
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
[in Japanese]2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages A1
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (76K)
-
Toshio KAWAHARA2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 377
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (159K)
-
Yuki WAKISAKA, Yuya IWASAKI, Hiromitsu UEHARA, Shingo MUKAI, Daiki KID ...Article type: Original
2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 378-383
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA log-spirally bent crystal Laue analyzer has been investigated and developed for highly sensitive in situ surface X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurement. Both calculations and experiments were conducted to obtain its intensity distributions on the different positions of the analyzer. A home-made log-spirally bent crystal Laue analyzer was made and evaluated. It was revealed that higher XAFS signals were obtained with the home-made analyzer than with the commercial one.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (874K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (874K) -
Arifumi OKADA, Urara TOYOTA, Kosuke MINOU, Masamichi YOSHIMURA, Kohei ...Article type: Original
2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 384-389
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn the present study, surface organic nanostructures consisting of melamine and terephthalaldehyde were prepared by solution method, i. e. solvent evaporations of the aqueous solutions. The prepared samples were observed using scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) in ultrahigh vacuum (UHV). In UHV observation, no oligomers as reaction products were imaged. Instead, unknown beltlike molecular rows and disordered phase appeared. In the case of coexisted area of the unknown and disordered phases, tip-induced phase transition was observed. The beltlike rows were attributed to the arrangement of terephthalaldehyde molecules. Based on the high-resolution observation, the tentative model of the TPA arrangement was proposed. The elongated keeping of the sample in UHV to progress the oligomer formation did not lead to formation of oligomers. From the present experimental results, we consider that the stability of the reaction products in UHV is low and such reactant molecules were probably included in the mobile disordered phases.
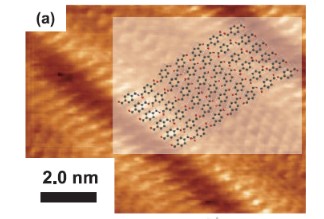 View full abstractDownload PDF (1005K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1005K) -
Yuhki YANASEArticle type: Current Topic
2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 390-394
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe identification of antigen that induces activation of mast cells and basophils in a patient is crucial to avoid symptoms of allergic diseases. Since surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRI) can visualize activation of individual cell, such as basophils without any labeling, SPRI sensor possesses a great potential for clinical diagnosis of allergy. However, conventional technique of SPRI requires freshly isolated basophils of patients and cannot analyze multiple samples in parallel. To overcome such problems, we developed devices for SPRI to make a broad observation area and a multi-well SPRI sensor chip with a hydrophobic membrane. The employment of human IgE receptor-expressing mast cell lines (RBL-48 cells) sensitized with serum, collected and stored from less than a microliter of patientʼs blood,allowed us to detect specific reactions of RBL-48 cells in response to antigens, suggesting this technique may be a useful tool as a screening system of type I allergy.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (724K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (724K) -
Tooru KAMATA, Keiko SASAKI, Noriaki SHIMA, Akihiro MIKI, Munehiro KATA ...Article type: Current Topic
2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 395-399
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHair analysis for detection of drug(s) is one of forensic analyses which are carried out in forensic science laboratories of each prefectural police in Japan. Longitudinal drug distribution in hair provides very important information to understand use history of the drug. The authors applied mass spectrometry imaging technique to a drug incorporated in hair. Methoxyphenamine, a noncontrolled analogue of methamphetamine, was systemically administered to volunteers as the model compound, and hair samples were collected from them at appropriate intervals. Imaging of methoxyphenamine in hair achieved by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry applied to longituidinal section cropped out by freeze-sectioning using a rotary microtome. Methoxyphenamine-positive regions were specifically observed to shift toward tips of hair according to its growth. Detailed investigation of methoxyphenamine distribution in hair suggested strongly that its incorporation occur at not only the hair bulb but also the tissue of the upper dermis.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (998K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (998K) -
 Kenta KURODA, Johannes REIMANN, Jens GÜDDE, Ulrich HÖFERArticle type: Current Topic
Kenta KURODA, Johannes REIMANN, Jens GÜDDE, Ulrich HÖFERArticle type: Current Topic
2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 400-405
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSUltrafast photoexcitation of the spin-polarized Dirac surface state in the topological insulator Sb2Te3 was investigated by using time- and angle-resolved two-photon photoemission spectroscopy combined with tunable mid-infrared pump pulses. It was revealed that mid-infrared pump permits a direct excitation between the occupied and unoccupied part of the surface Dirac-cone. Moreover, the direct optical coupling induces asymmetric transient populations in the surface states at ±k||, which reflects a macroscopic photoexcited electric surface current. By observing the decay of the asymmetric population and its temperature dependence, the ultrafast dynamics of the surface current was visualized in the momentum space.
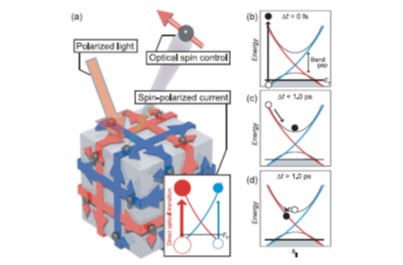 View full abstractDownload PDF (924K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (924K) -
Hisato YASUMATSU, Nobuyuki FUKUIArticle type: Current Topic
2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 406-412
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPreparation, catalytic activity and thermal stability of monatomic-layered uni-sized platinum cluster disks directly bound to a single-crystal Si surface are reviewed. The cluster disks were prepared by impact of uni-sized cluster ions onto the surface: cluster impact. Their catalytic activity in the CO oxidation was unveiled through surface-chemistry measurements; the low-temperature catalytic activity and reaction sites involved in the CO oxidation were studied with temperature-programed desorption (TPD) measurements, and anti-poisoning ability against CO around room temperature was elucidated by measuring the turnover rate in gas-flow reactions under steady-state conditions. The thermal stability was evaluated by means of scanning-tunneling microscope (STM) with repetition of the sample heating. These specific properties of the cluster disks were explained according to electron accumulation at the sub-nano interface between the cluster disk and the substrate surface through strong chemical interaction between them.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1560K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1560K) -
Jo ONODA, Ayhan YURTSEVER, Masayuki ABE, Yoshiaki SUGIMOTOArticle type: Current Topic
2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 413-418
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTitanium dioxide (TiO2) surfaces have been extensively studied for its broad range of applications such as photocatalysis, heterogeneous catalysis, gas sensors, and solar cells. Rutile TiO2 has also been investigated as a model system for studying the physical and chemical properties for studying more complex metal oxide surfaces. Here, we report studies of atomic-scale observation of TiO2 surfaces by atomic force microscopy (AFM). While AFM imaging mechanism on TiO2(110) has been understood well, we find the interpretation of AFM contrast on TiO2(011) is not straightforward. In addition, we also perform simultaneous AFM and Kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) measurements on subsurface charges and single Pt atoms on the TiO2(110) surfaces, respectively. We believe our findings in this report will be useful when investigate other catalytic system by AFM and KPFM
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1049K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1049K)
-
Yasuyuki YOKOTA, Akihito IMANISHI, Takafumi UEMURA, Jun TAKEYA, Ken-i ...Article type: Current Topic
2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 419-424
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe structural properties of ionic liquid/rubrene single-crystal interfaces were investigated using frequency modulation atomic force microscopy. The spontaneous dissolution of rubrene molecules into the ionic liquid was triggered by surface defects such as an oxidized rubrene or a vacancy, leading to the formation of a clean interface irrespective of the initial conditions. Force curve measurements revealed that a few solvation layers of ionic liquid molecules formed at the interface. We have also measured electric characteristics of electric double layer field-effect transistor based on the ionic liquid/rubrene single crystal interfaces. In contrast to usual devices, the mobility of field induced career was found to gradually increase with time for a day, consistent with the time scale of the spontaneous dissolution. These specific properties are discussed with respect to the microscopic understanding of electric double-layer transistors.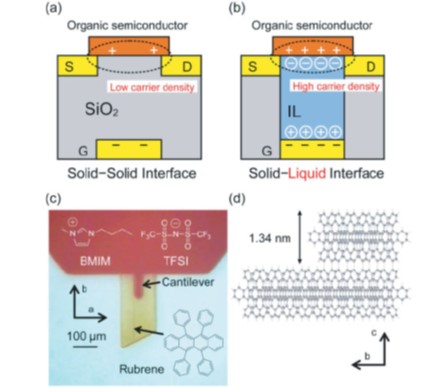 View full abstractDownload PDF (906K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (906K)
-
Eiji KUSANO2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 425-426
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Jun FUJII2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 427-428
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (345K)
-
2017Volume 38Issue 8 Pages 429
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 23, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (159K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
