Volume 87, Issue 1
Displaying 1-50 of 65 articles from this issue
-
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 1-16
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (15917K)
Clinical study
-
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 40-44
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (860K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 45-48
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (663K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 49-52
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (743K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 53-57
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (712K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 58-62
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (1003K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 63-67
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (957K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 68-71
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (718K)
Case report
-
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 72-75
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (1090K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 76-79
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (870K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 80-83
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (975K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 84-85
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (742K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 86-87
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (616K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 88-89
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (625K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 90-91
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (1020K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 92-93
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (918K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 94-95
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (612K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 96-97
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (759K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 98-99
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (1101K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 100-101
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (853K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 102-103
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (764K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 104-105
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (747K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 106-107
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (662K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 108-109
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (895K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 110-111
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (554K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 112-113
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (1110K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 114-115
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (921K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 116-117
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (1116K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 118-119
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (866K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 120-121
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (1072K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 122-123
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (991K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 124-125
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (1130K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 126-127
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (916K) -
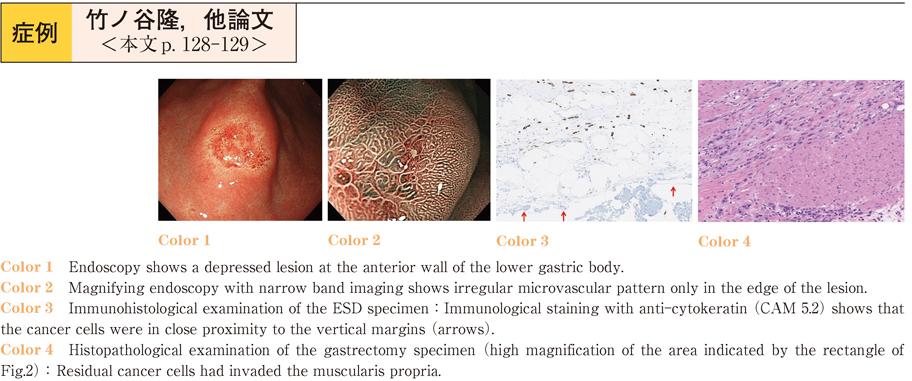
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 128-129
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (776K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 130-131
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (811K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 132-133
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (690K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 134-135
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (1113K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 136-137
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (668K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 138-139
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (935K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 140-141
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (848K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 142-143
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (749K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 144-145
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (941K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 146-147
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (967K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 148-149
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (784K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 150-151
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (902K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 152-153
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (840K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 154-155
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (934K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 156-157
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (745K) -
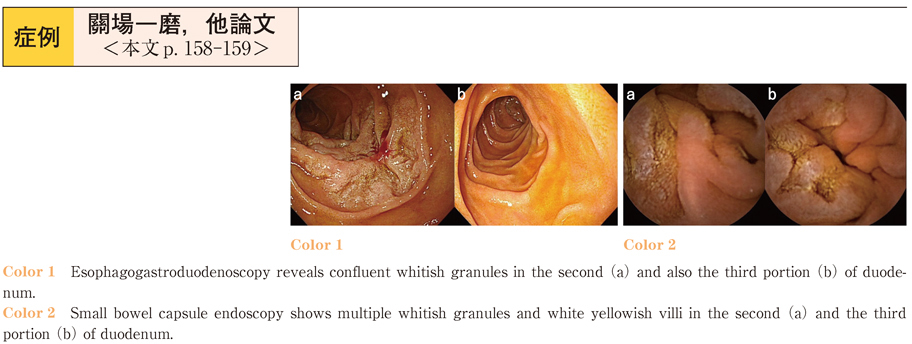
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 158-159
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (588K) -
2015Volume 87Issue 1 Pages 160-161
Published: December 12, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: January 06, 2016
Download PDF (692K)