Volume 86, Issue 1
Displaying 1-50 of 76 articles from this issue
-
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 1-16
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (16805K)
Technology and instrument
-
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 40-43
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (2024K)
Clinical study
-
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 44-48
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1294K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 49-52
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (694K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 53-57
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (676K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 58-62
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (777K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 63-65
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (786K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 66-69
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (607K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 70-73
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1191K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 74-78
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (973K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 79-82
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1016K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 83-86
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (661K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 87-89
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (687K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 90-93
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (643K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 94-98
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (991K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 99-103
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (837K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 104-107
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (639K)
Case report
-
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 108-112
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1726K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 114-115
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (580K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 116-117
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1004K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 118-119
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (798K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 120-121
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (582K) -
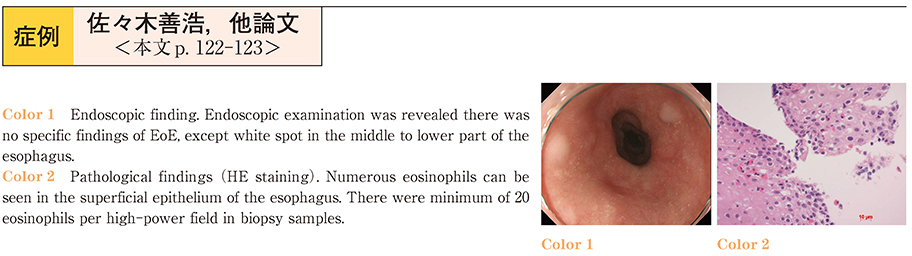
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 122-123
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (866K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 124-125
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1133K) -
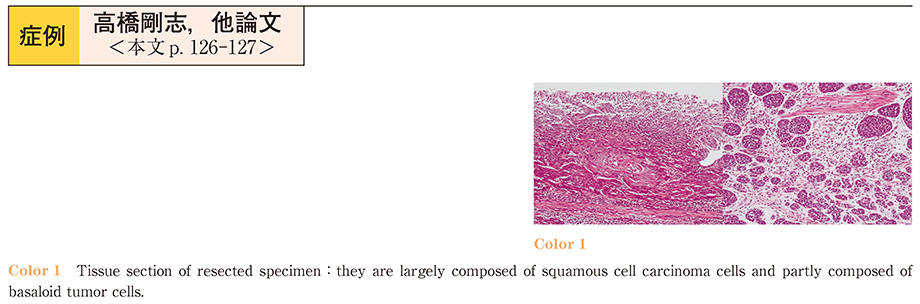
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 126-127
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (970K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 128-129
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (625K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 130-131
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (591K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 132-133
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1170K) -
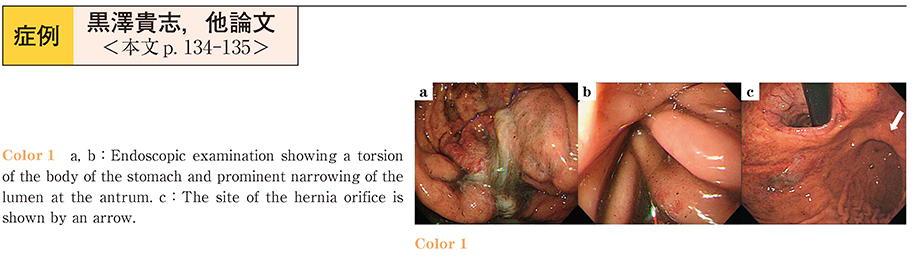
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 134-135
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (882K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 136-137
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (749K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 138-139
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (644K) -
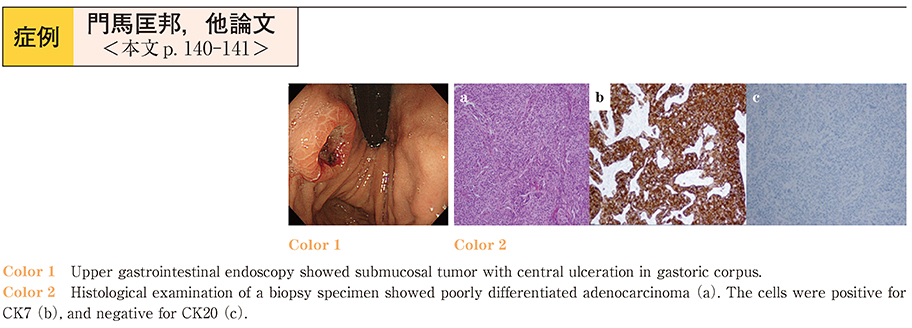
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 140-141
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (935K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 142-143
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1485K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 144-145
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (792K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 146-147
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1180K) -
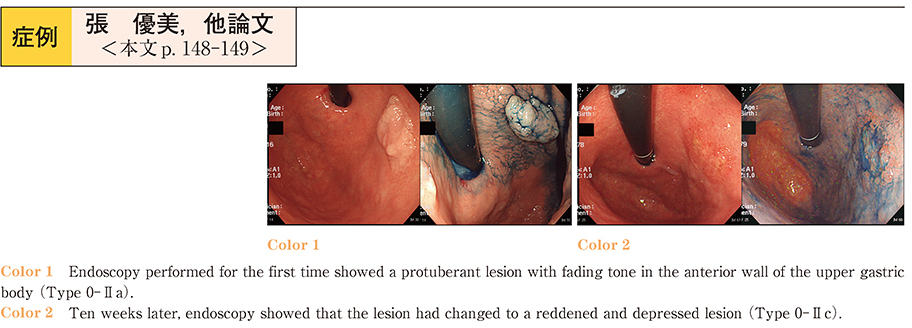
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 148-149
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1655K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 150-151
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (989K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 152-153
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (771K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 154-155
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (706K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 156-157
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1002K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 158-159
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1143K) -
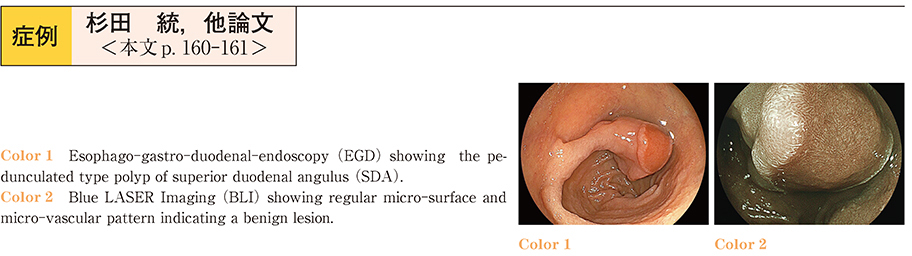
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 160-161
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (1169K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 162-163
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (852K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 164-165
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (896K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 166-167
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (994K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 168-169
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (974K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 170-171
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (846K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 172-173
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (934K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 174-175
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (750K) -
2015Volume 86Issue 1 Pages 176-177
Published: June 18, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 23, 2015
Download PDF (805K)