
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Yuwei Chen, Yongbo She, Ramandeep Kaur, Na Guo, Xiaohua Zhang, Ruisan ...2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 811-816
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/08/14ジャーナル フリー HTMLCardiovascular disease (CVD) has emerged as the leading cause of dealth worldwide today. Lowering circulating total cholesterol (TC) and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) is one of the most effective approaches of CVD prevention. Dietary guidelines and health organizations approved using plant sterols (PS) as the alternative to conventional method in attenuating circulating TC and LDL-C levels and risk of CVD. However, current findings apprear to be controversial on the efficacy of PS. Giving the rise of the field “Nutrigenetics", single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) such as CYP7A1-rs3808607 have been identified that strongly associate with cholesterol metabolism in response to PS intake, towards causing inter-individual variations. This review article aims to discuss the efficacy of dietary PS in managing cholesterol levels based on findings from recent studies. The scope includes reviewing evidence on supporting the efficacy, the metabolic claims, inter-individual variations as well as sitosterolemia associated with PS intake.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (441K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Songul Kesen2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 817-826
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/08/14ジャーナル フリーIn this study virgin olive oil obtained from cv. Nizip Yaglik (NY) was adulterated with different proportions (5 and 10%, v/v) of cotton (CO) and sunflower (SO) oils. Fatty acid and sterol profiles of olive oil were analyzed by using gas chromatography (GC). Also, difference of Equivalent Carbon Number 42 values (ΔECN42) of oil samples were determined by using GC and HPLC. Due to results of fatty acids analysis, the percentage of oleic acid was decreased when CO and SO were added. Palmitic acid was increased over the addition of CO, and decreased with the addition of SO. The ΔECN42 values were increased in adulterated oils. These values showed further increase in adulterated oils with SO. Beta-sitosterols decreased to 91.06 and 88.54% when mixed with 5 and 10% SO, respectively. On the other hand, decline was negligible when mixed with CO. According to principal component analyses (PCA), pure NY and adulterated oils were clearly separated in different parts of screen plot according to fatty acids, triacylglycerol (TAGs) and sterol profile. The outcomes of this first investigation provide valuable information for about the differences of fatty acids, ΔECN42 values and sterol compounds between Turkish olive oil from Nizip Yaglik cv. and its adulteration with cotton and sunflower oil. It was observed that fatty acids are not very effective in detecting adulteration of NY oil, but ΔECN values, sterols and Rmar values can be used to detect adulteration of NY olive oil.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (863K) -
Bingyu Jing, Wenjie Chen, Mengzhu Wang, Xiaohui Mao, Jia Chen, Xiuzhu ...2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 827-835
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/08/14ジャーナル フリー
電子付録Fifty traditional Tibetan ghee (TTG) varieties were collected and analyzed their systematic characteristic indices, including physicochemical parameters, minerals, fatty acid composition, and thermal behavior. Results show that TTG contains a large amount of fat (71.68%–93.3%) and a small quantity of protein (0.51%–1.81%). The acid and peroxide values of TTG vary from 0.02 to 1.30 mg/g and 0.07 to 5.93 meq/kg, respectively. The content of minerals varied with altitude level and region significantly (p < 0.05), and the regional variations of fatty acids in TTG were also observed significantly, these differences may be due to the high unsaturated fatty acids level in the cow diets.
 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (924K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (924K)
-
Asami Miyajima, Ryo Inoue, Erika Onishi, Miyuki Miyake, Ryo Hyodo2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 837-845
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/08/14ジャーナル フリーProducing structural viscosity in colloidal dispersions, such as vesicles and capsules, prevents separation of dispersed particles by increasing the viscosity between them, which is advantageous in terms of usability. So far, the separation behavior of various particles has been studied; however, there are very few examples wherein a stable dispersion state was constructed and controlled. In this study, we produced stable dispersions induced by the depletion effect in mixtures of vesicles of cationic surfactant derived from triethanolamine-based esterquat (TEQ) and a specific dextrin derivative (SDD) as a non-adsorptive polymer. In the composition region, where 8 to 16% of TEQ vesicles and 1.2% or less of SDDs were mixed, the viscosity increased proportionally with the particle concentration, and it was observed that stable dispersions were produced by structural viscosity. Furthermore, the effects of TEQ and SDD concentrations, and SDD size on the structural viscosity and cohesive energy were investigated, which were similar to the depletion effect in the Asakura–Oosawa (AO) theory. From the results, it was suggested that the structural viscosity of the mixed dispersions (TEQ vesicles and SDDs) was produced by the aggregated TEQ vesicle networks induced by the depletion flocculation.
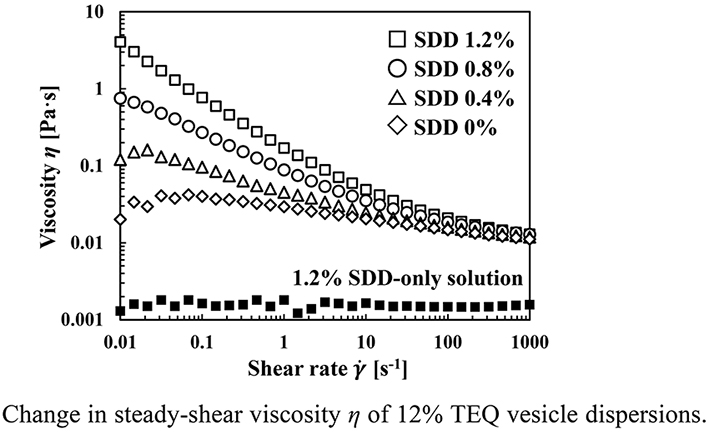 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1062K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1062K) -
Keisuke Matsuoka, Yuka Nakatani, Tomokazu Yoshimura, Tsubasa Akasaki2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 847-854
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
ジャーナル フリーMetal nanoparticles have the ability to remove superoxide via changes in the surface electronic states at the large surface area. Gold, silver, and platinum nanoparticles were prepared in the presence of three sugar-based nonionic surfactants using NaBH4 as a reducing agent. The surfactants (glycosyloxyethyl methacrylate: xGEMA) contain sugar oligomers of various lengths (x), are biodegradable, and act as protecting groups for the nanoparticles. Three types of xGEMA were used: dodecyl and hexadecyl chains containing amphiphilic oligomers (C12-3.0GEMA and C16-3.2GEMA) and multi-dodecyl chain with multiple sugar side chains (1.8C12-4.7GEMA). We found that the type of nonionic surfactant affected the size of the nanoparticles. The average size of the gold, silver, and platinum nanoparticles ranged from 1.9 to 6.6 nm depending on the surfactant. The trend in the size of gold nanoparticles in relation to the chosen surfactants was different from that for the silver and platinum nanoparticles. Moreover, the gold nanoparticles did not show effective antioxidant activity for superoxide, whereas the silver and platinum nanoparticles removed superoxide to a certain extent. The general order for superoxide scavenging activity increased in the following order: gold < platinum < silver. In particular, the largest size of silver nanoparticles capped with C16-3.2GEMA had a similar ability for the removal of superoxide as superoxide dismutase (ca. 3999 unit/mg) on the basis of the mass concentration.
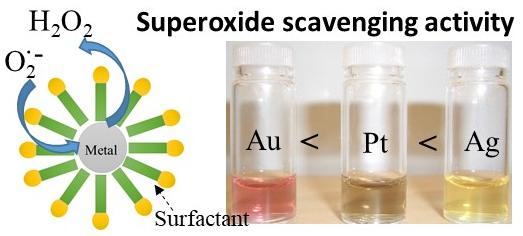 graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1291K)
graphical abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1291K) -
Youichi Takata, Yuka Ohtsuka, Takumi Ashida2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 855-861
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/08/14ジャーナル フリーWe investigated the solubilization behavior of the hydrocarbon surfactant lithium dodecyl sulfate (LiDS) and the fluorocarbon surfactant lithium 1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,8-heptadecafluoro-1-octanesulfonate (LiFOS) in an aqueous solution to determine the controlled release mechanism of solubilizate. The LiDS system solubilized Sudan III, a hydrocarbon compound, whereas the LiFOS system did not, because of the immiscibility of the hydrocarbon and fluorocarbon compounds. The solubilization ability of the LiDS and LiFOS mixtures gradually decreased with increasing LiFOS bulk composition because the micelles mainly composed of LiDS transformed into micelles mainly composed of LiFOS. Furthermore, Sudan III solubilized in the aqueous LiDS was deposited when an aqueous LiFOS was added. The difference in the solubilization behavior between LiDS and LiFOS enabled the controlled release of the solubilizate.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (755K) -
Ying Zhu, Yan Zhou, Tian Tian, Zhaoyun Wang, Baokun Qi, Xiaoyuan Zhang ...2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 863-871
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
ジャーナル フリーThe variations in average particle size, zeta potential, free fatty acids (FFA) release rate, and the bioavailability of menthol under in vitro simulated digestion conditions of peppermint oil nanoemulsion were investigated. 3D confocal laser scanning microscopy and Cryo-scanning electron microscopy were used to observe the microstructure characteristics of peppermint oil nanoemulsion, which indicated that soybean protein was completely adsorbed at the oil-water interface of the nanoemulsion and presented a core shell structure. And the results indicated that FFA release rate and menthol bioavailability of peppermint oil nanoemulsion prepared by using high-pressure homogenization were much higher. In the simulated gastric digestion phase, the average particle size and the zeta potential of the nanoemulsion increased, and droplet polymerization appeared. After the simulated intestinal, the interfacial protein of nanoemulsion was hydrolyzed, and the oil droplets were digested, which resulted in the decreased particle size and increased absolute value of zeta potential.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1321K) -
Hina Okawara, Koki Shinomiya, Yoshimune Nonomura2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 873-879
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/08/14ジャーナル フリーGels exhibit complex friction behavior. This study aims to evaluate the friction forces between two fractal agar gel substrates under sinusoidal motion to show the effect of rough surfaces on friction dynamics. In a previous study, we observed an asymmetric friction profile during reciprocating motion and an ultra-low friction state on flat agar gel surfaces. On the other hand, these distinct friction profiles were not observed on rough agar gel surfaces. We determined that this distinction was caused by the contact state between fractal agar gel surfaces; no thick water film was formed on the fractal surfaces because the rough structure provided channels to drain water from the interface. These physical insights are useful not only for developing biofunctional materials but also for understanding surface phenomena on biosurfaces including tongues and small intestinal walls.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2069K)
-
Hong Wang, Haoyuan Geng, Honglin Tang, Liqi Wang, Dianyu Yu, Junguo Wa ...2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 881-891
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/08/14ジャーナル フリーEnzyme-assisted aqueous extraction of rice germ oil (RGO) was performed in this study. The physicochemical properties, fatty acid composition, bioactive substances and antioxidant activity of RGO were analyzed. An enzyme composed of alcalase and cellulase (1:1, w/w) was found to be the most effective in the extraction yield of oil. The optimal oil yield of 22.27% was achieved under the conditions of an enzyme concentration of 2% (w/w), incubation time of 5 h, incubation temperature of 50°C, water to seed ratio of 5:1, and pH 6.0. The predominant fatty acids of RGO were oleic acid (39.60%), linoleic acid (34.20%) and palmitic acid (20.10%). The total saturated fatty acid (SFA), monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) composition of RGO were 22.50%, 39.60% and 36.00%, respectively. RGO yielded a high content of γ-oryzanol (530 mg/100 g oil), tocotrienol (62.96 mg/100 g oil), tocopherol (23.24 mg/100 g oil) and a significant amount of phytosterol (372.14 mg/100 g oil). It exhibited notable antioxidant activities with IC50 values of 32.37 and 41.13 mg/mL, according to the DPPH radical scavenging assay and β-carotene/linoleic acid bleaching test, respectively.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (554K)
-
Caixia Guo, Jinping Qiao, Shengwan Zhang, Meiping Li, Juan Li, Shaimaa ...2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 893-908
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/08/14ジャーナル フリーElaeagnus mollis oil (EMO), which is a type of plant oil, was extracted from the nuts of Elaeagnus mollis Diels that is known as a precious woodyoilcrop in China. The present study investigated the ameliorative effects of EMO on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and explored relative regulation mechanism. The analysis of EMO fatty acids showed that EMO rich in unsaturated fatty acids (92.07%), such as linoleic acid (48.24%), oleic acid (34.20%) and linolenic acid (7.57%). In addition, supplementation of EMO could ameliorate the increase in body weight, fat weight, and abnormal serum lipids induced by high-fat diet. A further important implication is that the levels of serum ALT, serum AST, hepatic TG, TC, SOD, GSH/GSSG ration and MDA were improved after supplementing with EMO. All these changes may be due to the ability of EMO to inhibit fatty acid synthesis via reducing the mRNA expression of SREBP-1c, PPARγ and FAS, and elevate fatty acid oxidation by increasing the mRNA expression of PPARα and CPT-1. Meanwhile, our results also showed that endogenously synthesized n-3 PUFAs could significantly increase after treating with EMO. In conclusion, the results suggested that EMO could be regarded as a healthy food for preventing NAFLD.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1646K)
-
Ting-ting Liang, Li-tao Tong, Dong-hui Geng, Li-li Wang, Xian-rong Zho ...2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 909-922
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
ジャーナル フリーThe objective of this research was to evaluate the effect of wheat gluten on gut microbiota from hamsters and also analyse whether alterations in microbiota could result in wheat gluten’s lipid-lowering properties. Four weeks male hamsters were divided into 3 groups (n=10). Two hypercholesterolemic groups were fed for 35 days with hypercholesterolemic diet, containing 20% (w/w) wheat gluten or casein. Wheat gluten significantly reduced serum total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) concentrations, and also decreased the liver total cholesterol (TC), free cholesterol (FC), cholesterol ester (CE), triglycerides (TG) concentrations. Wheat gluten group had a higher fecal lipids, total cholesterol (TC) and bile acids (BA) than that of casein group (p < 0.05). Moreover, wheat gluten significantly increased total short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) concentrations in feces. Sequencing of 16S rRNA gene revealed that intake of wheat gluten decreased the relative abundances of Firmicutes and Erysipelotrichaceae, but to increased the relative abundances of Bateroidetes, Bacteroidales_S24-7_group and Ruminococcaceae. The lipid lowering properties of wheat gluten was associated with the lower ratio of Firmicutes/Bateroidetes, the lower of the bacterial taxa Erysipelotrichaceae and the higher of the bacterial taxa Bacteroidales_S24-7_group and Ruminococcaceae. These results suggest that wheat gluten modulate cholesterol metabolism by altering intestinal microflora.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2045K) -
Kazuko Iwamoto, Hirokazu Kawamoto, Fumiaki Takeshita, Shinichi Matsumu ...2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 923-930
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/08/14ジャーナル フリーGinkgo biloba extract (GBE) is widely used as herbal medicine. Preventive effect of GBE against dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, has been reported. The bioactive compounds in GBE that impart these beneficial effects, flavonoids and terpene lactones, have poor bioavailability. Our previous study found distribution of bioactive compounds of sesame extract in mice brain after mixing it with turmeric oil. Here, we evaluate the distribution of bioactive compounds of GBE by combining it with the mixture of sesame extract and turmeric oil (MST). The content of terpene lactones in mice serum was significantly increased in a dose-dependent manner after administration of GBE. However, the contents of terpene lactones in mice brain were not significantly changed. Concentration of ginkgolide A in mice brain increased significantly when GBE was co-administrated with MST than when GBE was administered alone. These results suggest that MST may be effective in enhancing the bioavailability of ginkgolide A in GBE.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (324K)
-
Cheng Luo, Dong-Liang Li, Yang Wang, Shan-Shan Guo, Shu-Shan Du2019 年 68 巻 9 号 p. 931-937
発行日: 2019年
公開日: 2019/09/04
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/08/14ジャーナル フリーThe essential oil extracted from roots and rhizomes of Ligusticum jeholense Nakai et Kitagawa was investigated for its chemical composition by GC-MS analysis, and evaluated for its contact toxicity and repellency against Tribolium castaneum and Lasioderma serricorne, along with some of its individual components. The essential oil was rich in aromatics (65.34%) with low molecular weight. Major components included sedanolide (33.95%), 3-butylidenephthalide (18.76%), spathulenol (8.90%) and myristicin (6.76%). The results of bioassays indicated that the essential oil of L. jeholense and 3-butylidenephthalide possessed significant repellent activities against T. castaneum at 2 and 4 h post-exposure. Meanwhile, 3-butylidenephthalide had potent contact toxicity against L. serricorne (LD50 = 13.64 µg/adult). The minor component n-butylbenzene in the oil was highly toxic to T. castaneum (LD50 = 23.99 µg/adult) and L. serricorne (LD50 = 7.86 µg/adult) in contact assays, but failed to repel these beetles at all testing concentrations. Spathulenol and myristicin exerted good insecticidal and repellent effects on the two target insects. This work suggests that the essential oil of L. jeholense has promising potential for development as natural insecticide or repellent to control pest damage in warehouses.
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (301K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|