
- Issue 12 Pages 695-
- Issue 11 Pages 611-
- Issue 10 Pages 551-
- Issue 9 Pages 485-
- Issue 8 Pages 405-
- Issue 7 Pages 345-
- Issue 6 Pages 281-
- Issue 5 Pages 239-
- Issue 4 Pages 191-
- Issue 3 Pages 137-
- Issue 2 Pages 83-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- Issue Special_Issue P・・・
- Issue Supplement2 Pag・・・
- Issue Supplement1 Pag・・・
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Takuya Mori, Hiroaki Tanaka, Mami Yoshii, Tatsuro Tamura, Takahiro Toy ...Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
2021Volume 54Issue 7 Pages 437-446
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 29, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPurpose: The effects of gastrectomy on body weight, blood glucose, and lipids were investigated in patients with gastric cancer. Materials and Methods: Data from 299 patients with gastric cancer who received curative gastrectomy in our department between January 2014 and July 2018 were analyzed retrospectively. The body weight reduction ratio (BWRR) one year after surgery was calculated and changes of fasting blood sugar (FBS) and HbA1c in 58 cases with diabetes mellitus and those of total cholesterol and triglycerides in 74 cases with dyslipidemia were examined. Regarding above mentioned factors, patients with improvement of diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia were compared with those without improvement. Result: The median BWRR was 9.45% and there was a significant difference in surgical procedures (total gastrectomy vs distal or proximal gastrectomy: 14.5% vs 8.9%; P=0.0005). In patients with diabetes mellitus, the average FBS and HbA1c improved from 150 mg/dl to 128 mg/dl and from 7.06% to 6.51%, respectively. In patients with dyslipidemia, triglycerides significantly decreased from 189 mg/dl to 107 mg/dl. The changes of FBS, HbA1c, total cholesterol, and triglycerides were not significantly influenced by the surgical procedures. No significant factors were found that affected improvement of diabetes mellitus. However, patients with improvement of diabetes mellitus tended to have undergone Roux-en-Y reconstruction. Dyslipidemia tended to improve in patients with a high BWRR. Conclusion: Preoperative diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia both improved after gastric cancer surgery. Roux-en-Y reconstruction may be preferable, especially in patients with diabetes mellitus.
View full abstractDownload PDF (605K) Full view HTML -
Keiji Nagata, Taku Iida, Shigeyuki Harada, Aya Mori, Masato Matsuura, ...Article type: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
2021Volume 54Issue 7 Pages 447-455
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 29, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPurpose: The treatment strategy for acute cholecystitis (AC) is based on clinical guidelines such as the Tokyo Guidelines 2018, and early surgery is recommended. However, we sometimes encounter patients with AC who are high risk for early emergency surgery. Materials and Methods: From November 2013 to October 2018, 201 patients with AC underwent emergency surgeries at our hospital. These patients were divided into groups based on the time from AC onset to surgery and age: (1) early cholecystectomy within 72 hours of AC onset (n=159) and delayed cholecystectomy over 72 hours after AC onset (n=42); and (2) extremely elderly patients over 85 years old (n=23) and patients less than 85 years old (n=178). Clinical outcomes were compared for each of these groups. Result: In patients with early cholecystectomy, the rate of laparoscopic cholecystectomy (Lap C) was significantly higher (82.4% vs. 57.1%, P=0.0005), intraoperative blood loss was significantly lower (92.9 vs. 185.1 ml, P<0.0001), the postoperative complication rate was significantly lower (6.3% vs. 16.7%, P=0.03), and the postoperative hospital stay was significantly shorter (7.4 vs. 8.5 days, P=0.029). Extremely elderly patients had significantly higher intraoperative blood loss (166.1 vs. 105.2 ml, P=0.04) and a significantly longer postoperative hospital stay (14.2 vs. 6.8 days; P=0.0001) compared to patients less than 85 years old, but there were no differences in the rates of Lap C (65.2% vs. 78.7%, P=0.15) and postoperative complications (13.0% vs. 7.9%, P=0.40). Conclusion: Patients with AC who underwent surgery at more than 72 hours after onset and extremely elderly patients over 85 years old had increased intraoperative blood loss and a prolonged postoperative hospital stay. Therefore, careful perioperative management may be required in these high risk patients with AC.
View full abstractDownload PDF (514K) Full view HTML
-
Noriko Kawai, Makoto Omi, Satoko Yorinaga, Takehiro Maki, Hiroyuki Kan ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2021Volume 54Issue 7 Pages 456-463
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 29, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA 67-year-old woman was transferred to our hospital because of severe abdominal pain. An abdominal CT scan showed free air and fluid collection in the peritoneal space. Under a diagnosis of panperitonitis due to duodenal perforation, an emergency operation was performed. On laparotomy, multiple duodenal perforations were observed. Furthermore, extensive mucosal necrosis was present from the duodenal bulb to the second part beyond the papilla of Vater. Emergency pancreatoduodenectomy was performed, but digestive tract reconstruction was abandoned as damage control because the patient entered a shock state. After external fistulation tubes were placed in the bile duct, pancreatic duct and stomach, the abdominal wall was closed. Two-stage surgery for digestive tract reconstruction was performed 72 hours after the first surgery when the systemic condition had stabilized. Although complications such as bleeding, thyroid crisis, and intractable arrhythmia occurred postoperatively, the patient recovered and was moved to a rehabilitation ward 65 days after the first surgery. Emergency pancreatoduodenectomy due to duodenal injury or bleeding is relatively rare, and there has been no report of pancreatoduodenectomy for panperitonitis due to duodenal necrosis. Thus, we report this case as a rare use of this treatment.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1106K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1106K) Full view HTML -
Hikaru Aoki, Kenya Yamanaka, Ai Izumi, Tokuyuki Yamashita, Makoto Kuri ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2021Volume 54Issue 7 Pages 464-470
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 29, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThere are several treatment options for symptomatic polycystic liver disease, but no consensus has been established on the best surgical practice for this disease. The patient was a 49-year-old Japanese woman with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Her chief complaint was massive abdominal distention and early satiety. CT showed a polycystic kidney and liver, and the stomach was compressed by the massive polycystic liver. Liver and renal functions were within normal levels. The left lateral segment of the liver was almost replaced with large cysts and the posterior segment was occupied by several cysts. Hepatic left lateral segmentectomy and fenestration in the posterior segment were performed. After the surgery, her chief complaint improved, and the volume of the parenchyma increased by 20%, while that of the liver decreased to 54%.
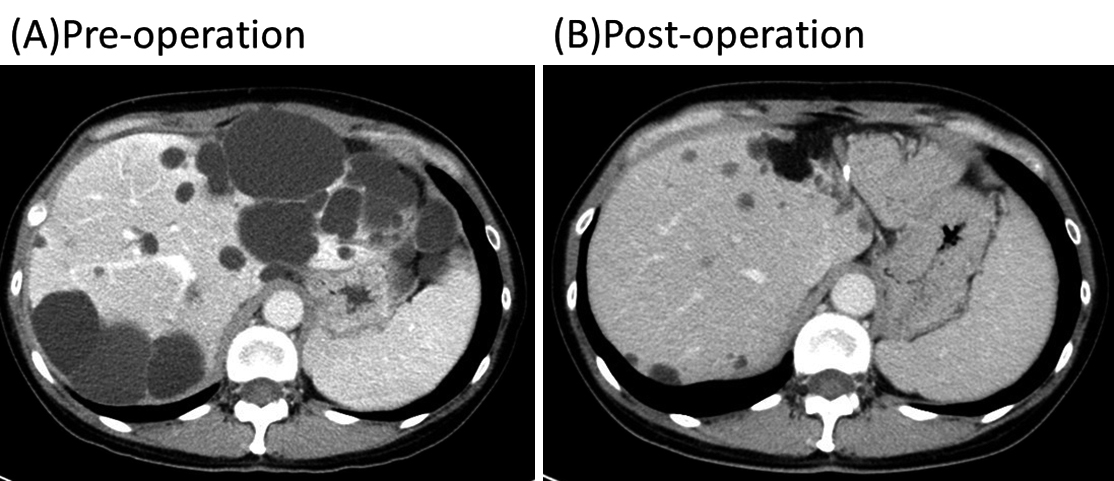 View full abstractDownload PDF (841K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (841K) Full view HTML -
Takashi Shigeno, Koji Ito, Yoshiteru Ohata, Hiroki Ueda, Toshiro Tanio ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2021Volume 54Issue 7 Pages 471-479
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 29, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA 66-year-old woman was referred to our hospital after CT incidentally revealed a tumor in the pancreatic head. Contrast-enhanced CT showed a multifocal and microcystic tumor of around 45 mm in the pancreatic head that was enhanced in the early phase. This imaging also showed a tumor of around 10 mm with poor contrast enhancement in the pancreatic body that was accompanied by pancreatic duct dilation. Pancreatic serous cystadenoma (SCA) in the pancreatic head and carcinoma of the pancreatic body were diagnosed, and total pancreatectomy was performed. Histopathological examination showed that both tumors were SCA. SCA is a benign tumor that generally occurs as a single lesion and is not associated with pancreatic duct stenosis. Multiple SCA is rare. SCA larger than 4 cm has been found to be more likely to cause subjective symptoms and is suitable for surgery. A tumor in the pancreatic body accompanied by stenosis of the main pancreatic duct may also be pancreatic carcinoma. For these reasons, we selected total pancreatectomy in our case.
View full abstractDownload PDF (942K) Full view HTML -
Kodai Abe, Minoru Kitago, Yohei Masugi, Masahiro Shinoda, Hiroshi Yagi ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2021Volume 54Issue 7 Pages 480-489
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 29, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCase 1: The patient was a 47-year-old woman who underwent subtotal stomach-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy (SSPPD) for suspected pancreatic cancer. The pancreatic tail was replaced by fat and the main pancreatic duct was not identified in the remnant pancreatic segment; therefore, the pancreatic segment was sutured without pancreaticojejunal anastomosis, and the upper intestine and pancreatic parenchyma were closely sutured. The patient was discharged on postoperative day 33 without evidence of endocrine dysfunction, although postoperative pancreatic juice leakage was observed. She has had no recurrence for 2 years and 5 months postoperatively, with good glucose tolerance. Case 2: The patient was a 46-year-old man with a history of chronic pancreatitis who underwent SSPPD for a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. The pancreatic parenchyma was replaced by fat and the main pancreatic duct could not be identified. Histopathological examination of an intraoperative frozen section revealed only islets of Langerhans in the specimen with main pancreatic duct regression; therefore, the pancreatic parenchyma was sutured closed and the remnant pancreas was left intact. Postoperatively, only a mild decrease in serum C-peptide was observed and the patient was administered Humalog 2-2-2 with regular follow-up. In patients who undergo pancreaticoduodenectomy for fat replacement of the pancreatic tail, pancreatectomy with pancreatic remnant preservation may achieve better glucose tolerance than total pancreatectomy. This is because the former procedure ensures that the islets of Langerhans remain intact as far as possible.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1581K) Full view HTML -
Shinya Kato, Kazuhiro Nishikawa, Takuya Hamakawa, Ryo Shimoyama, Masak ...Article type: CASE REPORT
2021Volume 54Issue 7 Pages 490-496
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 29, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA 39-year-old man underwent tumor resection for a left upper arm malignant melanoma in 2011, and was treated with nivolumab for recurrence in the lung and brain. In July 2017, he had an emergency check-up at our hospital because of a terrible abdominal pain in his right hypochondrium. Contrast-enhanced CT showed target signs suggesting multiple small intestinal intussusceptions, so we decided to perform emergency surgery. Upon laparoscopic observation, there were brown tumors and multiple small intestinal intussusceptions in several places in the small intestine. We finally confirmed 8 brown tumors and multiple intussusceptions in 5 places by palpation. All intussusceptions occurred due to the presence of tumors, and laparoscopy-assisted partial resection of the small intestine was performed. Histopathological diagnosis revealed melanin granules in atypical cells of the tumors, and immunostaining was positive for S-100, Melan-A, and HMB45. All these findings were consistent with small intestinal metastasis of cutaneous malignant melanoma. We report this case as a rare example of malignant melanoma with small intestinal metastases resulting in 5 multiple intussusceptions.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1389K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1389K) Full view HTML
-
Yudai Kuroiwa, Hiroaki Motoyama, Akira Shimizu, Tsuyoshi Notake, Kenta ...Article type: CLINICAL EXPERIENCE
2021Volume 54Issue 7 Pages 497-503
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 29, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe patient was a 66-year-old male who had undergone hepatopancreatoduodenectomy as treatment for bile duct cancer. Abdominal CT performed 5 months after primary surgery revealed a pancreatic pseudocyst (PPC) in the pancreaticojejunostomy. Two months after detection of the PPC, the patient developed abdominal pain and visited the emergency department. After a close examination, the cause of his abdominal pain was diagnosed as acute pancreatitis due to expansion of the PPC. Transjejunal endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage was performed under laparotomy using a laparoscopic trocar inserted into the blind end of the jejunal limb, and this resulted in successful endoprosthesis of the PPC content.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1106K) Full view HTML
-
Yusuke KinugasaArticle type: EDITOR'S NOTE
2021Volume 54Issue 7 Pages en7-
Published: July 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 29, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (151K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|