
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Shuji HASEGAWA2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 415
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (142K)
-
Eiji ARIMA, Yoshitaka NAITOH, Li YAN JUN, Yasuhiro SUGAWARAArticle type: Original
2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 416-421
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe magnetic exchange force is an interaction between spins and is very important for analyzing magnetic properties. Magnetic exchange force microscopy (MExFM), which can detect the magnetic exchange force between the magnetic tip and the magnetic surface, has achieved the atomic-resolution imaging of the spin states at surface. In MExFM, however, the separation between a structure and a magnetic state on the surface has not been performed. In this paper, we propose a new MExFM using ferromagnetic resonance to separate the magnetic and non-magnetic tip-sample interaction. Here, we demonstrate tip magnetization modulation using ferromagnetic resonance, nano-scale magnetic contrast imaging and, finally atomic-scale spin selective imaging by MExFM using ferromagnetic resonance.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (925K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (925K) -
Structural Analysis of Native Passive Films on Stainless Steels Using Synchrotron X-ray SpectroscopySumera SHIMIZU, Shinichi ITO, Hideo ASAI, Toshihiko MIYAKAWA, Masataka ...Article type: Original
2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 422-428
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA native passive film is formed on the SUS304 surface at ordinary temperature and pressure1, 2). As a structural model of the film, a network-structure composed of Cr-oxide and -hydroxide has ever been proposed1, 3), but experimental evidences for the structure have not been reported yet. We examined the detailed film structure using synchrotron X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The XAFS spectra clearly showed an ordered network-structure (at least < 10 Å) of Cr(IV) oxide. Additionally, the XPS spectra indicated that the chromium oxide is transformed into a chromium oxyhydroxide such as a -O-Cr-OH- structure. These results are the first evidence that the network structure exists actually in the native passive film of SUS304.
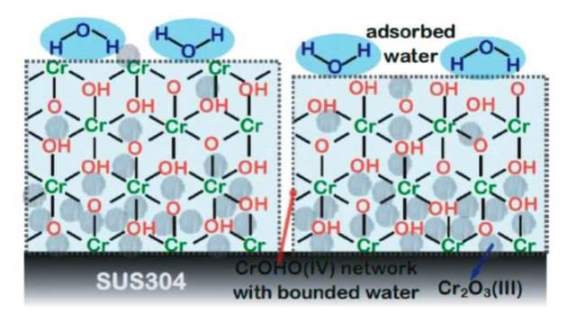 View full abstractDownload PDF (1754K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1754K) -
Ryohei TSURUTA, Yuta MIZUNO, Takuya HOSOKAI, Tomoyuki KOGANEZAWA, Hisa ...Article type: Original
2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 429-434
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSEngineering of the donor-acceptor molecular contacts is one of the most crucial demands for development of organic semiconductor devices such as organic solar cells. In the present study, surface science methodologies are applied to a molecular pn-heterojunction for accurate investigation of the contact structures; namely the single crystal surfaces of pentacene are used as “substrates” for building well-defined interfaces with C60 overlayers whose crystallographic structures are defined by means of grazing incidence x-ray diffraction (GIXD). A heteroepitaxial relationship of the (111)-oriented face-centered cubic C60 lattice on the pentacene single crystal surface is clearly demonstrated. The present high-resolution GIXD measurements also reveal significantly wide average crystalline size of over 100 nm of these heteroepitaxial C60 overlayers.
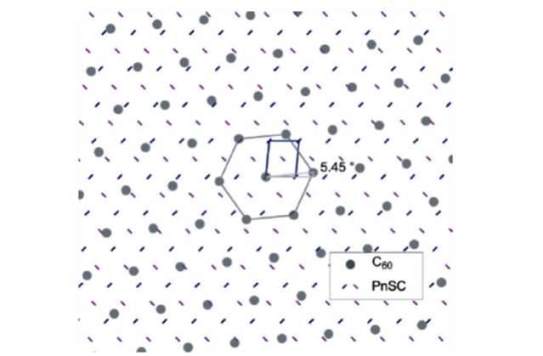 View full abstractDownload PDF (678K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (678K) -
Masahiro YANAGISAWA, Takayuki HOMMAArticle type: Current Topic
2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 435-440
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNew technique for analyzing buried interface has developed based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy. It consists of plasmonic sensors and spectrometer equipped with high precision mechanisms. Performance of the system involves in-situ measurement of interfaces, i.e. liquid/solid or solid/solid, with high sensitivity and high depth resolution on a variety of samples. Additional functions are in-situ temperature measurement by anti-Stokes/Stokes ratio, simultaneous acquisition with laser heating, time-resolved measurement, and pulsed laser Raman spectroscopy. A depth profile of layered ultra-thin films, i.e. diamond-like carbon (DLC) or highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG), was analyzed in atomic scale resolution at solid/solid interface. Molecular configuration and bonding feature of liquid organic molecules, i.e. lubricants for magnetic disks or reducing agents for a plating, were analyzed at liquid/solid interface. Oxidation process or decomposition process of ultra-thin DLC films was analyzed for a variety of DLC films. Spectral change with irradiation time by pulsed laser heating exhibited a kinetic change of molecular structures in a chemical reaction with in-situ heating temperature measurement.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (949K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (949K) -
Yasunobu ANDO, Satoshi WATANABEArticle type: Current Topic
2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 441-445
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSOn the basis of first-principles calculations within the density functional theory, we report possibility of control of metal-insulator property by ion adsorption on Ti2C MXene dioxide, Ti2CO2. Our simulation reveals that Ti2CO2 is insulating with indirect band-gap of 0.44 eV, while atomic adsorption of any of H, Li, and Na onto it turned it to be metallic. This metal-insulator change may be applicable to switching devices with high on/off ratio and small energy consumption by controlling ionic movements like ion batteries.
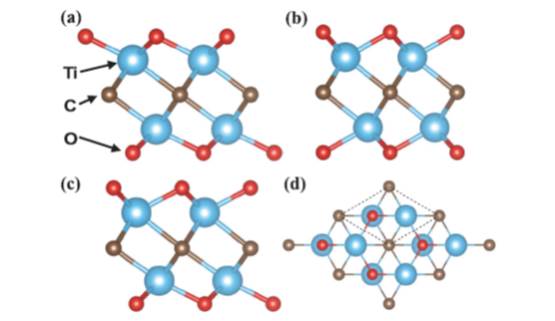 View full abstractDownload PDF (612K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (612K) -
Hidehito ASAOKA, Yuki UOZUMIArticle type: Current Topic
2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 446-450
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe have focused on stress measurements of the reconstructed Si(111) 7×7 and the hydrogen (H)-terminated Si(111) 1×1 surfaces. In order to obtain information on both the surface stress and the surface structure simultaneously, we have combined the surface-curvature and the reflection high-energy electron-diffraction instrumentations in an identical ultrahigh vacuum system. The surface stress behaviors during desorption and adsorption processes of hydrogen on the Si(111) surfaces reveal that the Si(111) 1×1 surface releases 1.6∼1.7 N/m (= J/m2), or 1.3∼1.4 eV/ (1×1 unit cell), of the surface energy from the strong tensile Si(111) 7×7 reconstruction.
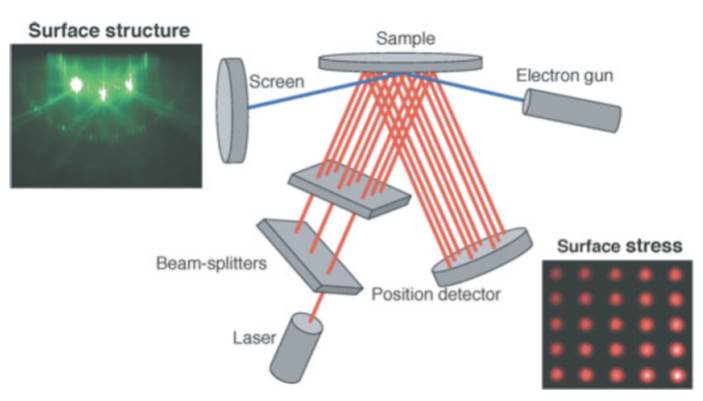 View full abstractDownload PDF (540K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (540K) -
Izumi MOCHIZUKI, Hiroko ARIGA, Yuki FUKAYA, Ken WADA, Masaki MAEKAWA, ...Article type: Current Topic
2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 451-456
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe detailed structure of the rutile-TiO2(110)(1×2) surface, which had been under debate for the past 30 years, was investigated using the newly developed technique of total-reflection high-energy positron diffraction (TRHEPD), which is a positron counterpart of reflection high-energy electron diffraction (RHEED). The rocking curves for the 00 spot extracted from the experimental diffraction patterns were compared with the curves for various models calculated using a full-dynamical diffraction theory. The rocking curves matched those for a surface consisting of a Ti2O3 composition, originally suggested by Onishi and Iwasawa [H. Onishi and Y. Iwasawa. Surf. Sci. 313, L783 (1994)], but with a further modification of atomic positions close to the ones proposed by Wang et al. [Q. Wang, A. R. Oganov, Q. Zhu and X. F. Zhou, Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 266101 (2014)].
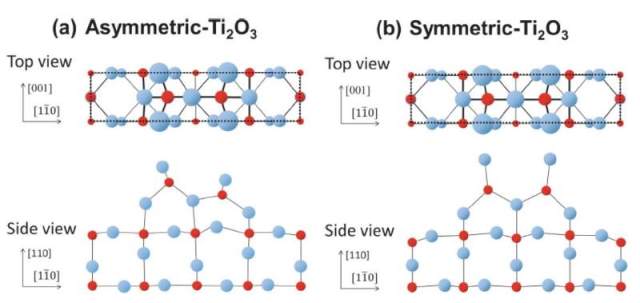 View full abstractDownload PDF (919K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (919K)
-
Hiromitsu NAKAMURA2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 457-458
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Qingshuo WEI2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 459-460
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (301K)
-
2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 461
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1193K)
-
2016Volume 37Issue 9 Pages 462
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 21, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (167K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
