Volume 90, Issue 1
Displaying 1-50 of 60 articles from this issue
Clinical study
-
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 46-50
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (722K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 51-54
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (1040K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 55-58
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (901K)
Case report
-
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 59-61
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (1070K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 62-65
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (1173K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 66-69
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (961K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 70-71
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (874K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 72-73
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (805K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 74-75
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (633K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 76-77
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (591K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 78-79
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (775K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 80-81
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (896K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 82-83
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (943K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 84-85
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (838K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 86-87
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (586K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 88-89
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (792K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 90-91
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (631K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 92-93
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (801K) -
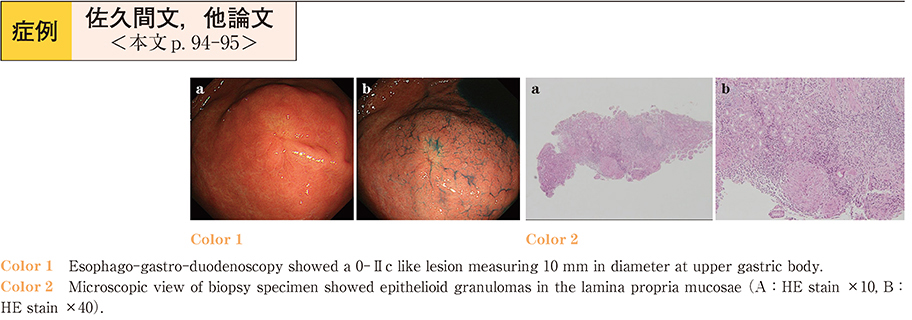
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 94-95
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (698K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 96-97
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (853K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 98-99
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (781K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 100-101
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (748K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 102-103
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (581K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 104-105
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (866K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 106-107
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (709K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 108-109
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (1092K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 110-111
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (811K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 112-113
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (805K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 114-115
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (772K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 116-117
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (842K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 118-119
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (943K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 120-121
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (774K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 122-123
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (871K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 124-125
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (906K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 126-127
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (640K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 128-129
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (651K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 130-131
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (1197K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 132-133
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (933K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 134-135
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (1003K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 136-137
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (1407K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 138-139
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (760K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 140-141
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (759K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 142-143
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (680K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 144-145
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (1077K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 146-147
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (903K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 148-149
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (784K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 150-151
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (755K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 152-153
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (1039K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 154-155
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (807K) -
2017Volume 90Issue 1 Pages 156-157
Published: June 09, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2017
Download PDF (877K)