leading to an increase in neutrophil elastase, oxidative stress, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 expression, which causes vascular wall weakness and damage. Immunohistological analyses have indicated that isoflavone significantly inhibits the activation of ET-1, angiotensinogen and the AT1 receptor in nicotine-administered mice. Additionally, isoflavone suppressed elastic fiber destruction and decreased areas positive for MMP-2, neutrophil elastase, and malondialdehyde in the vascular wall of nicotine-administered mice. Considered together, these findings suggest that isoflavone shows potential for preventing vascular wall injury induced by nicotine administration, and that food containing isoflavone may protect against abdominal aortic aneurysms.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2373K)
-
Yusuke Murakami, Hisakatsu Iwabuchi, Yukie Ohba, Harukazu Fukami2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1251-1260
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリーThe Habanero pepper is characterized by its strong pungency and fruity aroma. The aim of the present study was to extract the volatile compounds of Habanero peppers, using solvent extraction and solvent-assisted flavor evaporation (SAFE) methods, and to analyze them using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The analysis detected 66 volatile compounds, including 6-methyl-(E)-4-heptenyl 3-methylbutanoate 1, which was reported previously, and 6-methyl-(E)-4-heptenyl 2-methylpropanoate 2, the corresponding butanoate 3, 2-methylbutanoate 4, and 6-methyl-(E)-4-heptenol 5, which were found in both Habanero and other peppers. 6-Methyl-(E)-4-heptenyl 3-methylbutanoate 1 and related compounds were synthesized. Furthermore, principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) of the volatile profiles generally grouped the pepper samples by species and indicated that Habanero peppers are characterized by the presence of 6-methyl-(E)-4-heptenyl esters.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (819K)
-
Issei Takeuchi, Yuudai Kanno, Hiromi Uchiro, Kimiko Makino2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1261-1270
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリーPEGylated liposomes are one of the useful boron carriers for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Recently, a method of adding PEG after liposome formation (post-insertion) was reported. In this study, we prepared polyborane-encapsulated PEGylated liposomes for BNCT with half the amount of DSPE-PEG of the conventional method using post-insertion technique (post-PEG liposomes), and their usefulness were evaluated in comparison with conventional PEGylated liposomes (pre-PEG liposomes). From the results of physicochemical property measurements, it was confirmed that particle size distributions, surface charge densities, and fixed aqueous layer thicknesses of these liposomes were equivalent. In vitro cytotoxicity and cell uptake tests were also carried out using B16 melanoma and RAW264.7 cells. Polyborane solution and bare liposomes were used for comparison. From the results of these tests, we confirmed that post-PEG liposomes and pre-PEG liposomes have the same influence of PEGylation. To evaluate biodistribution properties at 24 h post-administration, these liposomes and polyborane solution were injected into the tail veins of tumor-bearing mice. Boron concentration and tumor/blood ratios of PEGylated liposomes were 73.2-77.6 µg/g of tumor tissue and 5.5-5.8, respectively. From these results, it was found that by using post-insertion technique, liposomes for BNCT having same effect as the liposome prepared using the conventional method can be prepared with half amount of DSPE-PEG.
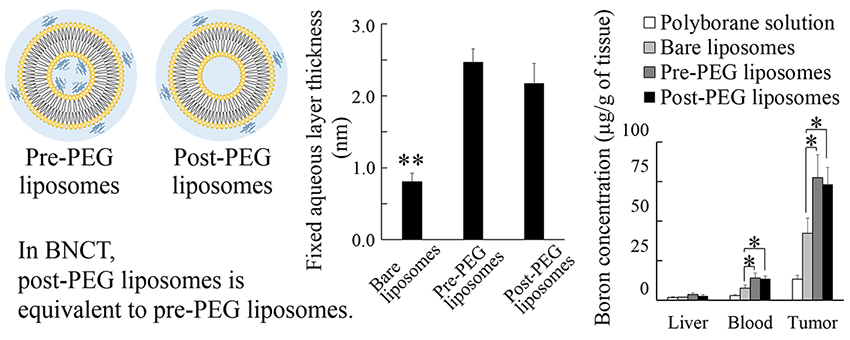 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (586K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (586K) -
Nobuya Shirai2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1271-1277
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリーHerein, gas chromatography is used to determine and quantify organic acids in Japanese green tea leaves, and the established method is employed to profile the acid components of Matcha, Gyokuro, Sencha green teas, and green tea varieties and thus acquire data needed to ensure the high quality and safety of green tea. The tea leaves were esterified with 10 vol% sulfuric acid in 1-butanol at 100℃ for 2 h. Oxalic acid contents were high in Asatsuyu and Okuyutaka samples and were low in Sofu, increasing in the order of Sencha < Gyokuro < Matcha, while citric acid content increased in the order of Sencha < Matcha < Gyokuro. Moreover, the oxalic acid content of Gyokuro only slightly increased with increasing tea grade. The relative contents of the different fatty acids did not strongly vary between the different green tea varieties. However, the n-3 to n-6 ratio was found to be low in Sofu. The progressing maturity increased the n-3 to n-6 ratio of Yabukita. The n-3 to n-6 ratio was low in high-grade Matcha, Gyokuro, Sencha green teas, and was related to the green tea quality. The developed method was concluded to be suitable for the evaluation of green tea quality.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (477K) -
Nara Nantarat, Kouichi Nakagawa, Ryo Miyamoto, Sunee Chansakaow, Jakka ...2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1279-1285
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリーThe free radical scavenging activities of black and white sesame seed hulls and the powder of black and white sesame seed cakes were investigated using noninvasive continuous wave electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and antioxidant assays. With black sesame seed hulls and the powder of black sesame seed cakes, EPR detected the very strong single-line signal intensities that correspond to the stable organic radicals, while the spectrum of the white sesame seed hulls and the white sesame seed cakes showed no signal. The in vitro antioxidant activities of black and white sesame seed cake extract were evaluated by DPPH free radical scavenging activity, hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity, and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay. The results indicated that the extract from black sesame seed cake possessed a greater DPPH radical inhibitory activity and hydrogen peroxide inhibitory activity than white sesame seed cake extract, with IC50 values of 0.847 ± 0.011 mg/mL and 0.338 ± 0.007 mg/mL, respectively. Black sesame seed cake extract also showed a strong reducing power with a FRAP value of 1.307 ± 0.037 mM Fe (II)/g of extract weight and an EC1 value of 0.683 ± 0.002 mg/mL. The main compounds from the black and white sesame seed cake extracts were analysed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The results revealed that the main compounds in black and white sesame seed cake extracts were in a group of water-soluble lignans, mainly sesaminol triglucoside and sesaminol diglucoside. However, sesaminol diglucoside was found in large amounts in the black sesame seed cake extract, while it was found in a very small amount in the white sesame seed cake extract. Therefore, these results demonstrated considerable antioxidant capacity of the sesame seed, especially in the black strain.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (577K) -
Shun Sato, Tokuma Fukuoka, Azusa Saika, Tatsuyuki Koshiyama, Tomotake ...2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1287-1294
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー
電子付録We applied matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/MS) to screen for glycolipid-type biosurfactant (BS) producers. A crude extract of Pseudozyma antarctica, a well-known mannosylerythritol lipid (MEL) producer, was initially subjected to MALDI-TOF/MS. The spectrum of the extract showed the accumulation of diacylated MELs in culture. We then screened 80 environmental samples for BS-producing yeasts, and extracts from broth cultures of the selected five strains were examined using MALDI-TOF/MS. The results showed that all five strains produced MELs, whereas four strains also produced cellobiose lipids (CLs). By D1/D2 region sequence analysis, the MEL-producing strain was assigned to P. antarctica while the four MEL- and CL-producing strains were assigned to P. hubeiensis. These results demonstrate that MALDI-TOF/MS is a rapid and reliable tool to detect BS molecules in crude extracts of broth cultures to screen for glycolipid-type BS producers.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (815K) -
Kazuaki Yoshinaga, Arisa Tago, Aya Yoshinaga-Kiriake, Toshiharu Nagai, ...2019 年68 巻12 号 p. 1295-1301
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリーThe lactone content of butter, fermented butter, and margarine was compared using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. The main lactones in butters and fermented butters consisted of δ-decalactone, δ-dodecalactone, δ-tetradecalactone, δ-hexadecalactone, and γ-dodecalactone. In contrast, the main lactones in margarines were δ-decalactone and δ-dodecalactone. The total lactone content in butters and fermented butters increased by approximately two-fold upon heat treatment, whereas, heat treatment did not affect the lactone content in margarine. The changes in lactone content caused by heat treatment were greater in fermented butters than in butters. These findings suggested that the fermentation process could increase lactone or lactone precursor content in butter.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (314K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|