
- Issue 2 Pages 45-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Katsuhiko TAKEUCHIArticle type: Review Paper
2024 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 45-51
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
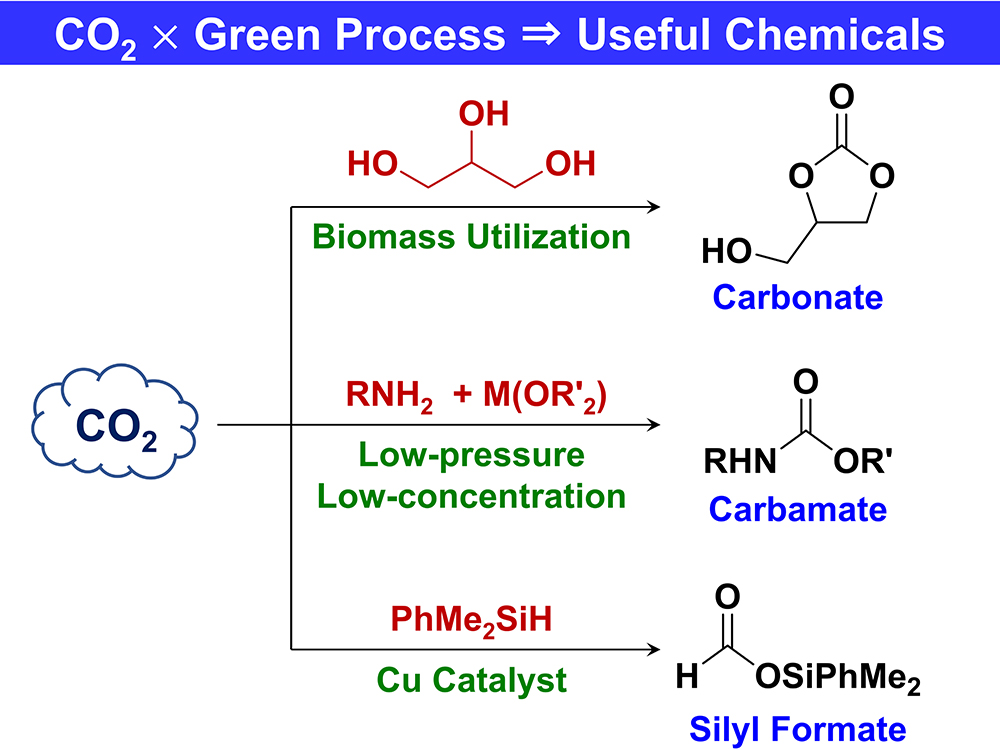
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis review describes our recent developments for the efficient synthesis of carbonate derivatives, carbamate derivatives, and silyl formates using carbon dioxide (CO2) as a raw material. CO2 emitted by combustion of fossil fuels and other sources is a major cause of global warming. Synthesis of useful chemicals from CO2 as a raw material has potential as an effective method of reducing CO2 emissions. However, the use of reagents and reaction processes with high environmental impacts must be avoided. Our present synthesis methods are notable for both simple use of CO2 and environmental friendliness due to the use of biomass resources, recyclable and reusable reagents, low quality CO2, and inexpensive zinc and copper catalysts. The target compounds are all useful chemicals: carbonate derivatives are raw materials for polycarbonates, carbamate derivatives are raw materials for polyurethanes, and silyl formates are reagents used for introducing the formyl group. We expect that these environmentally friendly methods to synthesize useful compounds will make important contributions to reducing CO2 emissions.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (500K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (500K) -
Hiroyasu FUJITSUKAArticle type: Review Paper
2024 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 52-60
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
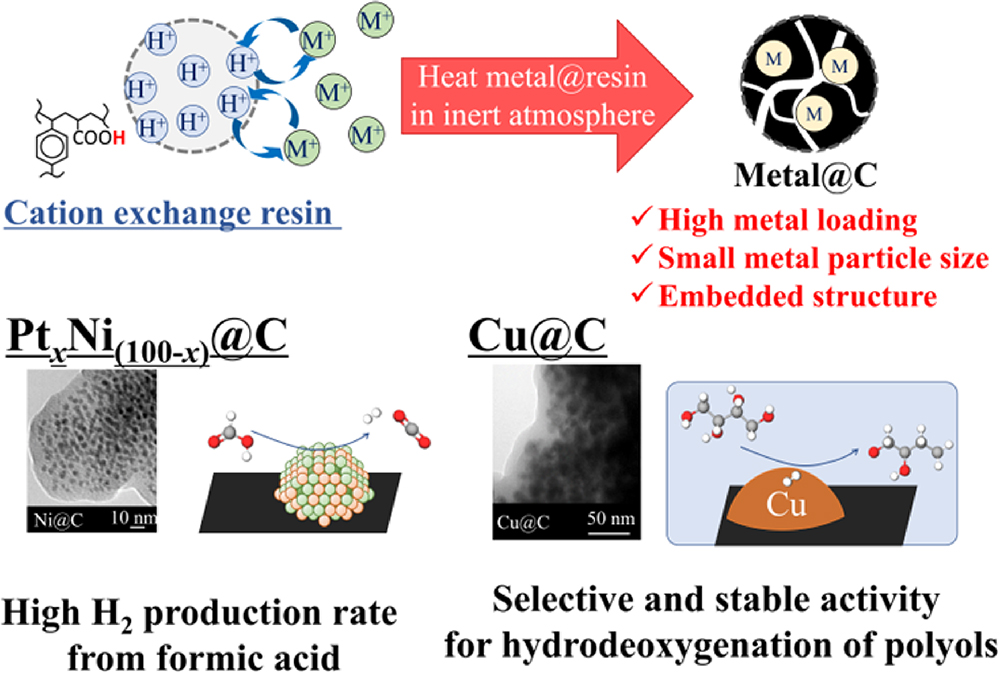
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCarbon supports are frequently used for catalyst supports due to their large surface areas and inert nature, which allows selective reactions on metal catalysts. However, carbon-supported metal catalysts exhibit poor stability because the interaction between the metal and carbon is not strong, and agglomeration of metal nanoparticles is likely to occur. To overcome this problem, the author focused on a new synthesis method for carbon-supported metal nanoparticle catalysts (metal@C) which uses ion-exchange resin as the carbon source. This method involves an ion-exchange step followed by a carbonization step. The carbon support and metal nanoparticles are formed simultaneously, so the metal nanoparticles are partially embedded in the carbon support. In this paper, the preparation procedure of metal@C catalysts and their physicochemical properties are described. The prepared PtNi@C exhibited high hydrogen production rate from formic acid because of the concentrated active sites, and the Cu@C showed high selectivity and stable activity for hydrodeoxygenation of polyols because of the inertness of the carbon support and metal embedded in the carbon structure, respectively.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3258K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3258K)
-
Hung Quang Viet NGUYEN, Kouki KUNIEDA, Shinya MATSUURA, Tadanori HASHI ...Article type: Regular Paper
2024 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 61-70
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
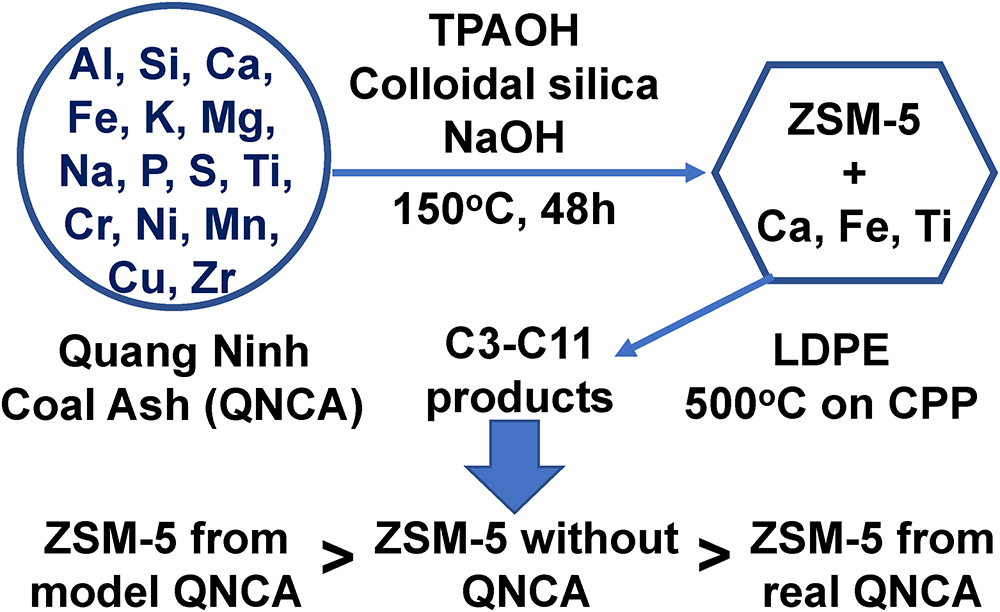
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCoal of Quang Ninh (QN) province (Vietnam) is high quality and famous worldwide. QN coal ash includes large amounts of Al2O3 and SiO2 which can be utilized for zeolite synthesis. In this study, inorganic components of QN coal ash were assembled to prepare ZSM-5 zeolite under several conditions. The effects of components, which are included in real coal ash but are not needed to prepare zeolite, were investigated on the preparation and the property of zeolite. Synthesis of ZSM-5 using tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (TPAOH) at 150 °C for 48 h confirmed that ZSM-5 crystals appeared at SiO2/Al2O3 ratios higher than 52 and developed completely at 78, based on XRD and nitrogen adsorption-desorption measurement. Similar results were observed for ZSM-5 synthesis both without QN coal ash components and with real QN coal ash, indicating that the effects of components other than Si and Al on the preparation of ZSM-5 are quite small. When these catalysts were used for the catalytic cracking of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) using the Curie point pyrolyzer (CPP) method, ZSM-5 prepared using model coal ash components exhibited the same or slightly higher conversion than conventional ZSM-5. In contrast, ZSM-5 prepared with real coal ash components exhibited slightly lower conversion, suggesting that some inorganic salts included in real coal ash might affect the activity for catalytic cracking of LDPE.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1128K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1128K) -
Keiju WACHI, Tomohiro YABE, Ryo NAKANO, Makoto YAMASHITA, Kazuya YAMAG ...Article type: Regular Paper
2024 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 71-79
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
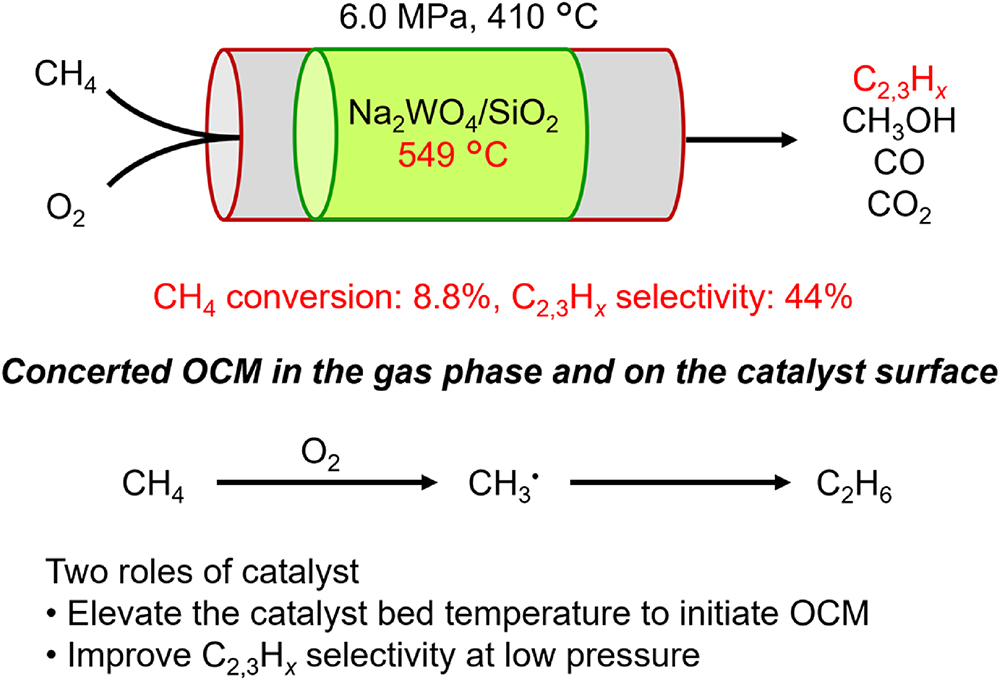
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDirect conversion of methane into useful chemicals has attracted great attention as an alternative to the current syngas process. Methane oxidation achieves high methane conversion under high-pressure conditions through homogeneous radical reactions; however, control of product selectivity using catalysts remains a challenge. This study found that the oxidative coupling of methane occurred efficiently at 410 °C and 6.0 MPa using Na2WO4/SiO2 as both initiator and catalyst. In this catalytic system, C2 and C3 hydrocarbons were mainly obtained from methane and oxygen through concerted reactions both in the gas phase and on the catalyst surface. Furthermore, methane oxidation experiments under various reaction conditions revealed that the selectivity of homogeneous methane oxidation in the gas phase shifted from methanol to C2 and C3 hydrocarbons, due to the exothermic catalytic reaction and the temperature increase in the catalyst bed. Furthermore, the catalytic reaction also improved the selectivity for C2 and C3 hydrocarbons at lower pressures. These different roles of the catalyst offer valuable insights for developing high-pressure partial oxidation of methane to form methanol.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2496K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2496K) -
Shotaro TANI, Yuichi ICHIHASHIArticle type: Regular Paper
2024 Volume 67 Issue 2 Pages 80-88
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
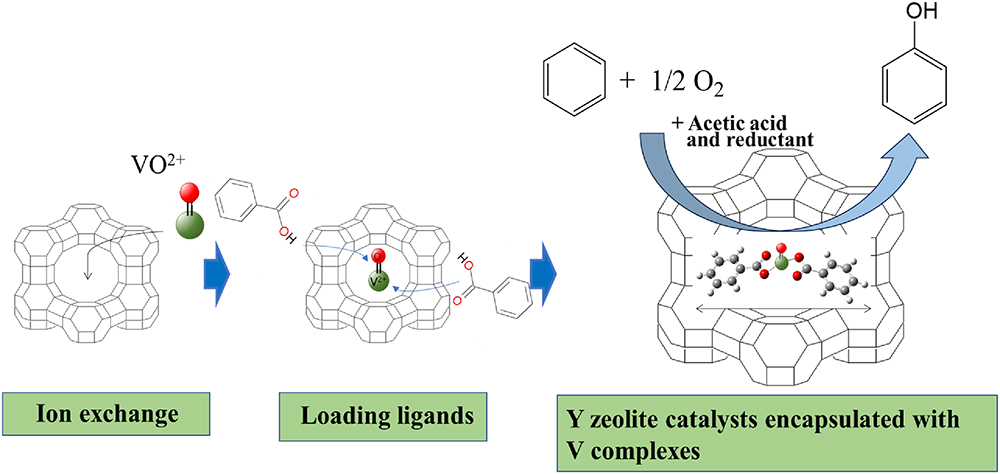
Supplementary materialVanadium-loaded catalysts used in direct liquid-phase oxidation of benzene have low reusability attributable to the elution of V species into the reaction solution. Herein, V complexes were encapsulated in Y zeolite to prevent the elution of V species in the catal+yst used for phenol formation during the direct oxidation of benzene in the liquid phase. V complex catalysts encapsulated in Y zeolite were prepared by mixing Y zeolite loaded with V species using solutions containing different ligands. Using acetic acid as the solvent improved the reusability of the encapsulated V complex catalyst. The catalytic activity of the V complex catalyst for phenol formation was influenced by the ligand effect. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations indicated that the type of ligand also affected the energy gap between V3+ and V4+, which is directly related to phenol formation in the present reaction. DFT calculations were further used to identify the mechanism for the liquid-phase oxidation of benzene.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3930K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3930K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|