Volume 56, Issue 4
Displaying 1-9 of 9 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
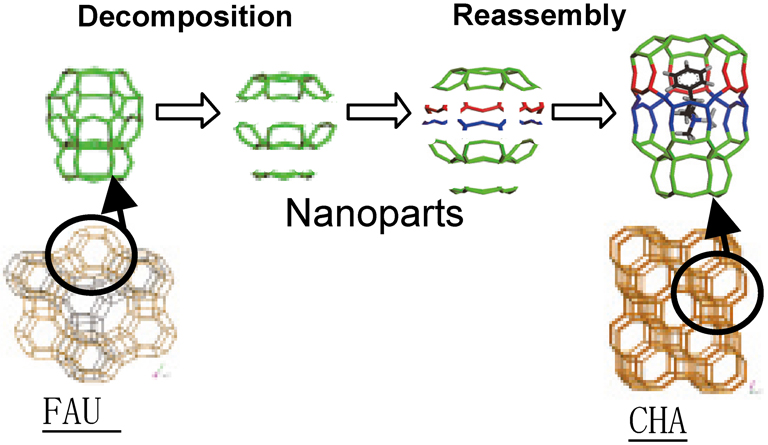
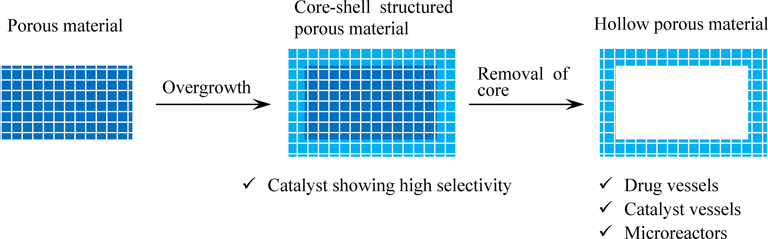
Review Paper -Feature Articles: Novel Synthetic Processes of Zeolites-
-
Article type: Regular Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 4 Pages 183-197
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2013
Download PDF (5405K) -
Article type: Review Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 4 Pages 198-205
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2013
Download PDF (4641K) -
Article type: Review Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 4 Pages 206-213
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2013
Download PDF (1665K)
Review Paper
-
Article type: Review Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 4 Pages 214-220
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2013
Download PDF (7172K)
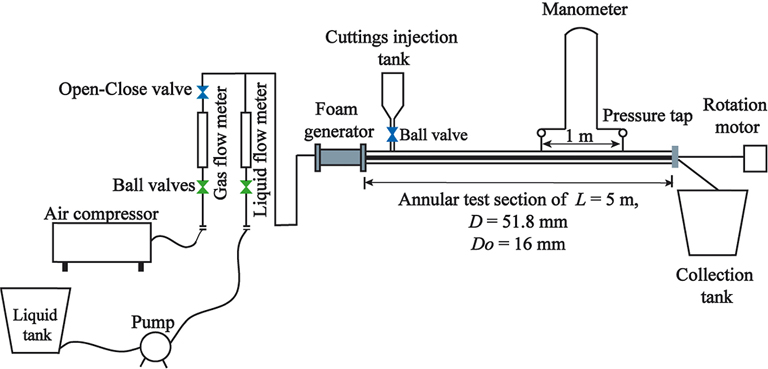
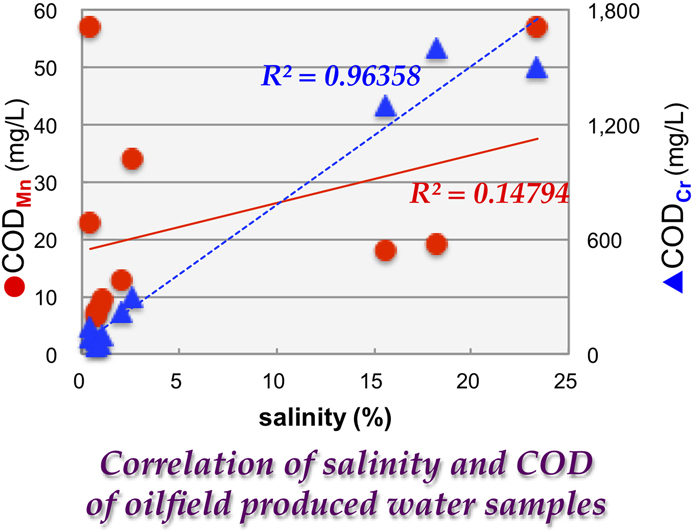
Regular Paper
-
Article type: Regular Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 4 Pages 221-229
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2013
Download PDF (700K) -
Article type: Regular Paper
2013 Volume 56 Issue 4 Pages 230-235
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2013
Download PDF (919K)
Research Note
-
Article type: Research Note
2013 Volume 56 Issue 4 Pages 236-243
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2013
Download PDF (706K)
Technical Report
-
Article type: Technical Report
2013 Volume 56 Issue 4 Pages 244-248
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2013
Download PDF (672K)
Letter
-
Article type: Letter
2013 Volume 56 Issue 4 Pages 249-252
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2013
Download PDF (1710K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|