
- Issue 4 Pages 279-
- Issue 3 Pages 181-
- Issue 2 Pages 99-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Akira Mitani2025 Volume 83 Issue 4 Pages 279
Published: April 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 08, 2025
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (156K)
-
Keisuke Nishikawa, Momochika Kumagai, Tomoki Tsuruta, Yoshiki Morimoto2025 Volume 83 Issue 4 Pages 280-292
Published: April 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 08, 2025
JOURNAL RESTRICTED ACCESSThe epoxide-opening cascade biogenesis was originally proposed for ionophoric polyether antibiotics as in the Cane-Celmer-Westley hypothesis and has been utilized as an efficient method to rapidly construct natural polyether skeletons. For example, teurilene, the marine polyether derived from red algae, was synthesized from squalene tetraepoxide, a hypothetical biogenetic precursor, via a three-step, 5-exo selective epoxide-opening cascade cyclization triggered by Brønsted-acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the terminal epoxide. In previous work, it was shown that the epoxide-opening cascade cyclization that produces tetrahydrofuran (THF) products in acidic aqueous media instead yields tetrahydropyran (THP) in neutral water. The THP formation proceeded via an epoxonium-ion intermediate by simple heating in neutral water. In this report, we successfully established a “ring-size-divergent” synthetic method to divergently construct five-, six-, and seven-membered ether rings from identical diepoxides, achieving the synthesis of seven-membered (oxepane) ring under acidic conditions using Lewis acid. With this new synthetic strategy, we also accomplished the divergent synthesis of nerolidol-type sesquiterpenoids and feroniellins, revising the proposed stereochemistry of certain natural products and determining their absolute configurations. Additionally, we evaluated the anti-inflammatory activities of the synthetic samples.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2861K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2861K) -
Goh Sennari, Tomoyasu Hirose, Toshiaki Sunazuka2025 Volume 83 Issue 4 Pages 293-304
Published: April 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 08, 2025
JOURNAL RESTRICTED ACCESSTotal synthesis studies of bioactive natural products have served as the foundation in drug discovery research. Particularly, it plays an important role when only a small quantity of materials can be gained through the natural source. Puberulic acid, stipitatic acid, and new troponoid congeners, viticolins A-C were isolated as antimalarial agents from the culture broth of a fungal strain at our institute. Their great biological potential and unique structures led us to undertake the synthetic study of this natural product class. We identified that the core highly oxidized tropone motif in puberulic acid well maps on the common structural feature of carbohydrates, which are often referred to as the “chiral pool”. Instead of taking advantage of the stereochemical information, we were drawn to utilize their carbon-oxygen bond backbone as a “framework source”. In this Account, we summarize previous total syntheses of puberulic acid and detail our efforts toward the gram-scale synthesis of this natural product and related congeners.
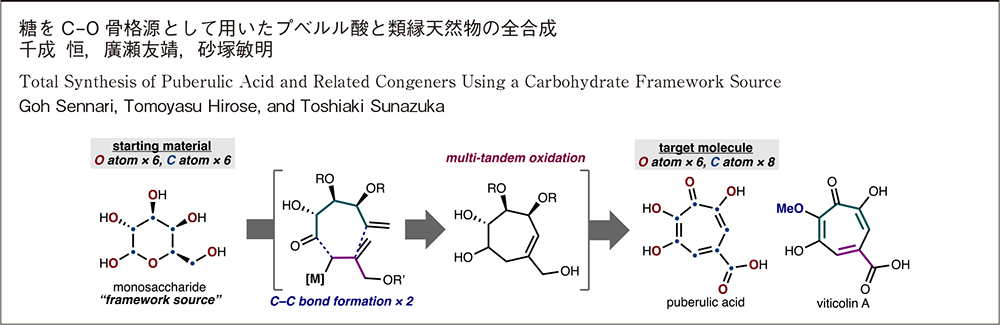 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1181K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1181K) -
Yousuke Yamaoka, Kiyosei Takasu2025 Volume 83 Issue 4 Pages 305-314
Published: April 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 08, 2025
JOURNAL RESTRICTED ACCESSHeterocycles are an important and attractive class of compounds for medicinal and material chemistries because of their biological importance and structural features. Meanwhile, ynamides have received much attention as fascinating building blocks for the synthesis of nitrogen-containing compounds because of their availability and unique reactivity. In particular, the ring-forming reactions of ynamide are an efficient and atom-economical method for the synthesis of nitrogen-containing cyclic molecules. In the review, we introduce our recent transformations of ynamides with acid catalysts to construct heterocyclic compounds. First, we demonstrated Brønsted acid promoted arene-ynamide cyclization to construct multicyclic quinolines toward the total synthesis of marinoquinolines and aplisiopsamine A. Moreover, Lewis acid catalyzed diastereoselective domino reaction of ene-ynamide with external nucleophiles to yield spiroindolopyrrolidine derivatives was developed. Finally, we demonstrated efficient synthesis of medium-sized nitrogen heterocycles by Brønsted acid-catalyzed cyclization of ene-ynamides.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1419K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1419K) -
Kotohiro Nomura, Akito Nishiyama, Shuko Kuwahara2025 Volume 83 Issue 4 Pages 315-325
Published: April 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 08, 2025
JOURNAL RESTRICTED ACCESSRecent reports for synthesis of group 5 transition metal-alkylidene complexes (especially vanadium and niobium complexes possessing multiple metal-carbon bonds in high oxidation state) have been reviewed. Some of these complexes display unique characteristics as catalysts for olefin/alkyne metathesis polymerization. In particular, the (arylimido)vanadium and the niobium complexes demonstrate unique characteristics as the thermally robust, highly active, stereospecific catalysts for ring opening metathesis polymerization of cyclic olefins and alkyne metathesis polymerization, that are not attained by conventional Schrock-type (molybdenum, tungsten) and Grubbs-type ruthenium catalysts.
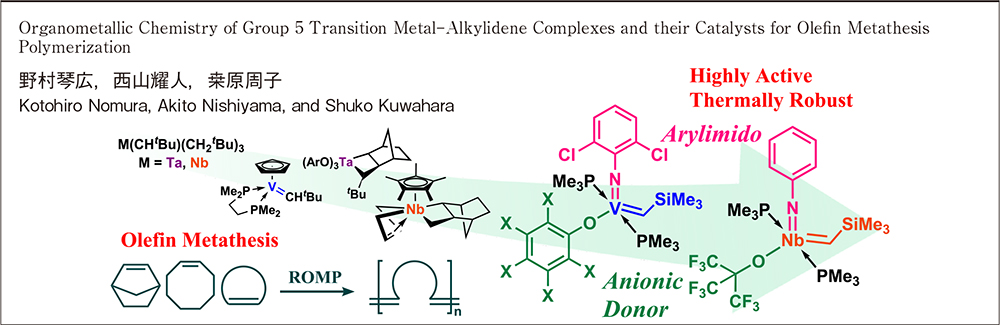 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2455K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2455K) -
Masaki Yoshida2025 Volume 83 Issue 4 Pages 326-338
Published: April 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 08, 2025
JOURNAL RESTRICTED ACCESSStimuli-responsive luminescent materials, so-called “luminescent chromic materials,” have attracted increasing interest due to their wide range of applications, including optoelectronic devices, luminescent sensors, and probes. In particular, self-assembled square-planar platinum(II) complexes have occupied a unique position because of their intense and stimuli-responsive luminescent properties arising from the metallophilic interactions. However, the design strategies for the chromic platinum(II) complexes remain a significant challenge. The author has recently focused on the development of this molecular design strategy for the stimuli-responsive luminescent platinum(II) complexes. In this account, the design principle of strongly luminescent platinum(II) complexes is first introduced, followed by the principle of luminescence color change due to metallophilic interactions. Finally, our concept of designing luminescent chromic platinum(II) complexes with counter cations is presented, as a means to more conveniently and strategically design metastable and transient states.
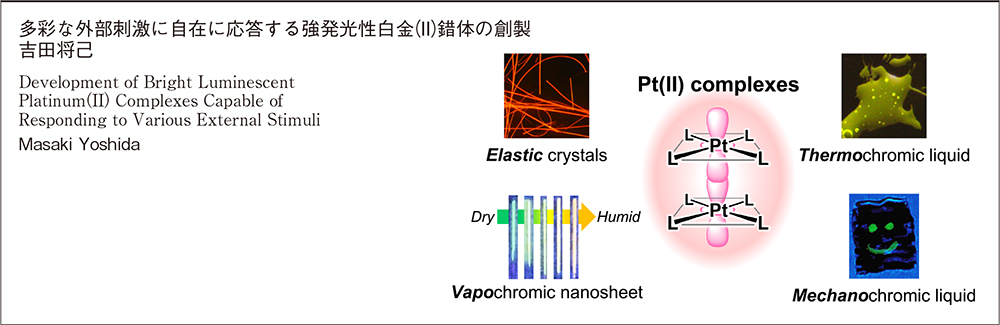 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (10091K)
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (10091K)
-
Kenta Tanaka2025 Volume 83 Issue 4 Pages 339-340
Published: April 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 08, 2025
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMacrolactones are structurally important motifs found in a variety of natural products and bioactive compounds. Conventional approaches to their synthesis include the use of seco acids via activation of acid. This short review focuses on the recent progress in photochemical macrolactonization by controlling radical reactivity. The macrolactonization via radical processes introduces a new methodology for total synthesis of natural products.
View full abstractDownload PDF (493K)
-
Kazunobu Igawa2025 Volume 83 Issue 4 Pages 341-344
Published: April 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 08, 2025
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (403K)
-
[in Japanese], [in Japanese], [in Japanese], [in Japanese], [in Japane ...2025 Volume 83 Issue 4 Pages 345
Published: April 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 08, 2025
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (222K)
-
Takeshi Ohkuma2025 Volume 83 Issue 4 Pages 347-351
Published: April 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: April 08, 2025
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1089K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|