All issues

Successor
Volume 34, Issue 12
Displaying 1-12 of 12 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Preface
-
Masaru TSUKADA2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 623
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (208K)
Special Issue: Numeric Simulations of Reactions at Electrode
-
Kazuto AKAGI2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 624-625
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe purpose of this article is introducing each topic and showing the relation among them. Various strategies to make an appropriate model to discuss elementary red-ox processes and another data-driven type approaches to explain and predict experimental facts are briefly mentioned.View full abstractDownload PDF (220K) -
Masahiro YAMAMOTOArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 626-631
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe theory of electrical double layer has 100 year history since Gouy and Chapman proposed. Since then the three-dimensional numerical solutions of Poisson-Boltzmann (PB) equation were widely applied for many systems such as chemically modified electrode or the electrode with micro-pore. However there are some shortcomings in PB theory for strongly electrified interface, ion-ion interaction in concentrated solution, and multivalent counter ions. In this article the canonical Monte Calro simulation with primitive model, which is simplest way to simulate the electrical double layer, is introduced. View full abstractDownload PDF (997K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (997K) -
Ryosuke JINNOUCHI, Yu MORIMOTOArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 632-637
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis article reviews two types of electronic structure calculations on electrode reactions:conventional density functional theory (DFT) calculations on electrically neutral surfaces in vacuum and calculations combining DFT and a modified Poisson-Boltzmann theory (DFT-MPB) on electrified surfaces in modeled electric double layers. After brief descriptions on essential equations and approximations of these methods, applications are shown on Pt dissolution from Pt nano-particles and sulfuric acid anion adsorption on Pt(111).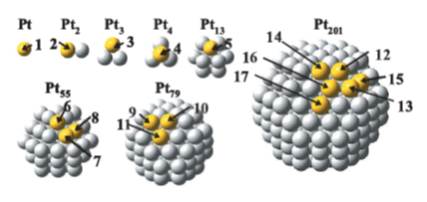 View full abstractDownload PDF (968K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (968K) -
Ikutaro HAMADA, Osamu SUGINOArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 638-643
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe describe our modeling of the electrode/electrolyte interfaces and our simulations of electrochemical reactions (electrode reactions) performed to gain molecular scale understanding of the electrode reactions. Here we focus on our recent first principles molecular dynamics simulations on the hydrogen evolution reaction at a water/platinum interface. We also discuss how to improve the present level of modeling to finally realize the comprehensive and accurate simulation. View full abstractDownload PDF (893K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (893K) -
—Comparison between Experiments and Calculations at the Atomic Scale—Junji INUKAI, Donald A. TRYKArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 644-649
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA new standard was sought for the direct comparison of electrocatalytic activity with surface structure by examining the electrooxidation of CO in a CO-saturated solution on platinum single-crystal electrodes, with combined electrochemical measurements, in situ scanning microscopy, and density functional theory.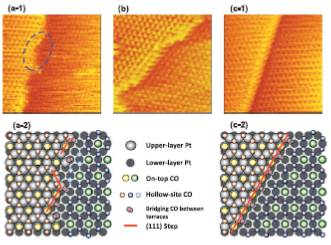 View full abstractDownload PDF (2154K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2154K) -
Hubert VALENCIA, Masanori KOHYAMA, Shingo TANAKA, Hajime MATSUMOTOArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 650-655
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe have performed density-functional theory (DFT) calculations of ionic-liquid/Li-metal interface models to understand the nature of electrolyte/electrode interfaces in Li-ion batteries. First, we have clarified the microscopic interactions between a pair of constituent anionic and cationic molecules and a Li surface via EMI+ ([C6H11N2]+)-BF4− pair adsorption on various Li surfaces. Second, we have found that the features of the interfacial interactions in the molecular-pair adsorption are also applicable to an ionic-liquid/Li-metal interface, via examination of an EMI-BF4 crystal/Li-metal interface. Finally, we have examined the effects of variations of anionic molecules on the properties of ionic-liquid/Li-electrode interfaces via EMI+-FSFSA− (fluoroalkyl-fluorosulfonyl amid) pair adsorption calculations, which are compared with recent experimental results of electric transport properties at the interfaces between the same ionic liquid and Li electrode. View full abstractDownload PDF (1023K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1023K) -
Nobuki OZAWA, Kosuke NAKAMURA, Yuji HIGUCHI, Momoji KUBOArticle type: Current Topic
2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 656-661
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFor improving the performance and durability of fuel cell materials, it is essential to elucidate the multi-physics phenomena such as mechanical property and degradation phenomena, which are complicated combination of chemical reactions and various physical processes. In this review, we introduce our successful clarification of the multi-physics phenomena in various fuel cells. In the polymer electrolyte fuel cell, we revealed chemical reaction dynamics of OH and H radicals, which leads to degradation of the electrolyte material. In the solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC), we found that chemical reactions of H2O advance the fracture and crack growth in the CeO2 electrolyte. We also established the multinanoparticle simulation method and it was successfully applied to the sintering process of Ni nano-particles in the porous Ni/YSZ anode of the SOFC. View full abstractDownload PDF (2984K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2984K)
Planning Series
Surface Science for Energy Issues
-
Seizo MORITA2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 662-663
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (424K)
Science Café
Research Abroad
-
Tomoko K. SHIMIZU2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 664-665
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (560K)
Qualifying Examination for Surface Science Engineers
-
2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 666
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1450K)
News & Trends
-
2013 Volume 34 Issue 12 Pages 667
Published: December 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: December 19, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (174K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
