
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Xinyi Cheng, Yaqi Huang, Zhuangzhuang Yang, Tong Wang, Xiaosan Wang2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 599-606
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセスPalmitoleic acid shows a variety of beneficial properties to human health. In this study, enrichment of palmitoleic acid from sea buckthorn pulp oil by two-step solvent crystallization and molecular distillation was investigated. Sea buckthorn pulp oil was first converted to its corresponding mixed fatty acids (SPOMFs) containing 27.17% palmitoleic acid. Subsequently, the effects of various factors on crystallization (i.e., crystallization temperature, type of solvent, ratio of SPOMFs to solvent (w/v), crystallization time) and molecular distillation (distillation temperature) were assessed on a 5-g scale. It was found that optimal primary crystallization conditions were a 1:15 ratio of SPOMFs to methanol (w/v), -20°C and 12 h. Secondary crystallization conditions were set to a 1:4 ratio of methanol to palmitoleic acid product obtained from the first step crystallization to methanol (w/v), -40°C and 6 h. For further purification of palmitoleic acid by molecular distillation, the optimal distillation temperature was determined to be 100°C. After purification by crystallization and molecular distillation under the optimal conditions, the final product consisted of 54.18% palmitoleic acid with an overall yield of 56.31%. This method has great potential for adoption by the food and medical industries for the preparation of palmitoleic acid concentrate for nutritional studies.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (396K) -
Fahad Y. Al-Juhaimi, Kashif Ghafoor, Mehmet Musa Özcan, Nurhan Uslu, E ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 607-613
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe oil recovery from Alyanak apricot kernel was 36.65% in control (unroasted) and increased to 43.77% in microwave-roasted kernels. The total phenolic contents in extracts from apricot kernel were between 0.06 (oven-roasted) and 0.20 mg GAE/100 g (microwave-roasted) while the antioxidant activity varied between 2.55 (oven-roasted) and 19.34% (microwave-roasted). Gallic acid, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, (+)-catechin and 1,2-dihydroxybenzene were detected as the key phenolic constituents in apricot kernels. Gallic acid contents varied between 0.53 (control) and 1.10 mg/100 g (microwave-roasted) and 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid contents were between 0.10 (control) and 0.35 mg/100 g (microwave-roasted). Among apricot oil fatty acids, palmitic acid contents ranged from 4.38 (oven-roasted) to 4.76% (microwave-roasted); oleic acid contents were between 65.73% (oven-roasted) and 66.15% (control) and linoleic acid contents varied between 26.55 (control) and 27.12% (oven-roasted).
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (247K) -
Aysun Yurdunuseven Yıldız, Hakan Karaca2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 615-632
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe skin of the walnut kernels can get dark during the pre- and post-harvest stages of the production. Dark kernels are less palatable for most consumers but are still edible and maybe preferable, especially in the ground form, for industrial use. In this study, we investigated the differences between oil oxidation indexes, fatty acid and tocopherol compositions of the oils, total polyphenol contents and antioxidant capacities of the extracts of light and dark walnuts. In addition, we evaluated the effects of packaging under nitrogen and vacuum-packaging techniques and storage temperature on these characteristics of both light and dark walnuts during storage for 6 months. Peroxide values and free fatty acid contents of all samples were higher at the end of storage compared to initial values, being more noticeable at 20°C than at 4°C. Increases in the free fatty acid contents were quite higher in dark walnuts than the light ones (6.1 and 3.1 fold, respectively) and the highest values of conjugated diene and peroxide were determined in the samples packaged under air and stored at 20℃. Dark walnuts had lower total phenolic, α- and γ-tocopherol contents and antioxidant activities compared to the light ones. Total phenolic and tocopherol contents decreased over time. We conclude that due to the antioxidant compounds in the fruit, oxidation parameters of dark walnuts are still acceptable at the end of 6-month storage even in the packages with air and at non-refrigerated conditions.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1516K) -
Jose Antonio Fermin Jimenez, Yayoi Miyagawa, Hidefumi Yoshii, Shuji Ad ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 633-635
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe major polyunsaturated fatty acids in krill oil extracted from Euphausia pacifica, known as Isada on the Sanriku coast, are eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic (DHA) acid. A kinetic model was proposed to explain the relationship between the fractions of unoxidized EPA (Y E) and unoxidized DHA (Y D) in the oil spray-dried with maltodextrin and stored at 25, 50, and 70℃. The relationship between Y E and Y D during storage was independent of the temperature and could be expressed using the proposed model. This indicated that the oxidation of EPA and DHA in krill oil was interdependent.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (264K)
-
Muhammad Nurdin, Haznan Abimanyu, Muhammad Naufalsar, Maulidiyah Mauli ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 637-645
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe objective of this study was to obtain optimization results from the biological hydrolysis of Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches (OPEFB) using Aspergillus niger (A. niger) BIOTROP 2173 isolated from grain. Optimized hydrolysis parameters include temperature, pH and time. The hydrolysis process was carried out by growing A. niger on OPEFB powder (± 30 mesh) through two schemes, namely hydrolysis on OPEFB pretreatment with 10% NaOH and hydrolysis on OPEFB non-pretreatment. The optimization results show that the best hydrolysis process of A. niger BIOTROP 2173 occurs in OPEFB pretreatment. The optimum conditions for temperature, pH and time obtained are 40°C, 6 and 24 hours, respectively. Although the amount of reducing sugar produced was lower than the OPEFB non-pretreatment, the performance of the cellulase enzyme during the hydrolysis process of OPEFB pretreatment was very good, with a fast hydrolysis rate. These results indicate that the performance of A. niger BIOTROP 2173 in the hydrolysis process is influenced by the pretreatment stage. The optimum conditions obtained then became a reference in the production of reducing sugar based on A. niger BIOTROP 2173. The amount of reducing sugar produced from OPEFB pretreatment was 0.94 mg.mL-1, while for OPEFB non-pretreatment was 15.83 mg.mL-1.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1755K) -
Yumiko Yamawaki, Taeko Mizutani, Yuri Okano, Hitoshi Masaki2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 647-655
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセスAlthough extracellular carbonylated proteins (CPs) are found at higher levels in sun-exposed skin, their impact on the cellular functions of fibroblasts and their involvement in the progression of photoaging skin are not fully clarified. In our previous study, we reported that extracellular CPs increase levels of intracellular oxidative stress and result in the accumulation of newly synthesized CPs in normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF). Furthermore, fibroblasts exposed to CP-BSA, which is a model of extracellular CPs, had upregulated expression levels of mRNAs encoding matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and interleukin-8/CXCL8 (IL-8/CXCL8). These facts suggested the possibility that extracellular CPs induce a fragile structure in the dermis through the degradation of collagen and elastin. The purpose of this study was to characterize the efficacy of natural carotenoids, such as astaxanthin analogs, produced by Hematococus pluvialis (CHPs) to improve the impaired functions of fibroblasts exposed to CPs. CHPs suppressed the intracellular CP levels elevated by CP-BSA, restored mRNA expression levels of factors involved in the formation and assembly of collagen and elastin fibers and improved the formation of those fibers impaired by CP-BSA. We conclude that CHPs function as antiaging substances due to their restoration of the impaired formation of collagen and elastin fibers caused by extracellular soluble CPs.
 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2685K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2685K) -
Li He, Feng-Jiao Zhang, Hao-Yun Li, Lei Li, Li-Ge Song, Yu Mao, Jing L ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 657-664
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセスDiabetes mellitus (DM) is a hyperglycemia-related multifactorial condition with an elevated risk of microvascular and microvascular complications associated with this disease. The current experimental study was to examine the antidiabetic activity of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced adropin against diabetic rats by altering the PI3K/Akt and insulin signaling pathways. STZ (60 mg/kg) was used for the induction of DM and rats were divided into different groups and received the adropin (20, 40 and 80 mg/kg) and glibenclamide (10 mg/kg) till 28 days. Body weight, plasma insulin, blood glucose and food intake were estimated, respectively. Biochemical enzymes, carbohydrate enzymes, lipid parameters, AMPK and insulin signalling pathway parameters were estimated. GLUT4 and PPARγ expression were also estimated. Oral administration of adropin significantly (p < 0.001) increased the glycogen, glucose-6-phosphatase dehydrogenase, insulin, hexokinase and belittled the blood glucose level, fructose 1-6-biphosphatase, glucose-6-phosphatase at dose dependent manner. Adropin significantly (p < 0.001) reduced the level of triglyceride, cholesterol, low density lipoprotein, very low density lipoprotein and increased the level of high density lipoprotein at dose dependent manner. Adropin significantly (p < 0.001) activated the Akt, IRS-2, IRS-1, IR, p-AKT and PI3k, which are the key modulator molecules of PI3K/Akt, AMPK and insulin signalling pathway in DM rats. The current experimental study confirms the anti-diabetic effect of adropin on DM rats induced by AMPK and insulin signalling pathway against STZ.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1613K) -
Xiangmei Yao, Xuezhong Gu, Song Jin, Keqian Shi, Xiaoli Gao, Qi Wang, ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 665-673
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセスCancer is the world’s biggest health problem and cancer-induced mortality happened all over the planet after the heart disease. The present study was to scrutinize the anti-leukemia effect of diosmin against Dalton Ascitic Lymphoma (DAL) induced leukemia in mice. DAL cell was used for induction the solid tumor. Body weight, life spans, tumor volume and mean survival time was estimated. Antioxidant, biochemical and pro-inflammatory cytokines were estimated. Diosmin showed the cell viability effect at dose dependent manner against the both cell lines. DAL induced solid tumor mice showed the decreased body weight, mean survival days, non viable cell count and increased the tumor volume, viable cell count and diosmin significantly (p < 0.001) reverse the effect of DAL. Diosmin significantly (p < 0.001) altered the hematological, differential leukocytes, antioxidant, biochemical, pro-inflammatory cytokines at dose dependently. Collectively, we can say that diosmin might alter the DAL induced abnormality via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1037K) -
Jin Liu, Weiming Wang, Limin Chen, Yachai Li, Shuimiao Zhao, Yijuan Li ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 675-683
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセスCyclophosphamide (CP) is very well-known anticancer drug and commonly used against various cancers. CP therapy is related to female ovarian cancer and causes female infertility. The ovarian cancer associated with the increase oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction. Syringic acid (SA) is very well phyto-constituent and already proof antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects on various diseases. We investigated the chemoprotective impact of SA on CP mediated ovarian damage, and the underlying mechanism. CP (75 mg/kg) was used to cause ovarian damage and rats were randomly divided into separate groups and received a different dose of SA for 14-day. Body weight, food and water intake were determined. Ovarian weight and tumor index was measured. Antioxidant parameters were determined in the serum and ovarian tissue. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, apoptosis parameters and inflammatory mediators were estimated in the serum. Hormonal parameters and Histomorphometry were estimated. Dose dependently treatment of SA significantly (p < 0.001) decreased the levels of biochemical parameter such as nitric oxide (NO), myeloperoxidase (MPO) and augmented the antioxidant parameters include catalase (CAT), glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) level in serum and ovarian tissue. SA treatment significantly (p < 0.001) suppressed the level of luteinizing hormones (LH), anti-mullerian hormone (AMH), estradiol (E2) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) as well as ovarian follicles. SA significantly (p < 0.001) down-regulated cytokines, inflammatory mediator and caspase-3 parameters. Taken altogether, we conclude that SA considerably reduced ovarian damage via reduced oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1085K)
-
Liangzhen Gu, Yanan Zhang, Shuang Zhang, Haijun Zhao, Yuan Wang, Dongf ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 685-696
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセス
電子付録The lipid metabolism disorder is the key role of Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Selenoprotein P plays an important role in the pathological process of lipid accumulation. Coix lacryma-jboi seed oil (CLSO) is an active component extracted from Coix lacryma-jobi seed (CLS) which has been found to be effective of reducing blood fat and antioxidative. But the effect and mechanism of CLSO on NAFLD are not clear. The aim of this study was to explore the therapeutic effect and mechanism of CLSO in the treatment of NAFLD. Our result showed that CLSO decreased the liver/body weight ratio, lowered the total cholesterol (TC) and triacylglycerol (TG), and elevated the high density lipoprotein (HDL) in serum. CLSO reduced the lipid deposition in the liver of NAFLD rats. In addition, CLSO could bring down the abnormal expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA). Moreover, CLSO significantly declined the liver apolipoprotein E (apoE), apolipoprotein E receptor (apoER) and selenoprotein P 1 (SePP1) expression. In vivo, CLSO decreased the lipid droplets and TG level, reduced the protein expression of SePP1, apoER, phosphor-adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK) in the cytoplasm of HepG2 cells induced by oleic acid and palmitic acid (OP). At the same time, lipid accumulation was observed in the Sepp1 high expression cells induced by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) activator tunicamycin (Tm). CLSO could identically reduce the protein expression of SePP1, apoER, p-AMPK in the cytoplasm of HepG2 cells induced by Tm. This result not only proved the CLSO had therapeutic effect on NAFLD, but also confirmed its mechanism associated with degrading the phosphorylation of adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) which led to the decrease of the expression SePP1/apoER2 in order to reduce lipid accumulation. The study suggests CLSO has great medicinal value in treating NAFLD besides its edibility.
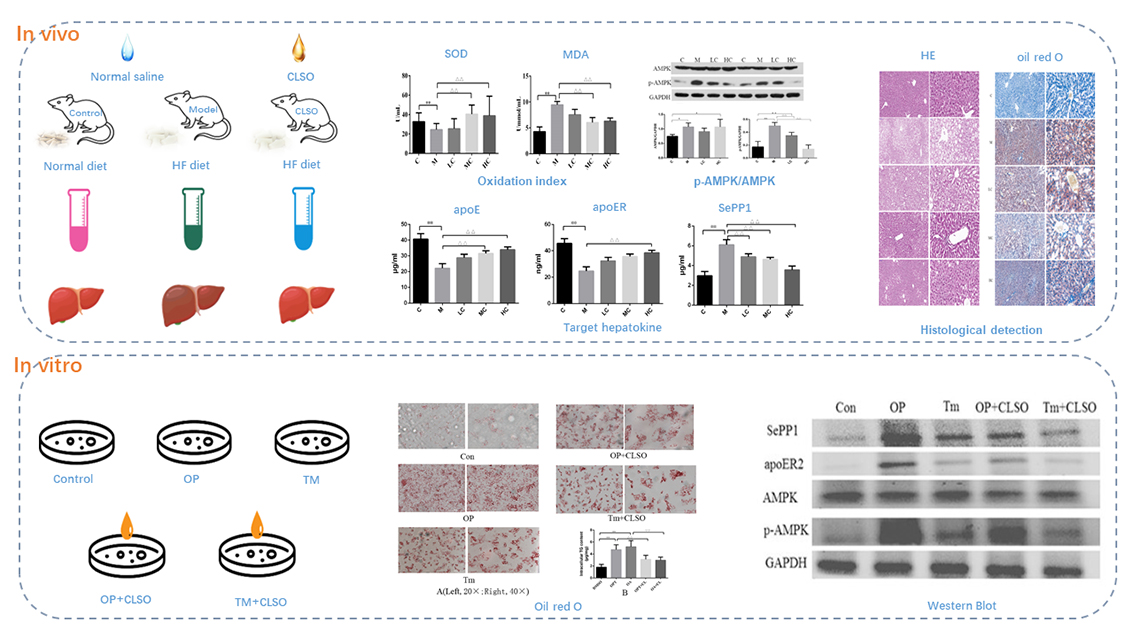 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4170K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4170K)
-
Mayu Hibi, Sakura Sugiura, Tomoyuki Nakagawa, Takashi Hayakawa, Masaya ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 697-702
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセスWe examined effects of a major lipotrope, myo-inositol, on the expression of primary glycolytic (glucokinase and phosphofructokinase) and fructolytic enzyme (ketohexokinase [KHK] and aldolase B) genes in the livers of rats fed a control diet, high-sucrose diet, or high-sucrose diet supplemented with 0.5% myo-inositol for 14 d. Supplementation with myo-inositol decreased the hepatic expression of fructolytic enzyme genes, but not that of glycolytic enzyme genes, and the levels of triglycerides, fatty acid synthase, and KHK proteins in high-sucrose diet-induced fatty liver. The study results suggest that myo-inositol represses primary fructlysis, but not glycolysis, in high-sucrose diet-induced fatty liver.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (326K) -
Ryota Hosomi, Toshifumi Tanizaki, Shintaro Ikawa, Tadahiro Tsushima, Y ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 703-712
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセス
電子付録The effects of 6,9,12,15-hexadecatetraenoic acid (C16:4n-1, HDTA), an n-1 polyunsaturated fatty acid (FA), on plasma and liver lipid content and distribution in blood and tissues were investigated. Mice were fed experimental diets containing 10% HDTA or eicosapentaenoic acid in ethyl ester form based on corn oil for four weeks. Dietary HDTA intake lowered plasma triacylglycerol content without affecting plasma total cholesterol content. HDTA barely accumulated in the epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT), while C18:4n-1, an HDTA metabolite, was detected in small amounts (< 1% of total FAs) in the plasma, liver, and eWAT.
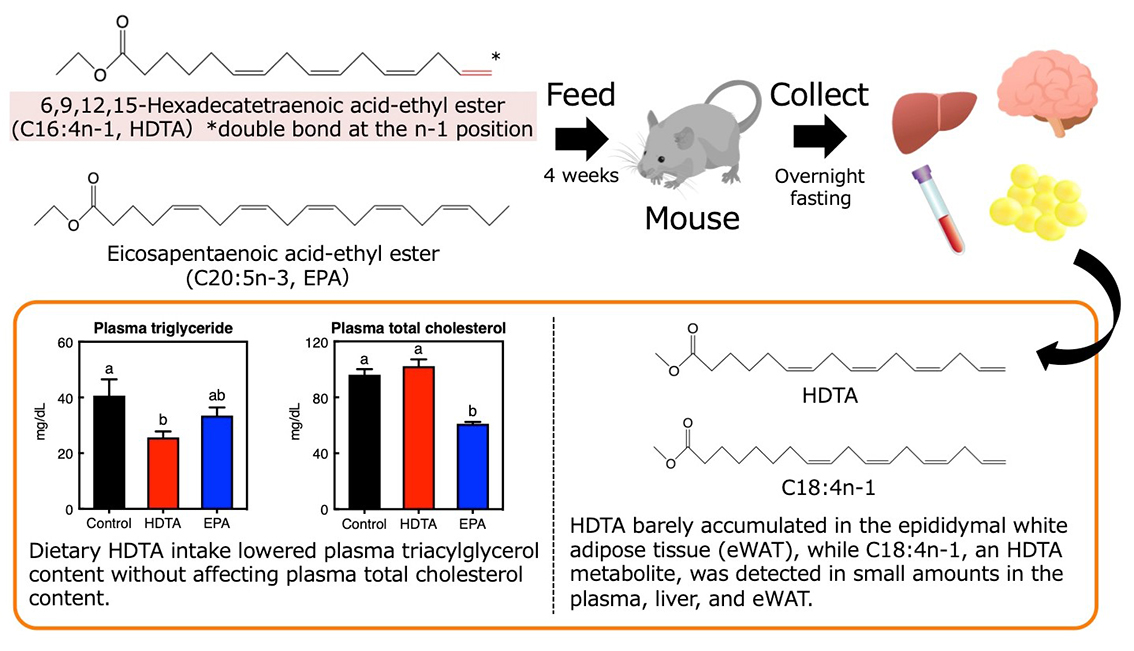 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2006K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2006K)
-
Lina M. Barhoumi, Reem N. Dabaibeh, Hala I. Al-Jaber, Safwan M. Obeida ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 713-719
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe volatile principles emitted from different aerial organs of two S. palaestina Benth. populations (Mediterranean (Med) and Irano-Turanian (IrT)) growing wild in Jordan were extracted by Solid Phase Micro-Extraction (SPME) and analysed by GC/MS technique. Sesquiterpene hydrocarbons dominated stems (59.38%, 49.67%) and leaves (93.28%, 32.39%) emissions from Med and IrT zones, respectively while monoterpene hydrocarbons had the major contribution to the aroma of pre-flowering buds (78.62%, 74.96%), opened flowers (76.12%, 59.99%) and petals (69.57%, 54.28%) and were mostly represented by sabinene (in Med zone) and ociemene isomers (Z & E) in IrT zone. Multivariate analysis classified the two populations into two different clusters based on their origin and indicated the occurrence of two ecotypes of this species. Different organs from the same collection site showed emission profiles of similar chemical composition.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2213K)
-
Kazuhiro Yamaguchi, Masahiro Maeda, Hitoshi Masaki, Tokuro Iwabuchi2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 721-730
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe performance of sunscreen products depends on their ultraviolet (UV) absorption ability through the film formed on the skin surface upon their application. Therefore, it is important that a uniform film is formed on the uneven skin surface for effective sunscreen performance. Because most UV filters are oil soluble, we hypothesized in this study that increasing the viscosity of the oil phase of a sunscreen product can improve the performance of the sunscreen. We first examined the association between the concentration of the oil thickener and the UV absorption ability of the sunscreen product using a skin-mimicking substrate (SMS). Among all thickeners examined (petrolatum, dextrin palmitate, silica silylate, and organoclay), organoclay and silica silylate significantly increased the UV absorbance of sunscreen on the SMS in a concentration-dependent manner. Thereafter, we examined film uniformity to elucidate the mechanism underlying the observed increase in UV absorption. The uniformity of film thickness on the SMS increased with increasing organoclay content, based on decreased standard deviations of film thickness. Our results showed that increasing the viscosity of the oil phase with organoclay resulted in the formation of a uniform film by preventing the sunscreen from flowing into the grooves when applied on the SMS, thereby increasing UV absorbance by more than two-fold that of sunscreen without organoclay. Thus, the use of thickeners, such as organoclay, increases the viscosity of the oil phase at a low shear rate after the high shear of application. This is an effective strategy for improving the overall quality and performance of sunscreen products.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1312K) -
Kazuaki Yoshinaga, Yota Mizuno, Samanthika Senarath, Aya Yoshinaga-Kir ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 731-736
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/04/12ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe n-3 type polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3PUFAs), including eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), from fish oil exhibit health benefits such as triacylglycerol- and cholesterol-lowering effects. Some pelagic fishes contain long-chain monounsaturated fatty acids (LC-MUFAs) such as eicosenoic acid (C20:1), which exert health-promoting effects. However, no study has evaluated beneficial effects of n-3PUFA and LC-MUFA combination. Here, we investigated effects of simultaneous treatment with n-3PUFA (EPA and DHA) and LC-MUFA (cis-5-C20:1 and cis-7-C20:1) and found that n-3PUFA and LC-MUFA combination significantly decreased lipid accumulation and reduced total cholesterol in HepG2 cells. Cholesterol level was significantly lower in DHA + cis-7-C20:1 group than in DHA + EPA group. These results suggest the importance of LC-MUFA as a functional molecule in fish oil.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (379K) -
Satoshi Horikoshi, Satoshi Yamazaki, Yuhei Arai, Daisuke Sakemi, Masah ...2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. 737-743
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2021/05/01
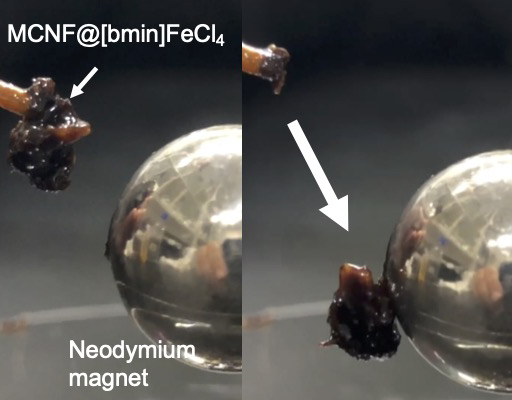
ジャーナル オープンアクセスThe present study focused on coupling cellulose nanofibers (alternative materials for plastics and metals) with a magnetic ionic liquid (synthesized by a microwave-assisted method) through mixing to yield magnetic cellulose nanofibers (MCNFs) that can be recycled by attracting them to a magnet. Accordingly, two types of ionic liquids were synthesized: (a) 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate(III) {[bmim] FeCl4} and (b) 1-glycidyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate {[glmi]FeCl4}, which were characterized by the fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry (FAB−MS) technique. Impregnation of the cellulose nanofibers with the {[bmim]FeCl4} ionic liquid caused the latter to be physically adsorbed onto the nanofibers to produce {MCNF@{[bmim]FeCl4}, whereas the corresponding {[glmi]FeCl4} ionic liquid was chemically bonded to the cellulose nanofibers to yield magnetic {MCNF@[glmi]FeCl4} nanofibers. Under the experimental conditions used, the corresponding magnetic moments were 0.222 A m2 kg-1 for {MCNF@ {[bmim]FeCl4} and 0.095 A m2 kg-1 for {MCNF@[glmi]FeCl4}.
 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1732K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1732K)
-
2021 年 70 巻 5 号 p. e1-
発行日: 2021年
公開日: 2022/01/21
ジャーナル オープンアクセスPDF形式でダウンロード (126K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|