All issues

Successor
Volume 36, Issue 2
Displaying 1-11 of 11 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Preface
-
Toshihiro KONDO2015 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 59
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (194K)
Special Issue: How to Make Hydrogen
-
Junji INUKAIArticle type: Introduction
2015 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 60-61
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this issue of Journal of Surface Society of Japan, the hydrogen-production processes are introduced by five invited writers, including reformation of methane, electrochemical, photochemical, and thermochemical decomposition of water, and biophotosynthesis.View full abstractDownload PDF (209K) -
Toshihiro MIYAO, Kazutoshi HIGASHIYAMA, Hisao YAMASHITA, Masahiro WATA ...Article type: Current Topic
2015 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 62-68
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe resent progress of the catalysts for the fuel processing of the residential fuel cell systems was reviewed. For the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX) reaction, Pt-Fe/Mordenite catalyst exhibited remarkable activity and selectivity. Catalytic activities of the Ni-Fe/CeO2-ZrO2 catalyst prepared by a hard template technique for the water-gas shift reaction were superior to those of a commercial Fe-Cr-based catalyst. The residual chlorine adsorbed on supported Ni catalysts suppressed CO2 dissociation and improved selective CO methanation. The catalytic activity and selectivity of a Ni/Al2O3 catalyst for selective CO methanation were significantly improved by vanadium addition. The maximum CO removal ability and catalyst durability of the Ni/AlVOx catalyst were dramatically improved by the MS coating.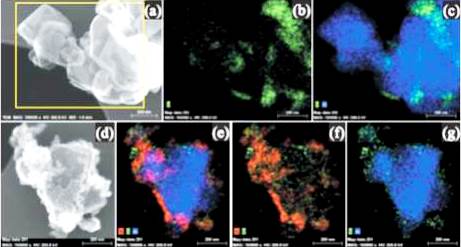 View full abstractDownload PDF (1617K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1617K) -
Tatsumi ISHIHARAArticle type: Current Topic
2015 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 69-73
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIntermediate temperature steam electrolysis has many advantages for production of hydrogen with high efficiency. In particular, by using unused heat as a source of steam, intermediate steam electrolysis can be used as the heat recovery and transport systems. In this review, technical advantages and current status of the intermediate temperature steam electrolyzer are explained. Performance of steam electrolysis of the cell using LaGaO3 based electrolyte is introduced and improvement of cathode activity by applying NiFe-Ce(Sm)O2 was demonstrated. View full abstractDownload PDF (1131K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1131K) -
Jun KUBOTA, Kazunari DOMENArticle type: Current Topic
2014 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 74-79
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHydrogen production by water splitting using photocatalysts under the solar irradiation is one of the artificial photosynthetic process to obtain sustainable hydrogen energy from water using photon energy. The solar energy conversion efficiency of powder photocatalysts has reached to ca. 0.3%, which is equivalent to that of general agricultural plants. For water splitting photocatalysts, surface modification with co-catalysts frequently plays as one of the important roles. In this manuscript, we discuss the function of surfaces of cocatalysts on semiconductor photocatalysts, which accept photogenerated carriers from the semiconductor and catalyze hydrogen or oxygen evolution reaction. View full abstractDownload PDF (1023K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1023K) -
Kaoru ONUKI, Hiroki NOGUCHI, Nobuyuki TANAKA, Hiroaki TAKEGAMI, Shinji ...Article type: Current Topic
2015 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 80-85
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThermochemical water-splitting process decomposes water using thermal energy by operating high temperature endothermic reaction(s) and low temperature exothermic reaction(s) cyclically, with which free energy of water decomposition is produced. The so-called sulfur family processes, which utilize thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid as the high temperature endothermic reaction, have attracted lots of interest among the many processes proposed so far. The IS process represents the pure thermochemical sulfur family processes. The continuous hydrogen production by IS process was demonstrated in laboratory, and the materials of construction for the IS process have been screened by corrosion tests performed in the severe process environment. At present, application of membrane technologies and development of catalysts are under study to improve the hydrogen production performance. Also, development is underway of the chemical reactors made of candidate materials such as ceramics.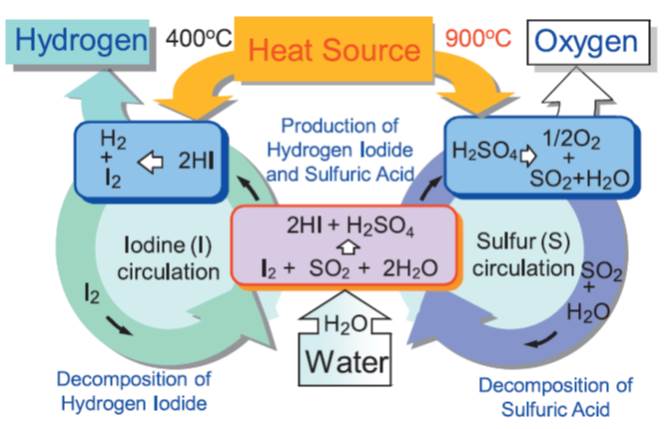 View full abstractDownload PDF (1611K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1611K) -
Takashi OSANAIArticle type: Current Topic
2015 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 86-90
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSBiotechnology of cyanobacteria takes much attention because of their ability to utilize light energy and assimilate carbon dioxide. Synechocystis species are unicellular, non-nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria, which are widely used for both basic and applied sciences. Here I introduce our study discovering new way to increase the productivity of hydrogen from Synechocystis cells. SigE, an RNA polymerase sigma factor, is a positive regulator of sugar catabolism and bioplastic production. The sigE overexpression also increases the hydrogen production during dark anaerobic conditions. Phenotypic analysis also reveals that the sigE overexpression alters the photosynthetic activity and cell sizes, indicating the close interaction among metabolism, photosynthesis, cell size maintenance, and bioproduction. These results demonstrate the novel method promoting hydrogen productivity using transcriptional regulator of cyanobacteria.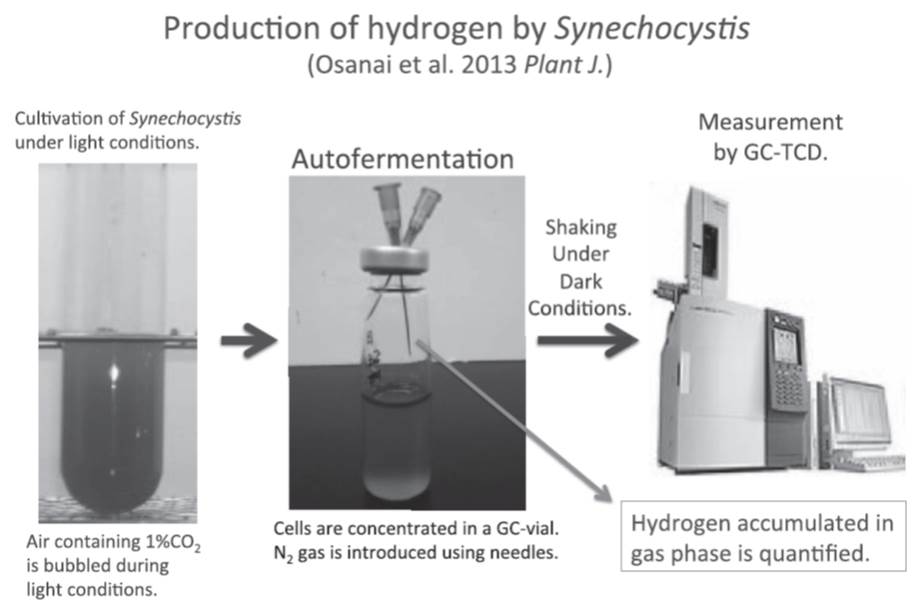 View full abstractDownload PDF (1471K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1471K)
Planning Series
Surface Science for Environmental Issues
-
Daisuke NAKAJIMA2015 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 91-93
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Science Café
Research Abroad
-
Toshio MIYAMACHI2015 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 94-95
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (665K)
Qualifying Examination for Surface Science Engineers
-
2015 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 96
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1221K)
News & Trends
-
2015 Volume 36 Issue 2 Pages 97
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 19, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (156K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
