Volume 78, Issue 2
Displaying 1-50 of 54 articles from this issue
-
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 1-14
Published: 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (7298K)
-
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 34-36
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (671K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 37-39
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (626K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 40-44
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (771K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 45-49
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (881K)
-
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 50-52
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (632K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 53-56
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (821K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 57-60
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (821K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 61-66
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (1056K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 67-69
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (597K)
-
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 70-73
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (729K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 74-77
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (930K) -
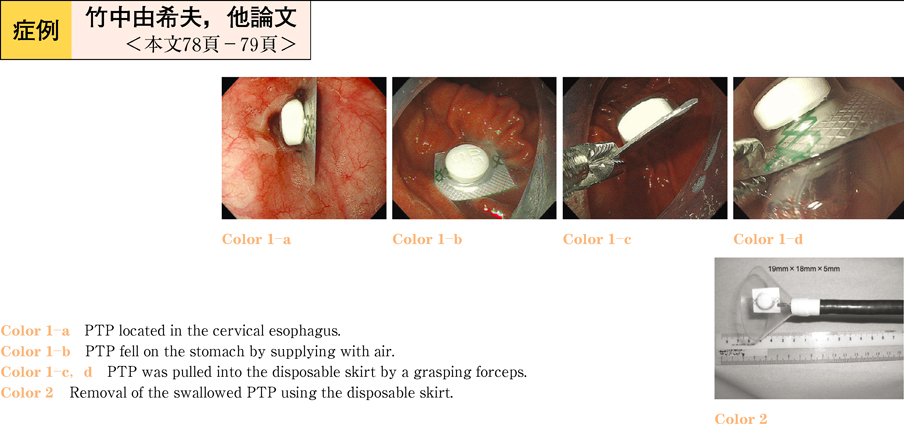
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 78-79
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (679K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 80-81
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (780K) -
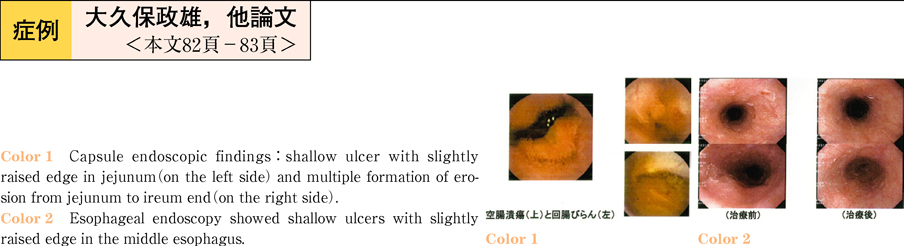
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 82-83
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (760K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 84-85
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (696K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 86-87
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (823K) -
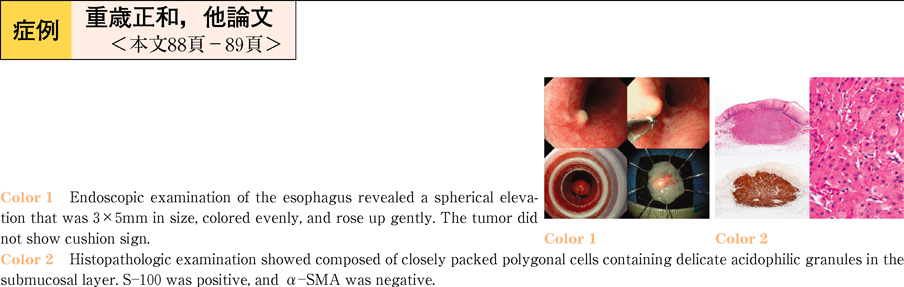
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 88-89
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (763K) -
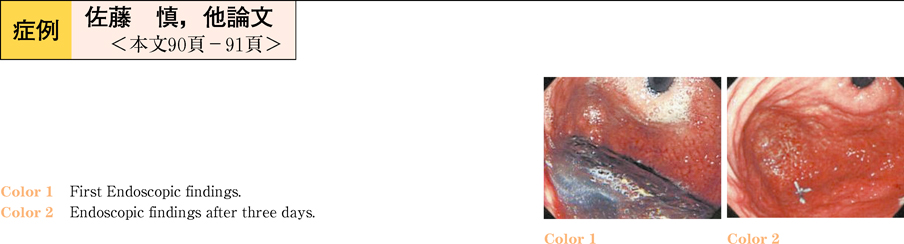
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 90-91
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (731K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 92-93
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (700K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 94-95
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (728K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 96-97
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (752K) -
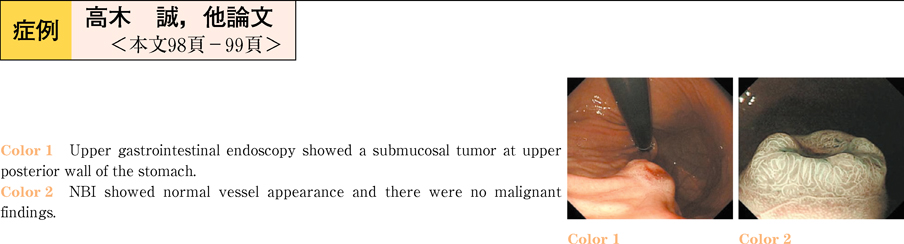
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 98-99
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (894K) -
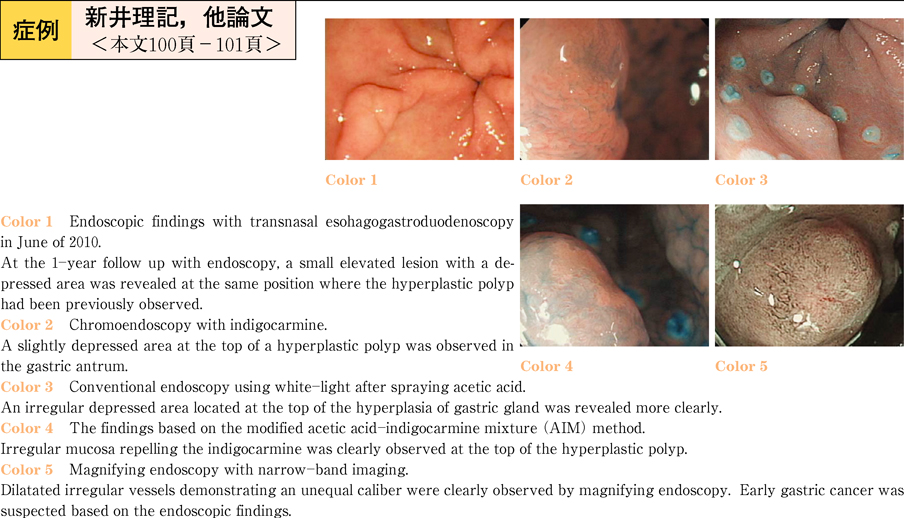
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 100-101
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (891K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 102-103
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (841K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 104-105
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (780K) -
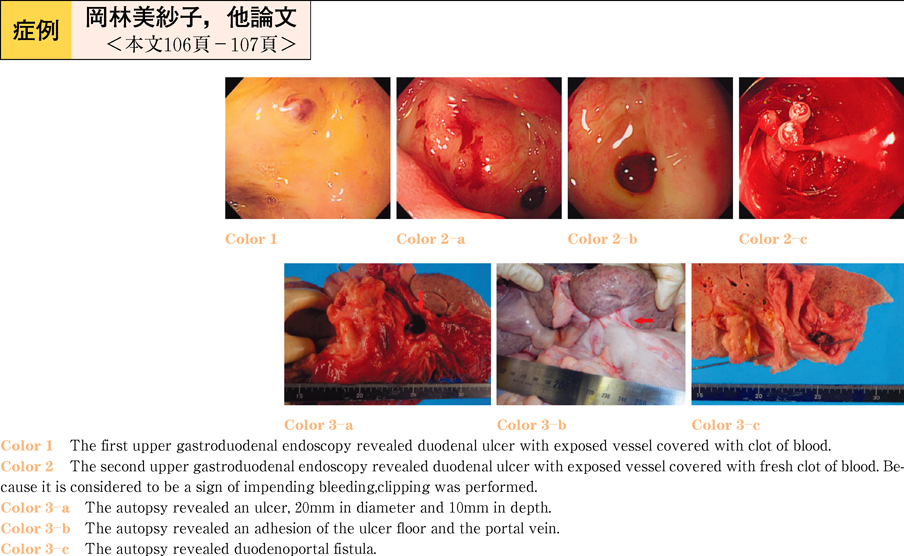
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 106-107
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (804K) -
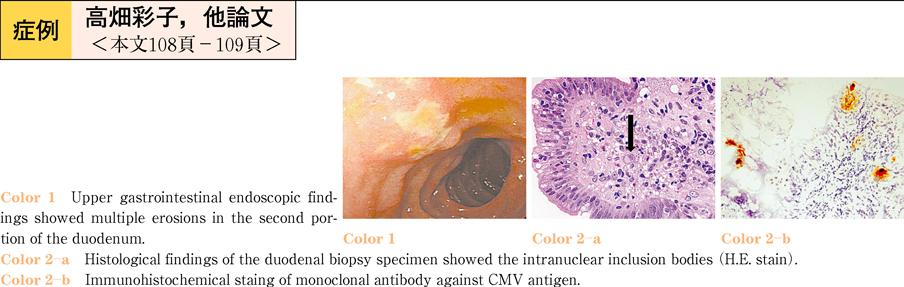
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 108-109
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (768K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 110-111
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (690K) -
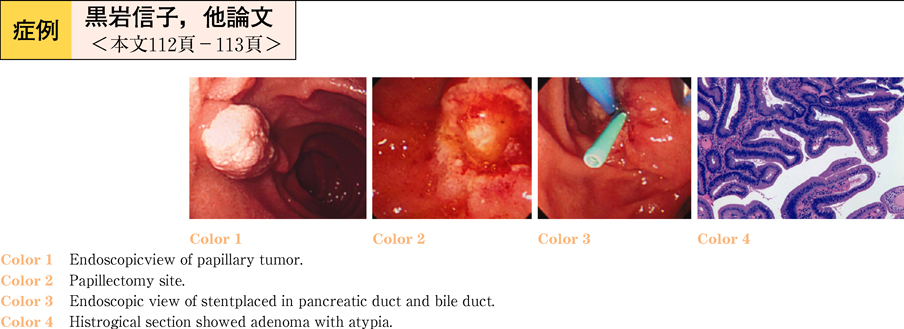
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 112-113
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (690K) -
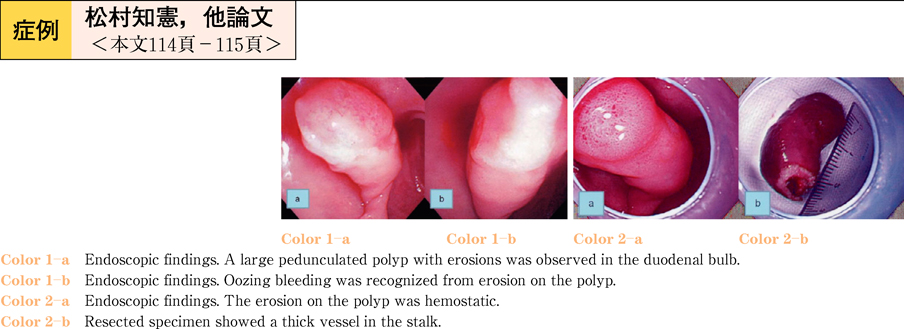
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 114-115
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (826K) -
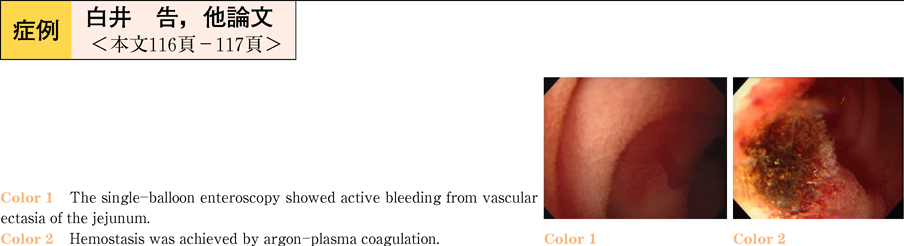
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 116-117
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (691K) -
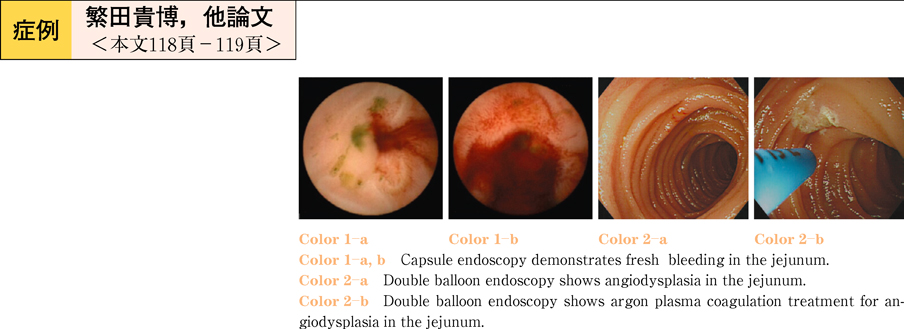
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 118-119
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (700K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 120-121
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (864K) -
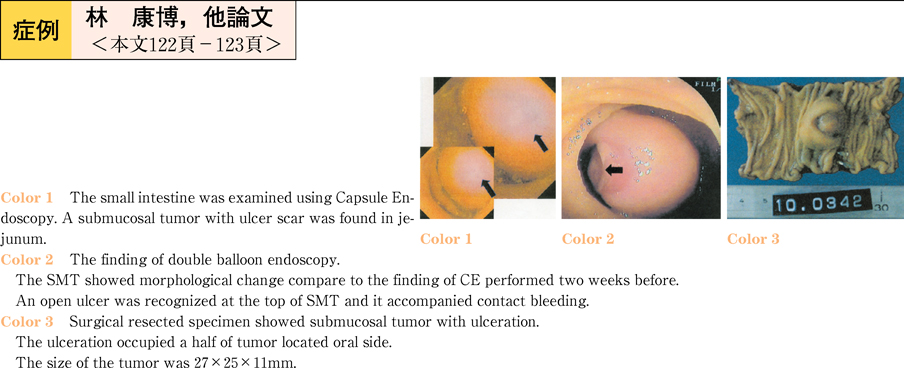
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 122-123
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (870K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 124-125
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (731K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 126-127
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (818K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 128-129
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (651K) -
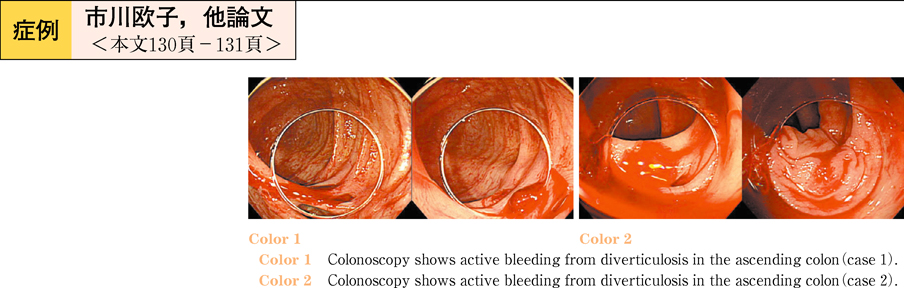
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 130-131
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (786K) -
A case of tubular adenoma of the vermiform appendix resected by Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 132-133
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (599K) -
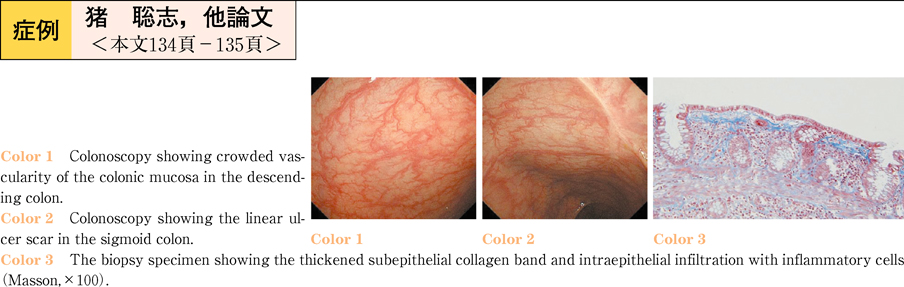
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 134-135
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (594K) -
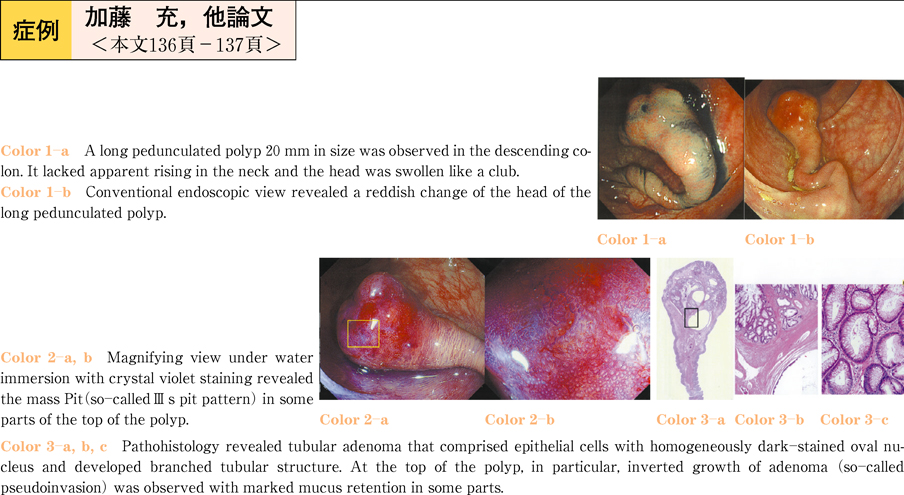
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 136-137
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (735K) -
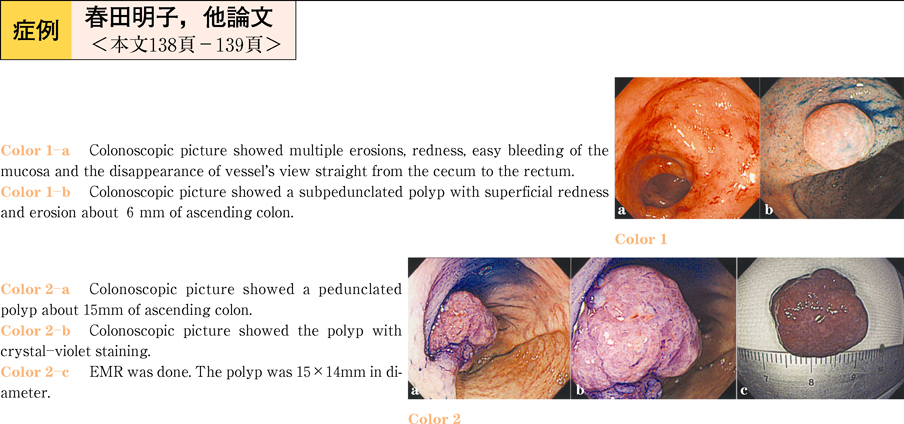
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 138-139
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (820K) -
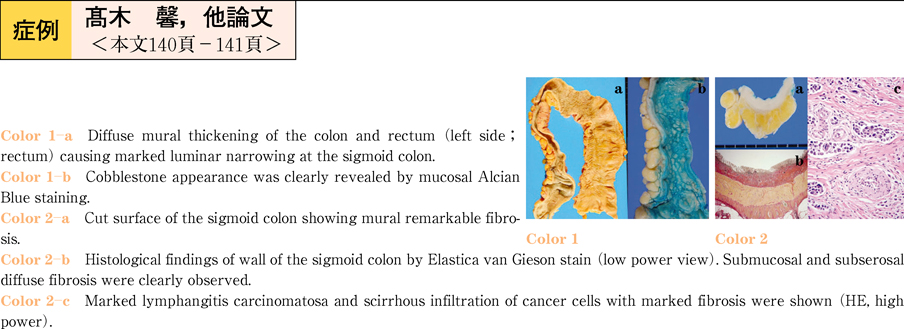
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 140-141
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (744K) -
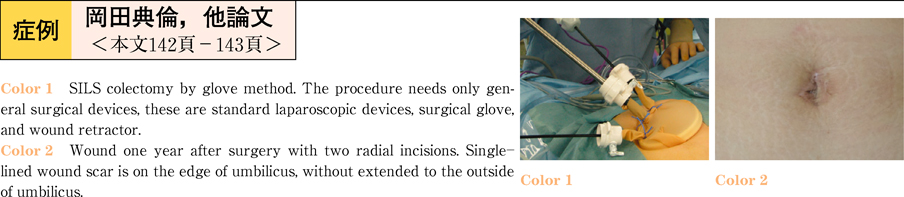
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 142-143
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (606K) -
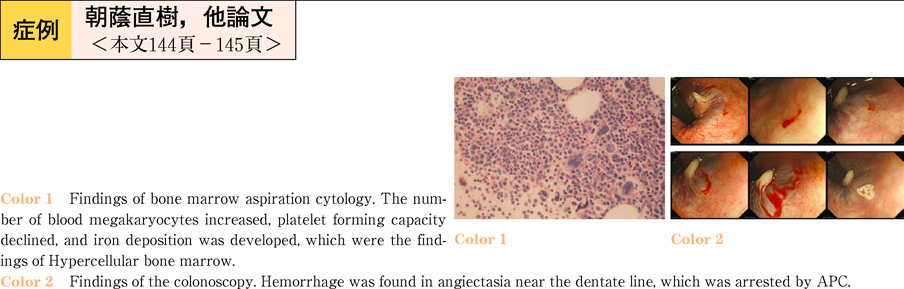
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 144-145
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (663K) -
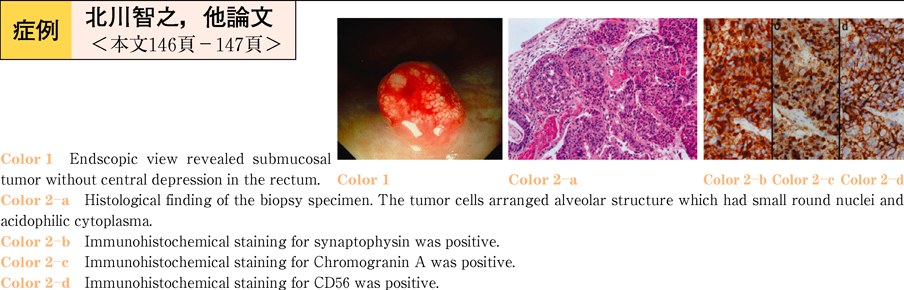
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 146-147
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (748K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 148-149
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (822K) -
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 150-151
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (891K) -
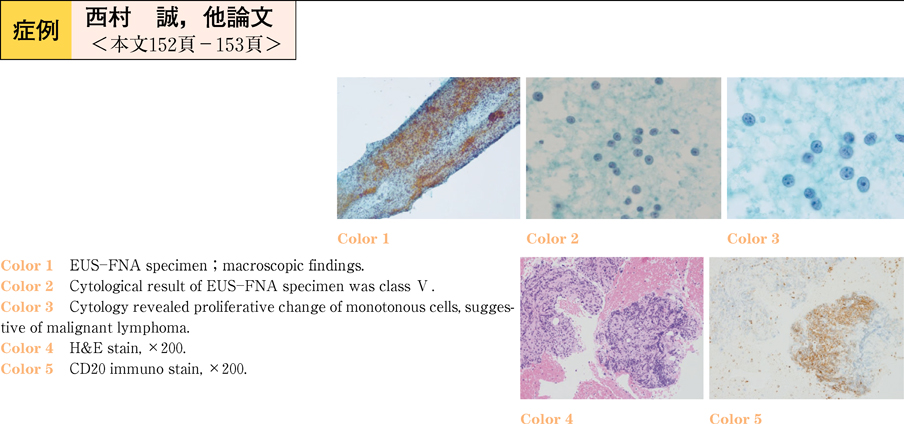
2011Volume 78Issue 2 Pages 152-153
Published: June 10, 2011
Released on J-STAGE: July 19, 2013
Download PDF (692K)