Volume 62, Issue 2
Displaying 1-50 of 52 articles from this issue
-
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 1-10
Published: 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (11180K)
Clinical study
-
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 26-30
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1981K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 31-35
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (699K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 36-40
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1079K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 41-44
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (461K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 45-49
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1765K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 50-54
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1846K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 55-59
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1971K)
Case report
-
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 60-62
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (293K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 64-65
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (588K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 66-67
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (450K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 68-69
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (867K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 70-71
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1166K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 72-73
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (612K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 74-75
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (930K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 76-77
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (900K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 78-79
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (692K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 80-81
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (231K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 82-83
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (746K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 84-85
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (245K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 86-87
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (907K) -
A case of gastric low grade MALT lymphoma regressed by second line of H. pylori eradication theraphy2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 88-89
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (685K) -
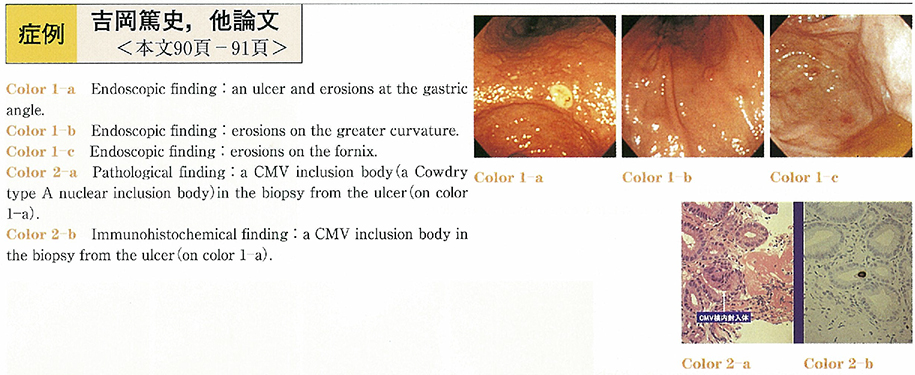
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 90-91
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (254K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 92-93
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (763K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 94-95
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1136K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 96-97
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1215K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 98-99
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (750K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 100-101
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (962K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 102-103
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (459K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 104-105
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (494K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 106-107
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (821K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 108-109
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1261K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 110-111
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (760K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 112-113
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (957K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 114-115
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (468K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 116-117
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1106K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 118-119
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (967K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 120-121
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (683K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 122-123
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (762K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 124-125
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (602K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 126-127
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (263K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 128-129
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (560K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 130-131
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (983K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 132-133
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (687K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 134-135
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (619K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 136-137
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (512K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 138-139
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (763K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 140-141
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (1213K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 142-145
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (997K) -
2003Volume 62Issue 2 Pages 144-145
Published: May 31, 2003
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2014
Download PDF (745K)