Volume 91, Issue 1
Displaying 1-50 of 60 articles from this issue
Clinical study
-
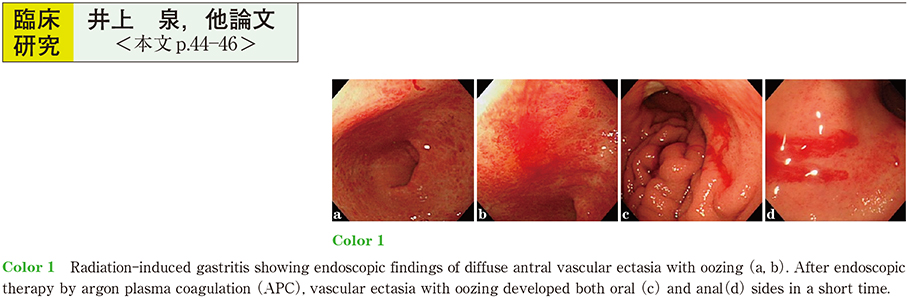
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 44-46
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (708K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 47-51
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (1305K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 52-56
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (1062K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 57-61
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (836K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 62-66
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (874K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 67-71
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (1161K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 72-75
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (724K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 76-80
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (847K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 81-84
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (781K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 85-89
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (1036K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 90-93
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (981K)
Case report
-
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 94-97
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (818K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 98-101
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (1051K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 102-105
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (783K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 106-108
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (849K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 109-113
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (943K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 114-117
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (1115K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 118-119
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (724K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 120-121
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (695K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 122-123
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (846K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 124-125
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (629K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 126-127
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (694K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 128-129
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (753K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 130-131
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (868K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 132-133
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (672K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 134-135
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (655K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 136-137
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (705K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 138-139
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (668K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 140-141
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (936K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 142-143
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (907K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 144-145
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (866K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 146-147
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (687K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 148-149
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (833K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 150-151
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (696K) -
A case of type A gastritis accompanied by eosinophil infiltration in the gastric and duodenal mucosa2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 152-153
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (756K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 154-155
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (592K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 156-157
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (667K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 158-159
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (668K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 160-161
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (784K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 162-163
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (1022K) -
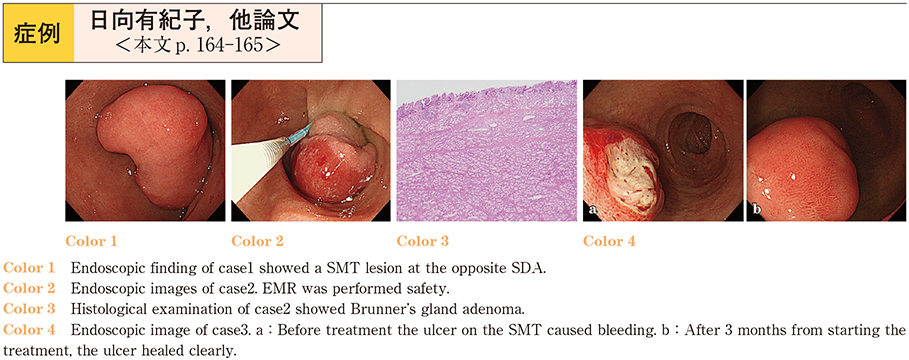
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 164-165
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (913K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 166-167
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (972K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 168-169
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (737K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 170-171
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (1387K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 172-173
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (787K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 174-175
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (905K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 176-177
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (837K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 178-179
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (645K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 180-181
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (646K) -
2017Volume 91Issue 1 Pages 182-183
Published: December 08, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2017
Download PDF (865K)