
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Ichiro Hatta, Hiromitsu Nakazawa, Noboru Ohta, Tomonobu Uchino, Kaori ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1181-1199
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLStudies on the effectiveness of substances such as drugs and cosmetics that act on the skin require structural evidence at the molecular level in the stratum corneum to clarify their interaction with intercellular lipid and soft keratin. For this purpose, when applying the substances to the stratum corneum X-ray diffraction experiment is one of the powerful tools. To detect minute structural changes in a stratum corneum sample, using a “solution cell”, dynamic synchrotron X-ray diffraction measurements were performed when applying aqueous solution of the substances to the stratum corneum: (1) It was found that a surfactant, sodium dodecyl sulfate, significantly disrupted the long-period lamellar structure. (2) To study the effects of water, structural modifications of the short-period lamellar structure and the soft keratin in corneocytes were measured as a function of time. At the initial water content of 15 wt%, the spacings of the short-period lamellar structure and the soft keratin increased toward those at the water content of 25 wt%, that is a key water content in the stratum corneum. (3) Nanoparticles composed of assembly of amphiphilic molecules are one of the leading pharmaceutical formulations. When the nanoparticles were applied, a new assembly of amphiphilic molecules originated from the nanoparticle appeared. This phenomenon suggests that the formation of the new assembly at the surface of skin is concerned with the release of the drug from the nanoparticles. (4) When ethanol was applied to the stratum corneum, only the liquid state in the intercellular lipid matrix was dissolved. After the removal of ethanol from this stratum corneum, the ordered hydrocarbon-chain packing structures appeared. From this fact we would propose that the liquid state region is the main pathway for hydrophobic drugs with a small molecular weight in connection with the so-called 500 Da rule. Here, not only the technique but also the background to these studies and the characteristic results obtained from these studies are explained.
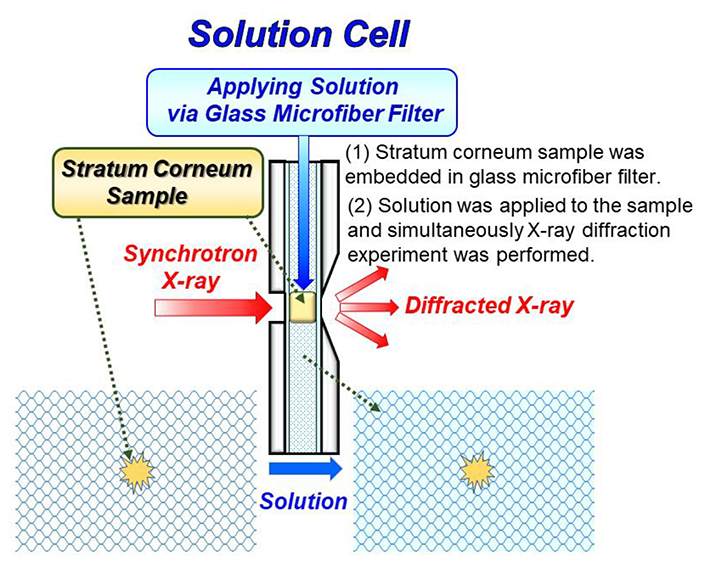 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5395K) HTML形式で全画面表示
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5395K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Choon Hui Tan, Chao Jie Lee, Sze Ning Tan, Dickson Tik Sang Poon, Cher ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1201-1210
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThis review is aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of the physicochemical properties and extraction processes of red palm oil, its nutritional properties and applications in food. Crude palm oil is firstly extracted from the fruit mesocarp and processed into red palm oil using pre-treatment of crude palm oil, with deacidification steps, and deodorization via short-path distillation. These processes help to retain β-carotene and vitamin E in red palm oil. Palmitic, stearic and myristic acids are the saturated fatty acids in red palm oil, while the unsaturated fatty acids are oleic, linoleic and linolenic acids. It is reported to overcome vitamin A deficiency, promote heart health and have anti-cancer properties.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (371K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Miao Lv, Wenbiao Wu2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1211-1223
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセスA method able to simultaneously obtain oil and defatted meal (rich in proteins) with high quality is preferable to others for processing black sesame seeds, which should also be green, healthy, highly efficient and sustainable. Methods including solvent extraction and hot-pressing currently available for the commercial production of oils are not able to meet all criteria just mentioned above. Therefore, development of new aqueous method of extracting black sesame oil has been promoted. In our study, we developed a new aqueous method using 1.95:10 aqueous salt solution-to-ground black sesame seed ratio which simultaneously recovered 96.54% black sesame oils and defatted meal with only 3.89% residual oils and 50.1% proteins (on dry weight basis). The oil produced had low acid value at 0.43 mgKOH/kg and peroxide value 3.37 mmol/kg and good other quality indexes. We found that proper amount of water added was essential for efficiently recover black sesame oils while other factors including temperature and time of baking raw materials to deactivate lipase activity, pore size of the sieve for ground black sesame seeds to pass through, addition of salt as well as temperature and time of agitating significantly affected the recovery efficiency. As compared with other methods, the new aqueous method had higher oil recovery rate or quality and was more environmentally friendly. No waste water was discharged during separation of oils. The experimental data can be applied to guide the design and manufacture of production line of black sesame oilseeds on a pilot or commercial scale.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3083K) -
Takao Roppongi, Yayoi Miyagawa, Hiroyuki Fujita, Shuji Adachi2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1225-1230
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe effect of oil-droplet diameter on lipid oxidation in O/W emulsions is unclear, and conflicting results have been reported. These conflictions may be due to different experimental conditions being used, such as the type of oil, the type of emulsifier, temperature, and the range of oil-droplet diameters tested. The method used to evaluate the oxidation could also have varied among studies. In O/W emulsions, oxygen dissolved in the aqueous phase is transferred to the oil phase through the oil-water interface and is consumed in the oil phase by oxidation. Therefore, the effect of the oil-droplet diameter on the lipid oxidation rate was evaluated by simultaneously solving the mass balance equations of oxygen and oil in the oil phase. The simulation showed that the oil-droplet diameter does not affect the lipid oxidation rate in O/W emulsions with oil-droplet diameters on the order of micrometers or less because the oxidation reaction itself is rate-limiting.
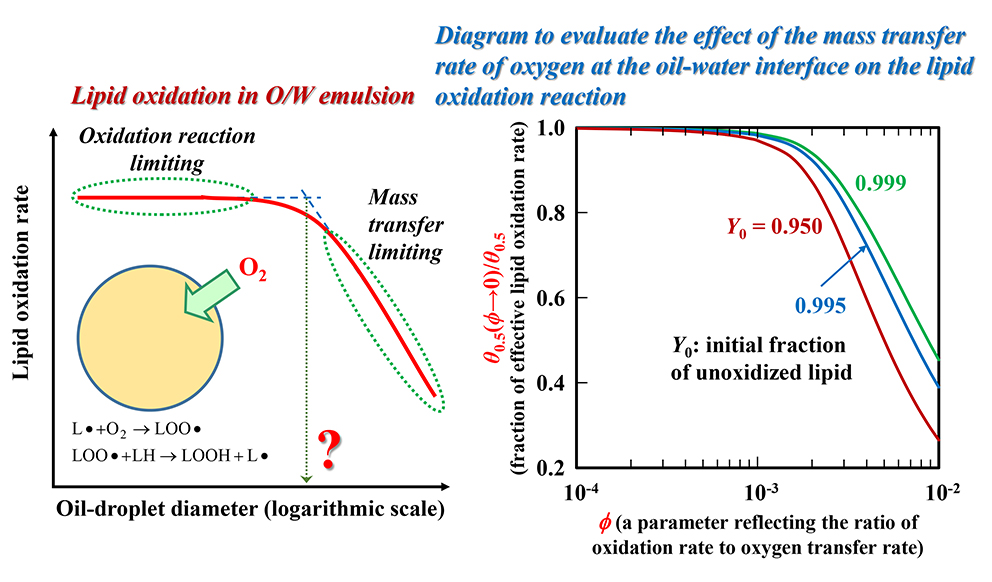 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (613K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (613K) -
Xingzhen Zhang, Tianyu Dong, Zeyu Wu, Yuequn Jing, Dianyu Yu, Hongwei ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1231-1238
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス
電子付録The solubility of hydrogen in n-hexane was determined using a homemade reactor. The solubility of hydrogen in soybean oil was established using the Peng-Robinson (PR) equation of state and the van der Waals mixing rule. The curve equation established a linear relationship between the solubility of hydrogen in oil and the number of moles of hydrogen in the reactor. Under the optimal temperature and catalyst, the relationship between the hydrogen consumption of the hydrogenation of oil and fat and the TFAs formed in the oil was determined. When the reaction pressure exceeded 3.0 MPa, the hydrogenation of oil was consumed. The amount of hydrogen, the rate of hydrogenation, and the change in the TFAs all stabilized. Therefore, the pressure of the general hydrogenation reaction should not exceed 3.0 MPa. This result provides a quick and simple method for controlling TFAs in oils and fats for industrial applications.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (541K)
-
Minako Okukawa, Yuika Yoshizaki, Shigekazu Yano, Yoshimune Nonomura2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1239-1246
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス
電子付録Fatty acids and their derivatives are interesting cosmetic ingredients because they show the selective antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). However, the antibacterial activity in mixed systems containing several active ingredients is unclear because previous studies focused antibacterial systems containing one kind of fatty acid. In the present study, the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the fractional inhibitory concentration (FIC) were evaluated for myristic acid/lauric acid, myristic acid/palmitoleic acid, and myristic acid/lactic acid mixed systems to show the effect of the coexisting components on the selective antibacterial activity of myristic acid. In the myristic acid/palmitoleic acid mixed system, the antibacterial activity against S. aureus was enhanced by additive effect, whereas the antibacterial activity was not observed against S. epidermidis. On the other hand, the myristic acid/lauric acid mixed system showed antibacterial activity against S. epidermidis: Lauric acid impaired the selectivity of antibacterial activity of myristic acid. These results suggest that the selective activity of myristic acid varies with the additives. The present findings are useful for designing formulations of cosmetics and body cleansers containing myristic acid.
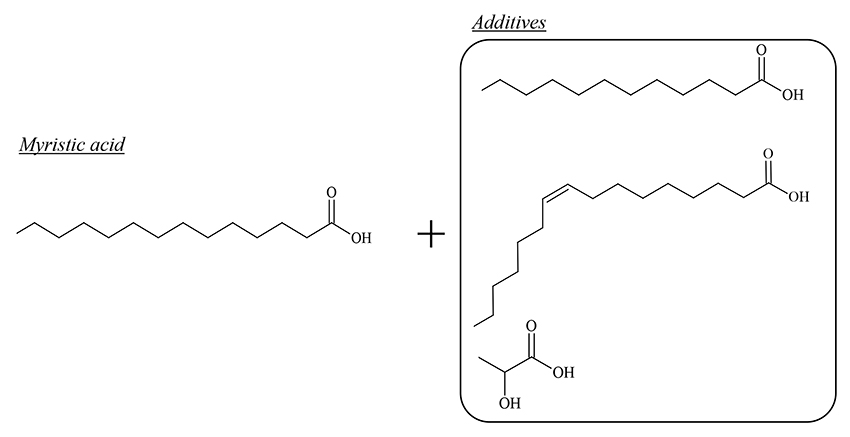 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (428K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (428K) -
Kenichi Sakai, Rina Ishii, Takanori Saito, Masaaki Akamatsu, Takaya Sa ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1247-1252
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセスWe characterized the adsorption and desorption of α-gel (α-form hydrated crystal) dispersions in aqueous media using a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) technique. The α-gel was formed from a mixture of N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]docosanamide (APA-22) L-lactic acid salt, 1-octadecanol (C18OH), and water. The solid substrate employed in this study as a model for hair was silica. The QCM-D measurements revealed that the α-gel dispersions yielded a rigid adsorption film on the negatively charged silica surface. The adsorption mass decreased with decreasing domain size (on the micrometer scale) of the α-gel dispersions. The adsorption film highly restricted the desorption of the α-gel from the silica surface even after rinsing with water. The adsorption film also exhibited excellent lubrication ability in aqueous media both before and after rinsing with water. We expect that the α-gel formed by APA-22 L-lactic acid is a potential ingredient for formulating an environment-friendly hair conditioner owing to its high adsorption, limited desorption, and excellent lubrication abilities on the solid surface.
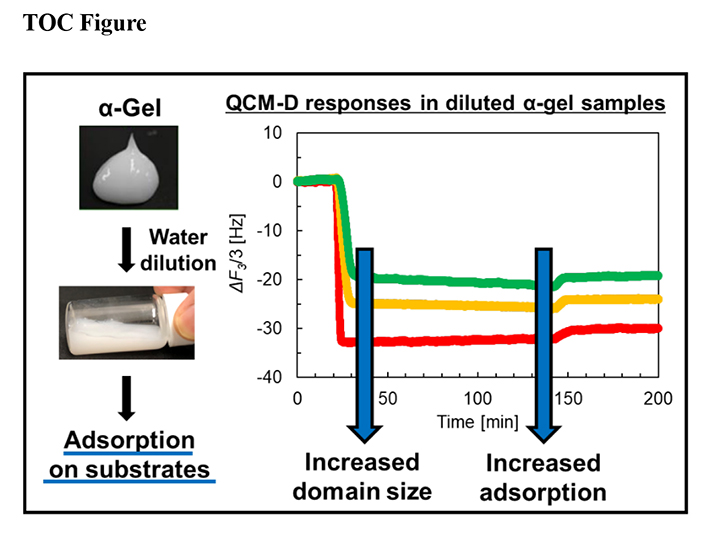 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1354K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1354K) -
Makoto Onoo, Koji Endo, Ken-ichi Iimura2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1253-1259
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
ジャーナル オープンアクセスCompression-induced formation of condensed-phase domains in adsorbed monolayers of alkylgalactosides (AGs) at the air/water interface was observed. When an aqueous solution of AGs was poured into a Langmuir trough, the AG molecules were spontaneously adsorbed from the solution at the air/water interface to form the adsorbed or Gibbs monolayer in an expanded, liquid-like phase at equilibrium. The monolayer was subsequently laterally compressed by the barriers of the trough, while simultaneously observing the system using a Brewster angle microscope (BAM). The surface pressure-film area isotherm upon compression showed a kink at a surface pressure (πkink) comparable to or several mN・m−1 higher than the surface pressure at the critical micelle concentration (πCMC), followed by a plateau region. BAM observations revealed that condensed-phase domains were formed in the homogeneous expanded phase at the plateau. Hence, the plateau corresponds to a first-order phase transition from the expanded phase to the condensed phase. As expected, the compressed adsorbed monolayer was in a metastable state because the surface pressure decreased with time, and the condensed-phase domains disappeared when compression was discontinued. The transient formation of a quasi-stable condensed phase may originate from the combined effect of the lower solubility of AG molecules in water, moderately strong attractive intermolecular interactions between AG molecules at the air/water interface, and high-rate compression.
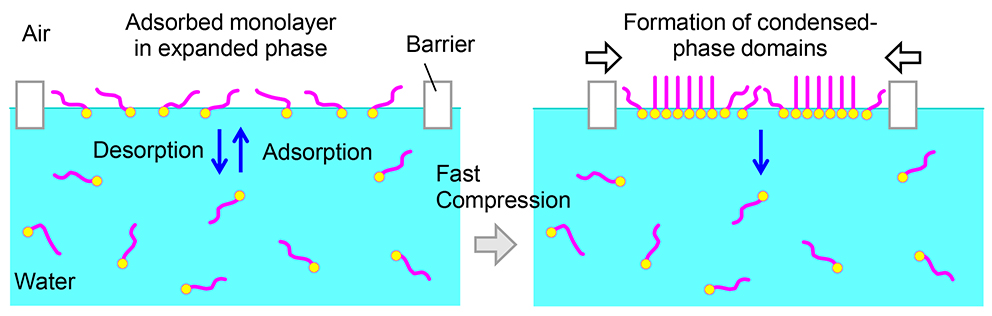 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (818K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (818K)
-
Jinhong Gao, Ruidan Wang, Xin Lu, Cong Jia, Qiang Sun, Jinian Huang, S ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1261-1274
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセスAs a valuable natural antioxidant, sesaminol can be used in food and medicine industries, but it is trace in sesame seeds and oil, and it is feasible to prepare sesaminol from sesaminol triglucoside (STG) which is abundant in defatted sesame cake. Therefore, in order to establish an effective enzymatic preparation method and elucidate the antioxidant structure-activity relationship of sesaminol, a suitable glycosidase for preparing sesaminol from STG were screened, enzymatic hydrolysis was optimized by single-factor test and response surface methodology, and finally, the structure-activity relationship of sesaminol was illustrated by comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). These results suggested that β-galactosidase was the optimal glycosidase for enzymatic hydrolysis of STG to prepare sesaminol. Under the optimal conditions of a reaction temperature of 50°C, reaction time of 4.0 h, pH of 5.5, substrate concentration of 1.0 mg/mL, and enzyme dosage of 20 mg/mL, the conversion rate of sesaminol was 98.88±0.67%. Sesaminol displayed excellent antioxidant ability in 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH, IC50 = 0.0011 mg/mL), 2,2’-azinobis-(3-ethyl-benzothiazoline-6-sulfonate) (ABTS, IC50 = 0.0021 mg/mL) radical scavenging activities and Ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP, 103.2998 mol/g) compared to other sesaminol derivatives. According to -log (IC50 of DPPH) and -log (IC50 of ABTS), CoMFA models were successfully established based on Q2 >0.5 (QDPPH 2 = 0.558, QABTS 2 = 0.534). The active site of sesaminol tended to be located on the hydroxyl group of the benzene ring (R1 position). A positive correlation between the bulky and positively charged groups at the 1H, 3H-furo [3, 4-c] furan group, the small, negatively charged groups at the R1 position and the antioxidant activity of sesaminol. This study provides an effective method to prepare sesaminol, reveals the structure-activity relationship of sesaminol and provides theoretical basis to design the novel compound.
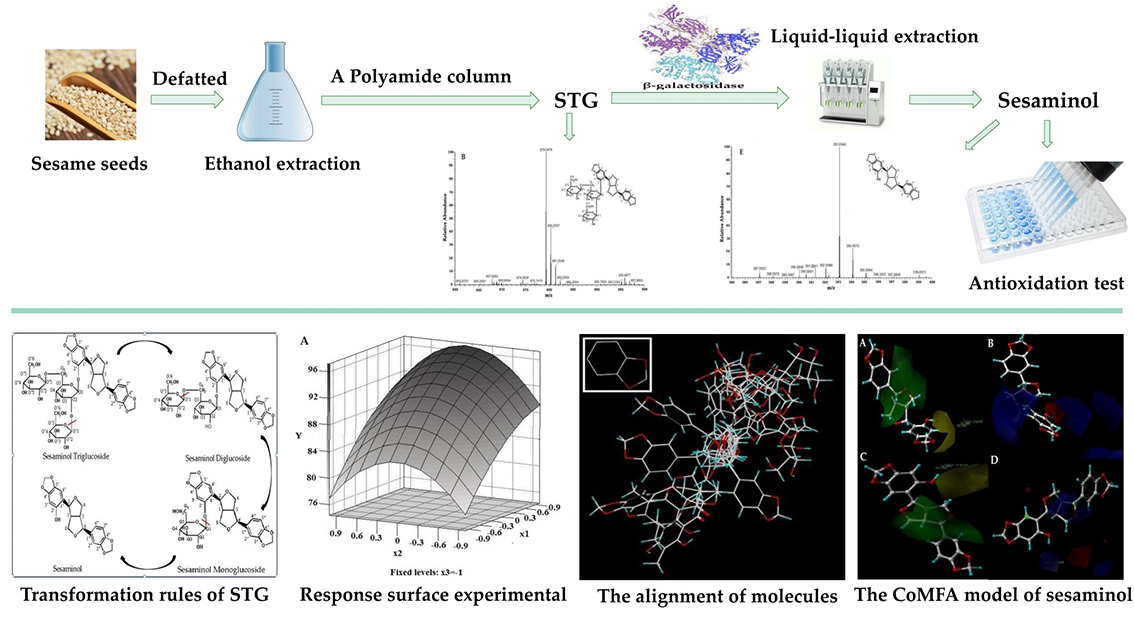 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2914K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2914K) -
Ahmet Gokhan Aggul, Parham Taslimi, Muslum Kuzu, Naim Uzun, Sinan Bilg ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1275-1283
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
ジャーナル オープンアクセスRecently, carbonic anhydrase (CA, E.C.4.2.1.1) inhibitors from natural product have paved the way for novel drug design in the treatment and prevention of some global diseases such as glaucoma, diabetes, and cancer. For this purpose, the inhibition effects of oleuropein and verbascoside from olive (Olea europaea L.) oil on human carbonic anhydrase I, and II (hCA I, and II) isoenzymes were evaluated in the current study. The inhibition effects of both natural compounds were determined by the esterase activity (in vitro). IC50 value of oleuropein and verbascoside was calculated as 1.57 and 1.73 µM for hCA I isoenzyme, respectively. At the same manner, K i values were determined as 1.25 ± 0.42 and 2.00 ± 0.42 µM, respectively. Then, IC50 value of each compound for hCA II isoenzyme was calculated as 2.23 and 1.90 µM, respectively. Similarly, K i values were determined as 2.37 ± 0.87 µM and 1.49 ± 0.33 µM, respectively. Also, the inhibitory effects and potent binding mechanisms of oleuropein and verbascoside on hCA I, and II isoenzymes were realized by molecular docking studies. Consequently, both natural phenolic compounds demonstrated the potent inhibition profiles against the both isoenzymes. Therefore, we believe that these results may break new ground in the drug development for the treatment of some global disorders.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2318K) -
Iram Liaqat, Sajida Naseem, Sana Eijaz, Uzma Hanif, Saima Rubab, Nauma ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1285-1293
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
ジャーナル オープンアクセスThis study aims at investigating the effects of cultured gut microbiota (GM) of obese human coupled high fat diet (HFD) or chow diet (CD) in development of obesity in mice. 20 stool samples were collected from obese patients and isolated bacteria were identified morphologically and biochemically. Identified isolates were mixed in equal proportions to synthesize obese GM. In vivo study was performed using obese GM combined with HFD/CD using mouse model for three months. Albino mice were treated with ampicillin from one week prior to birth until weaning of the pups at seven weeks of age and then inoculated with obese GM. Sixteen mice were divided into four groups: i.e. group 1 (G1) mice fed with CD, group 2 (G2) mice with HFD, group 3 (G3) mice with GM + HFD and group 4 (G4) mice with GM + CD. Mice from groups 3-4 were considered synthetic community (SC) mice due to transfer of synthesize human GM. 16S rRNA sequencing identified five abundant bacteria as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus sp., Escherichia coli, Morganella morganii, and Klebsiella oxytoca (accession numbers: MZ150742-MZ150746). In vivo study indicated that GM combination with either HFD/CD caused significantly increased body weight in SC mice (BMI; Kg/m2) compared to HFD or CD fed mice groups. One way ANOVA revealed highly significant increase (p ≤ 0.001) in levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides and low density lipoprotein (LDL) in GM coupled diet groups (G3-G4; SC mice) compared to significant increase in HFD group (G2) versus CD group (G1). Our study is first of its kind to report significant effects of using purified strains as obese GM plus diet (HFD/CD) in inducing obesity in SC mice and elevated serum liver parameters as metabolic indicators, hence providing strong evidence about significance of modified GM combination with HFD in developing obesity in SC mice.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (967K) -
Lifen Hou, Xiangyang Sun, Li Pan, Keren Gu2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1295-1306
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe nutritional and structural properties of phytosterols (PS)/phytosterol esters (PEs) facilitate their use as substitutes for cholesterol in liposome encapsulation systems designed for oral drugs and health products. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of phytosterol butyrate ester (PBE) on the properties of liposomes. PBE was encapsulated within liposomes (approximately 60 nm) prepared using soybean phosphatidylcholine using the thin-film hydration method. There was no significant change in the average particle diameter and zeta potential of these liposomal vesicles corresponding to the increasing amounts of encapsulated PBE. The incorporation of PBE increased the polydispersity index (PDI) independent of concentration. Additionally, we observed that the storage stability of PBE liposomes with uniform particle size and approximately spherical shape vesicle was better at low concentration. The results of Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy showed that PBE was positioned at the water interface, which increased the order of hydrophobic alkyl chains in the lipid membranes. The incorporation of PBE led to an increase in the trans conformation of hydrophobic alkyl chain and consequently, the thermal stability of liposomes, which was confirmed by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The results of powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis confirmed that PBE was present in an amorphous form in the liposomes. Additionally, the incorporation of PBE reduced the micropolarity of the lipid membrane. Thus, when preparing liposomes using thin-film hydration, the presence of PBE affected the characteristics of liposomes.
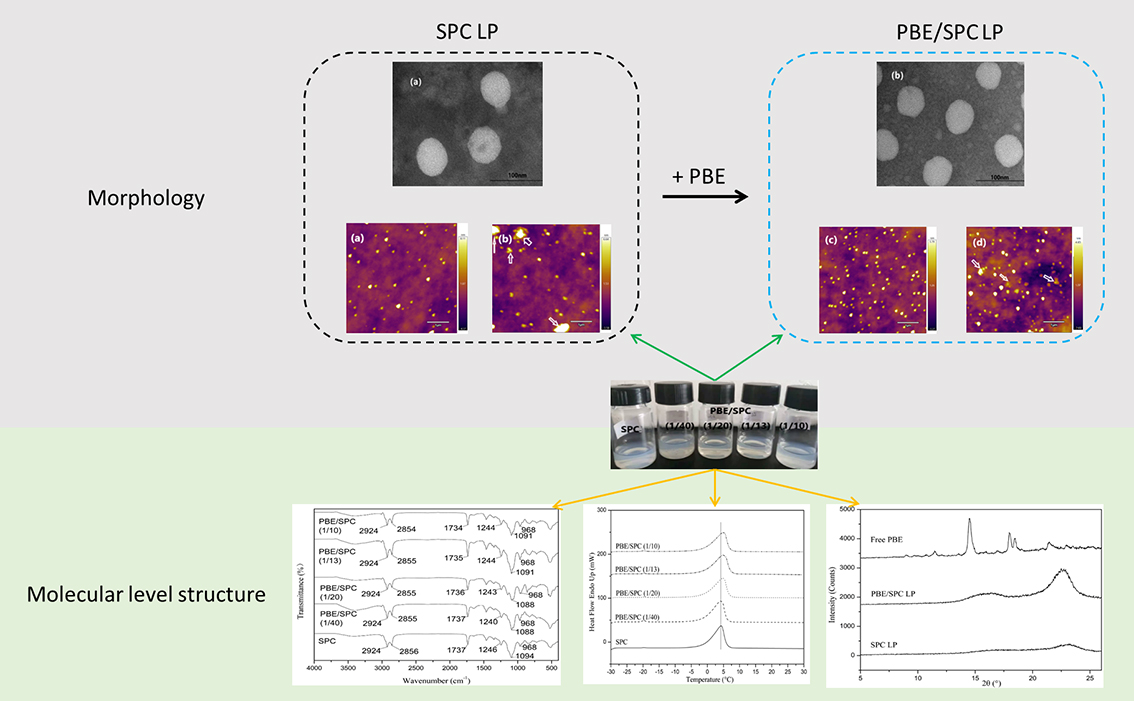 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1864K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1864K)
-
Chikako Kiyose, Haruka Takeuchi, Yoshimi Yabe, Tomoki Nojima, Mana Nag ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1307-1315
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe study aim was to evaluate the potential anti-inflammatory effects of vitamin E analogs, especially α-tocopherol and δ-tocopherol. We used male C57BL/6JJcl mice, which were divided into four groups: the control (C), high-fat and high-sucrose diet (H), high-fat and high-sucrose diet+α-tocopherol (Ha) and high-fat and high-sucrose diet+δ-tocopherol (Hd) groups. The mice were fed for 16 weeks. To the high-fat and high-sucrose diet, 800 mg/kg of α-tocopherol or δ-tocopherol was added more. The final body weight was significantly higher in the H group than in the C group. On the other hand, the final body weight was drastically lower in the Ha group and Hd group than in the H group. However, the energy intake was not significantly different among all groups. Therefore, we assumed that α-tocopherol and δ-tocopherol have potential anti-obesity effect. Besides, inflammatory cytokine gene expression was significantly higher in the epididymal fat of the H group than in the C group. These results showed that inflammation was induced by epididymal fat of mice fed a high-fat and high-sucrose diet for 16 weeks. Unfortunately, addition of α-tocopherol or δ-tocopherol to the diet did not restrain inflammation of epididymal fat. Investigation of the anti-inflammatory effects of α-tocopherol or δ-tocopherol in co-cultured 3T3-L1 cells and RAW264.7 cells showed that δ-tocopherol inhibited increased gene expression of the inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β, IL-6, and iNOS. These results suggest that an anti-inflammatory effect in the δ-tocopherol is stronger than that in the α-tocopherol in vitro. We intend to perform an experiment by in vivo sequentially in the future.
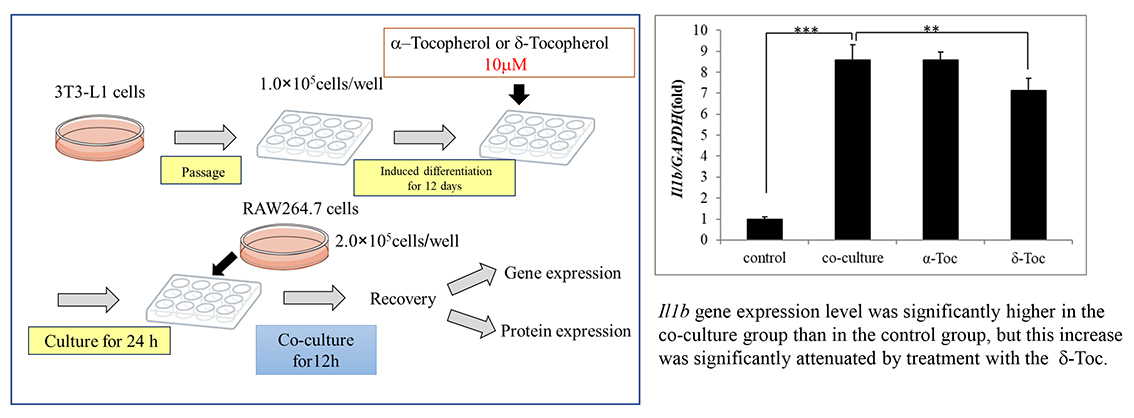 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1037K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1037K) -
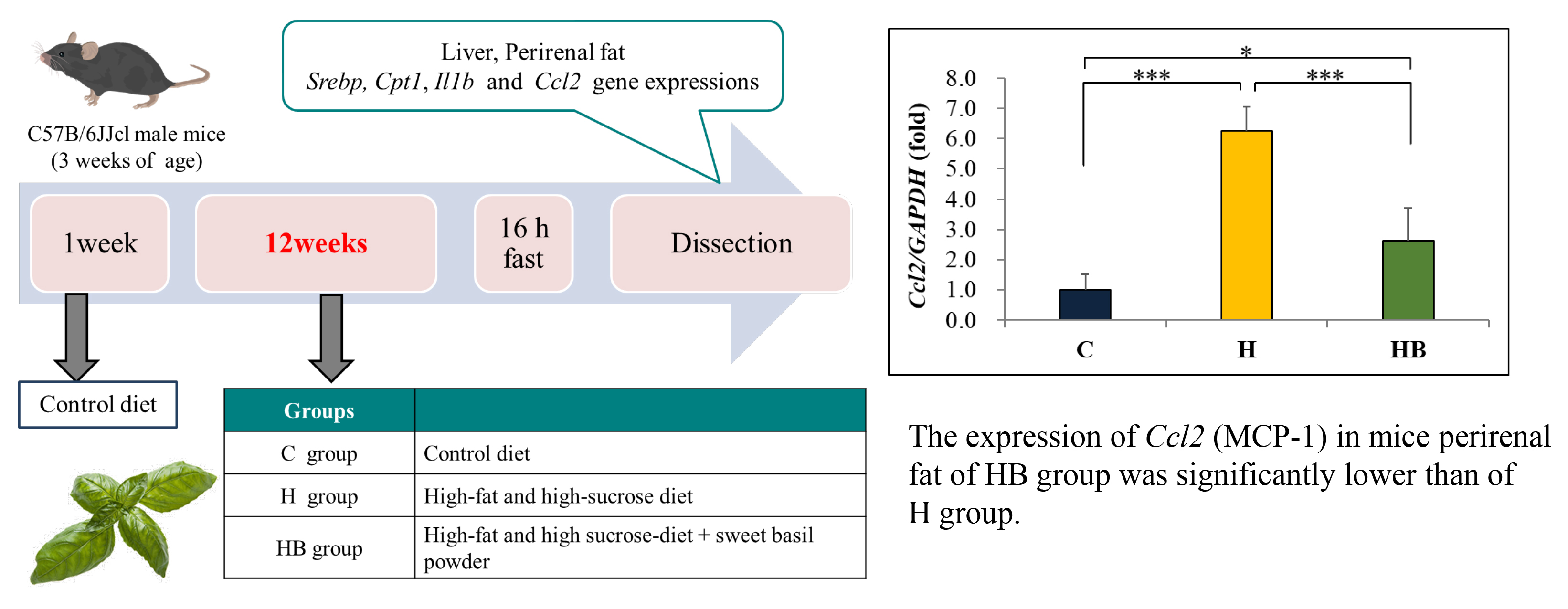
Chikako Kiyose, Haruka Takeuchi, Yoshimni Yabe, Tomoya Koike, Kazutaka ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1317-1323
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセスThis study aimed to determine if there are anti-inflammatory and anti-obesity effects of sweet basil, an herb, in mice. Sweet basil was administered as a powder to male C57BL/6JJcl mice, which were divided into three groups: the (control [C], high-fat and high-sucrose diet [H], and high-fat and high-sucrose diet plus sweet basil powder [HB]) groups. The mice were fed for 12 weeks and the dry sweet basil powder comprised 1% per kg of the diet. From experiment third week, the average body weight was significantly higher in the H group than in the C group. The average body weight was significantly lower in the HB group than in the H group, but food intake did not significantly differ between the H and HB groups. Liver weight was drastically lower in the HB group than in the H group. Perirenal fat weight and epididymal fat weight were not significantly different between the H and HB groups. Therefore, we assumed that body-weight reduction caused by sweet basil powder intake depended on inhibition of liver enlargement. We then examined lipid metabolism-related gene expression in the mice livers. Expression of the sterol response element binding protein 1-c gene tended to be lower in the HB group than in the H group (p=0.056). We speculated that sweet basil inhibited liver enlargement by suppressing fatty acid synthesis. Moreover, expression of the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene in epididymal fat was significantly lower in the HB group than in the H group. Sweet basil powder appears to have a potent anti-inflammatory effect in the adipose tissue of mice fed a high-fat and high-sucrose diet.
 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (752K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (752K) -
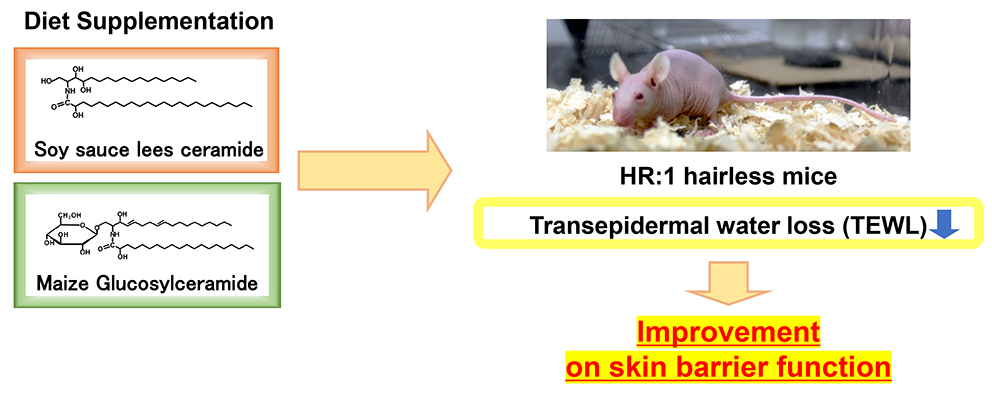
Kazushi Ohta, Shinobu Hiraki, Masakatsu Miyanabe, Tatsuro Ueki, Yuki M ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1325-1334
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセス
電子付録Dietary sphingolipids such as glucosylceramide and sphingomyelin are known to improve the skin barrier function of damaged skin. In this study, we focused on free-ceramide prepared from soy sauce lees, which is a byproduct of soy sauce production. The effects of dietary soy sauce lees ceramide on the skin of normal mice were evaluated and compared with those of dietary maize glucosylceramide. We found that transepidermal water loss value was significantly suppressed by dietary supplementation with soy sauce lees ceramide as effectively as or more effectively than maize glucosylceramide. Although the content of total and each subclass of ceramide in the epidermis was not significantly altered by dietary sphingolipids, that of 12 types of ceramide molecules, which were not present in dietary sources, was significantly increased upon ingestion of maize glucosylceramide and showed a tendency to increase with soy sauce lees ceramide intake. In addition, the mRNA expression of ceramide synthase 4 and involucrin in the skin was downregulated by sphingolipids. This study, for the first time, demonstrated that dietary soy sauce lees ceramide enhances skin barrier function in normal hairless mice, although further studies are needed to clarify the molecular mechanism.
 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1143K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1143K)
-
Ahmed Hamd, Aftab Aslam Parwaz Khan, Mohamed Shaban, Hadi M Marwani, A ...2021 年70 巻9 号 p. 1335-1341
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/08/06ジャーナル オープンアクセスTo overcome the key challenges associated with cement dust, such as inhalable size, toxic ions, and the existence of large quantities of useless materials, researchers investigated an innovative and unusual conversion of toxic cement dust into Mayenite nanoparticles. Mayenite is a natural structure that can be used as a filler in a variety of industrial applications. The formation of Mayenite nanoparticles was achieved through a thermal reaction at 1000°C for 2 h between cement dust and aluminum oxide. Different techniques were used to characterize the synthesized Mayenite nanoparticles, revealing the formation of the target phase as well as the reduction of toxic ions present in cement dust. According to Scherrer’s equation, the crystallite size of bypass and synthesized Mayenite nanoparticles is 45 and 30 nm, respectively. Also, with the aid of TEM analysis, the particle size distribution of the produced Mayenite nanoparticles was found to be 27±7 nm. The toxic ions, especially chlorides and sulphates, were reduced by 86% and 50%, respectively, according to X-ray fluorescence results. These findings are important for the future use of Mayenite, 12CaO.7Al2O3 (C12A7), nanoparticles formed from toxic cement dust recycling.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3042K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|