All issues

Successor
Volume 33, Issue 9
Displaying 1-10 of 10 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Preface
-
Toshio TAKAHASHI2012Volume 33Issue 9 Pages 491
Published: September 10, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2012
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (195K)
Special Issue: Surface and Interface Analyses by X-ray Diffraction and Scattering
-
Osami SAKATAArticle type: Review
2012Volume 33Issue 9 Pages 492-500
Published: September 10, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2012
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe author introduces what kind of information on surface, thin film, and nano structures are deduced using x-ray diffraction. Some titles of researches that involved him are listed to give readers the information. He briefly summarizes a main idea of x-ray diffraction and gives the outline from its measurement to modeling a structure. A diffraction-intensity distribution and a shape as well as dimension of respective Bragg conditions are recorded, while structure of a crystalline sample is achieved on an atomic scale through the relation of the Fourier transformation between the real space and the reciprocal-lattice space. He discusses a total structure factor of a sample that is composed of a surface-layer part and a bulk crystal part. The structure factor is expressed using the same coordination, i.e. the same origin and the same in-plane unit-cell parameters, in the real space. Typical measurement methods are mentioned with technical notes. Some results of researches he principally conducted are described. View full abstractDownload PDF (2362K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2362K) -
Isao TAKAHASHIArticle type: Current Topic
2012Volume 33Issue 9 Pages 501-506
Published: September 10, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2012
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSGrazing incident X-ray diffraction and X-ray reflectivity (XR) including non-specular XR can be effectively utilized for the study of structure and morphology of polymer thin films. In this article, some results on crystallinity of biodegradable polymers and glass transition phenomenon of ultrathin polymer films are briefly described. View full abstractDownload PDF (770K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (770K) -
Masamitu TAKAHASIArticle type: Current Topic
2012Volume 33Issue 9 Pages 507-512
Published: September 10, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2012
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSurface sturctures of GaAs(001) under growth conditions have been investigated using in situ X-ray diffraction. Theatomic arrangements of GaAs(001) surface stabilized at an elevated temperature under As pressure were quantitativelydetermined in a molecular-beam epitaxy chamber integrated with an X-ray diffractometer. With the help of high angularresolution of synchrotron radiation, disordered sructures appearing in the transition from (2×4) to other phases wereclarified. Energy tunability of synchrotron X-rays allowed for element-sepcific analysis of the c (4×4) struture,providing direct evidence for Ga-As heterodimer formation. View full abstractDownload PDF (757K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (757K) -
Shinichiro HATTA, Tetsuya ARUGAArticle type: Current Topic
2012Volume 33Issue 9 Pages 513-518
Published: September 10, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2012
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCritical behavior and structural change during the phase transitions of charge-density-wave (CDW) states on In/Cu(001) and In/Si(111) have been studied by surface X-ray diffraction (SXRD). The In/Cu(001) surface exhibits critical behavior of the two-dimensional Ising model, indicating an order-disorder transition at T=345 K, ∼60 K lower than the electronic metal-insulator transition (MIT). It has been found that the scale-down of lattice correlation to the CDW correlation length (∼60 Å) causes instability of the CDW state, giving rise to MIT. For In/Si(111), the superstructure spot belonging to CDW shows an intensity drop in a temperature range (115-125 K) where MIT also takes place without critical scattering and with concomitant intensity increase of the other spot. Considering other experimental and theoretical results, we suggest a pseudo-first-order transition mechanism. View full abstractDownload PDF (755K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (755K) -
Kenji HIRAI, Shuhei FURUKAWAArticle type: Current Topic
2012Volume 33Issue 9 Pages 519-523
Published: September 10, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2012
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSOver the past decade, porous coordination polymers (PCPs) or metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have been intensively studied due to their potential applications for gas storage, separation, catalysis and chemical sensing. Although many PCP/MOF structures have been synthesized, only a few studies on the crystal surfaces of PCP/MOF have been reported despite its significance for the development of new porous materials. The investigation of PCP/MOF crystal surfaces will give us new guidelines for creating and designing novel porous materials. This article describes recent progress of the surface chemistry of PCP/MOF.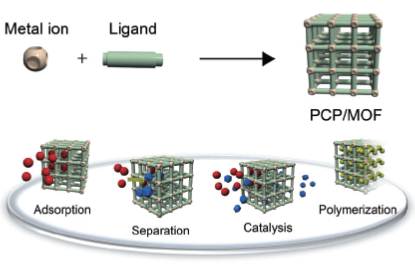 View full abstractDownload PDF (1243K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1243K) -
Kazuhisa TAMURAArticle type: Current Topic
2012Volume 33Issue 9 Pages 524-529
Published: September 10, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2012
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSElectrochemical reaction is one of the reactions which occur at solid/liquid interfaces. In the last three decades, relationships between reactivity and structure of solid/liquid interface, especially, electrode surface structure were uncovered using various techniques. Thus, nowadays it has been well recognized the importance of the study of electrode surface structures in in situ condition. However, dynamics of electrode surface structure has been well uncovered because the time resolution of scanning probe microscopes is not enough fast to monitor electrochemical processes. Surface X-ray scattering (SXS) is one of the in situ techniques which can be applied to the study of the solid/liquid interface structures. Especially, SXS is suitable for dynamics study. One of the advantages of SXS is that measurements can be carried out under ideal electrochemical conditions, i. e., low solution resistance and ideal diffusion condition. In this review, dynamics in underpotential deposition process of Bi on Au(111) electrode studied using surface X-ray scattering will be reported. View full abstractDownload PDF (637K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (637K)
Science Café
Research Abroad
-
Hiroko ARIGA2012Volume 33Issue 9 Pages 530-531
Published: September 10, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2012
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (486K)
Report of International Symposium
-
—Towards Nano-, Bio-, and Green Innovation—Tomihiro HASHIZUME, Satoshi WATANABE2012Volume 33Issue 9 Pages 532-533
Published: September 10, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2012
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (527K)
News & Trends
-
2012Volume 33Issue 9 Pages 534
Published: September 10, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2012
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (178K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
