Volume 86, Issue 1
Displaying 51-76 of 76 articles from this issue
Case report
-
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 178-179
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1111K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 180-181
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (735K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 182-183
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (894K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 184-185
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (911K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 186-187
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (835K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 188-189
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (895K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 190-191
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1078K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 192-193
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (835K) -
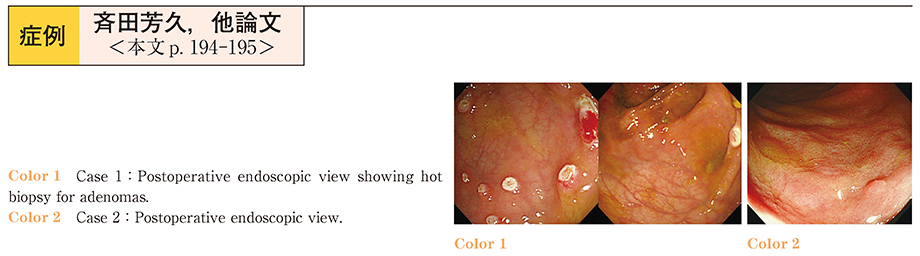
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 194-195
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1308K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 196-197
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (737K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 198-199
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1050K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 200-201
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1053K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 202-203
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1058K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 204-205
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1179K) -
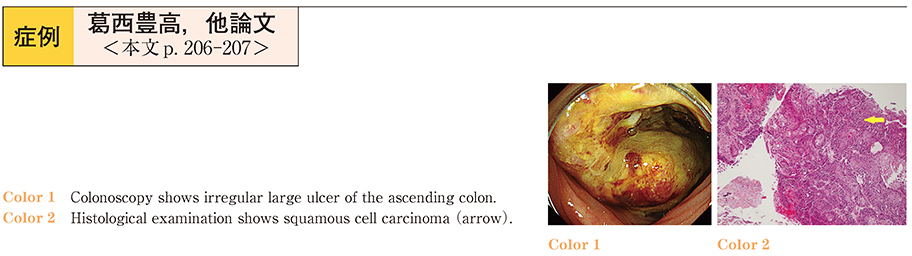
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 206-207
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (682K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 208-209
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1061K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 210-211
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (883K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 212-213
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (889K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 214-215
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (892K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 216-217
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (764K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 218-219
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1018K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 220-221
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (673K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 222-223
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1164K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 224-225
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (825K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 226-227
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (831K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 228-229
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (706K)