-
Lu Xie, Yue-Ming Wang, Xiang Xiong, Zhao-Ke Chen, Ya-Lei Wang
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1867-1871
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
Advance online publication: November 09, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
The Fe-based (iron-based) amorphous coatings were prepared by detonation spray at various oxygen fuel rates. The microstructure and wear properties were examined. The amorphous phase contents of coatings were calculated to be 89.73%, 86.23% and 81.46%, respectively, which were higher than those fabricated by other thermal spray techniques. The porosity was tested to be 2.1%, 1.4% and 0.8%, respectively. The wear resistance of Fe-based amorphous coatings was four times better than the stainless steel substrate. The oxygen fuel rate of 1.2 m3/h∼1.0 m3/h was proved to be the optimal parameter of fabricating Fe-based amorphous coating. The effects of oxygen fuel rate were discussed.
View full abstract
-
Shuhei Murakami, Minho O, Masanori Kajihara
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1872-1877
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
To examine the kinetics of the reactive diffusion in the solid-Ni/liquid-Zn system, an isothermal bonding technique was used to prepare semi-infinite Ni/Zn diffusion couples. The diffusion couples were isothermally annealed in the temperature range of T = 773–923 K for various periods up to t = 10.8 ks (3 h). In this temperature range, the β1 and γ phases are the stable intermetallic compounds in the binary Ni–Zn system. During isothermal annealing, however, only the γ phase forms as a visible compound layer at the original Ni/Zn interface in the diffusion couple. The γ layer grows mainly towards the liquid-Zn and slightly into the solid-Ni. The mean thickness l of the γ layer is described as a power function of the annealing time t. According to the observation, the exponent of the power function is rather close to 0.5 independently of T. Thus, we may consider that the square of l is proportional to t at T = 773–923 K: l2 = Kt. This relationship is called a parabolic relationship. The temperature dependence of K was evaluated from the experimental results. The evaluation provides the activation enthalpy of 40 kJ/mol for the layer growth.
View full abstract
-
Chengbo Li, Cheng Wen, Jun Du, Wenfang Li, Meiyan Zhan
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1878-1886
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Mg–3%Al alloys containing different trace Fe contents were treated by carbon combining with Ca inoculation. The holding time after being inoculation was adjusted from 5 to 80 min. The effect of holding time on grain refinement and the structures of nucleating particles were systematically investigated. Significant grain refinement is obtained for the Mg–3%Al alloys containing trace Fe refined by carbon combining with Ca inoculation. The grain size keep stable with prolonging the holding time and exhibit significant fading-resistance. The duplex-phase particles of Al–Fe coated with Al–C-rich phase could be easily observed and they should actually act as potent nuclei for Mg grains. The Ca content in the Al–C-rich shell is obviously higher than that in the Mg matrix. The segregation of Ca on the surfaces of different phases contributes to the formation of duplex-phase particles and keeps the duplex phase structure particles stable. Consequently, no inoculant-fading of carbon-inoculation occurred due to the high stability of the duplex phase structure particles.
View full abstract
-
Seong-Min Lee
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1887-1891
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
Advance online publication: October 15, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
This work details how devices mechanically separated from wafers with a dummy pattern in their scribe region can undergo serious reliability degradation due to Si3N4 damage. Experimentally, it was found that although chipping damage occurs only within the scribe region, Si3N4 damage can grow up to the active region, which is far away, beyond the chipping damage range, because inappropriate Si3N4 coverage in the scribe region can be a carrier for damage propagation during sawing. Further, this work shows that Si3N4 damage existing in the scribe region even after wafer separation completion can further attack the active region and cause device failure during thermal-cycling. So, this work suggests that appropriate design of the amorphous Si3N4 layer in the scribe region is essential in order to allow the devices to have better reliability margins during thermal-cycling as well as mechanical wafer separation.
View full abstract
-
Woo-Young Kim, Ryo Matsumoto, Hiroshi Utsunomiya
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1892-1897
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Deformation behavior of metallic foams is complicated due to changes in bulk density and volume during deformation. In the previous studies, repeated compression tests were conducted with cylindrical specimens of open-cell type nickel foam and closed-cell type aluminum foam to investigate changes in density and dimensional change. In this study, Oyane’s yield criterion which was originally developed for powder sintered materials and the associated flow rule were used to describe the deformation behavior of the metallic foams with consideration of changes in density, i.e., volumetric strain. The material constants in Oyane’s equation were determined for the two metallic foams based on the experimental results. The obtained constants were a = 2.12 and m = 0.3 for the both foams. Deformation behavior in uniaxial compression is successfully reproduced with the obtained material constants.

Fig. 5 Prediction and experimental results of changes in diameter and bulk density for (a) Celmet and (b) ALPORAS.
Fullsize Image
View full abstract
-
Phan Hong Phuong, Luu Cam Loc, Hoang Tien Cuong, Nguyen Tri
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1898-1902
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
A series of Ni/SBA-15 catalysts was prepared by impregnation method. Effect of NiO content (30–60 mass%), calcination time (0.5–2 h at 800°C), and reduction time (1–2 h at 800°C) on catalytic performance in combined steam and CO2 reforming of CH4 (CSCRM) was studied. N2 physisorption measurements, powder X-ray diffraction, Hydrogen temperature-programmed reduction, CO2-temperature-programmed desorption, and transmission electron microscopy were used to investigate physico-chemical properties of the catalysts. The catalytic performance of Ni/SBA-15 in CSCRM was assessed in the temperature range of 550–800°C. The results revealed suitable time for calcination and reduction being 0.5 h and 1.5 h, respectively. After these treatments, 40 mass% NiO/SBA-15 catalyst was more active and exhibited higher activity than others. At 750°C, conversion of CH4 and CO2 on this catalyst in CSCRM was 91.05% and 78.11%, respectively. High surface area, better reducibility, and good affinity with CO2 contribute to the high performance of this catalyst.
View full abstract
-
Norifumi Kochi, Yoshitaka Nishiyama
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1903-1910
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Steam oxidation resistance of Fe–20Cr–30Ni (at%) austenitic stainless steels with Nb, Mo, Ta, and W was investigated at 700°C. The Cr2O3 layer uniformly formed at the boundary between a spinel-type oxide scale and a metal substrate of alloys containing Nb, Mo, or W inhibits the growth of the oxide scale to improve steam oxidation resistance. During the heating at a high temperature, intermetallic compounds consisting of Fe and the added elements precipitate in the alloy and alter the chemical composition of the solute elements. The Cr activity gradient becomes large between the alloy substrate and the Cr depletion zone beneath the oxide scale since the amounts of precipitation differ between them, leading to enhancement of the Cr flux outward. It is indicated that an increase in the Cr flux accelerates the formation of the Cr2O3 layer.
This Paper was Originally Published in Japanese in J. Japan Inst. Met. Mater. 81 (2017) 427–434.
View full abstract
-
Ryota Kondo, Seiya Nakamichi, Ryusei Azuma, Yuya Takahashi, Yasushi Ob ...
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1911-1914
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
Advance online publication: November 09, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
To identify the reasons why Ti–Pd alloys for hydrogen storage materials show good hydrogenation properties, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and the Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction were used to investigate a small amount of Pd added Ti–Pd alloys. Pd in or on Ti oxide films is in a valence state of 0 (Pd0). Catalytic activity was shown by Pd0 in the Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. Therefore, the enhanced hydrogenation properties of Ti–Pd alloys for hydrogen storage materials is due to Pd0’s catalytic activity in dissociating hydrogen molecules. In addition, the potential catalytic activity of Ti–Pd alloys was shown to be based on a Pd catalyst.
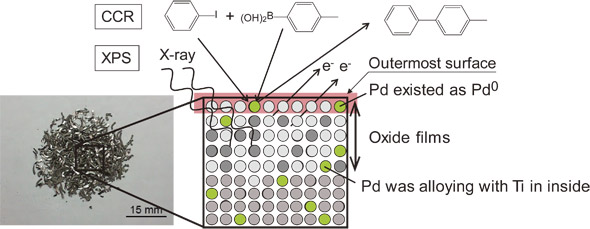
XPS and cross-coupling reaction (CCR) were used to investigate the surface property of Pd in Ti-Pd alloys. Pd was present in a valence state of 0. Despite the flack-like shape of the alloy, the cross-coupling reaction proceeded up to 94% in product without pretreatment, such as heating in H
2 atmosphere and in air conditions.
Fullsize Image
View full abstract
-
Jaime Alfredo Mariano-Torres, Arturo López-Marure, Margarita García-He ...
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1915-1919
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
Advance online publication: November 09, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
The synthesis of a new hybrid polymer derived from glycerol citrate polymer (GCP) and yttrium oxide nanoparticles was performed without catalyst and using an equimolar concentration. The biocompatibility and antimicrobial capacity of citrate-based polymers suggest it to be involved in biomedical applications since citric acid is a natural molecule. Glycerol citrate polymer and yttrium oxide (Y2O3) nanoparticles were synthesized by autocatalytic polymerization and sol-gel methods respectively. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), antibacterial effect and cell viability assay were performed to characterize the material. The cubic crystalline Y2O3 nanoparticles dispersed in glycerol citrate polymer could be the cause of the increased antibacterial effect presented in the pure glycerol citrate polymer; supporting the potential of the hybrid polymer as a biotechnological material. The cytotoxicity was evaluated trough human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell.
View full abstract
-
Masashi Hara, Masafumi Namba, Shin Tajima, Masaaki Tani, Takeshi Hatto ...
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1920-1927
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
To improve the properties of powder magnetic core for motors, such as iron loss, resistivity and strength, pure iron powder was deformed into flaky-shaped and then annealed to decrease strain by deformation. It was confirmed that the strength of iron core increased with increasing the aspect ratio of powder. However, the resistivity extremely decreased. The iron core showed properties as follows; density d = 7.66 Mg·m−3, resistivity ρ = 2.5 × 104 µΩ·m, iron loss Pc (the maximum magnetic flux density, Bmax = 1 T, frequency, f = 400 Hz) = 30 W·kg−1, iron loss Pc (Bmax = 1 T, f = 800 Hz) = 63 W·kg−1, radial crushing strength σ = 95 MPa. Especially, eddy current loss coefficient Ke was 0.008 mWs2·kg−1, extremely lower than electromagnetic steel sheet and powder magnetic core reported ever.
This Paper was Originally Published in Japanese in J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metallurgy 64 (2017) 638–645. To show the shape of the powder more clearly, Fig. 2 was replaced.
View full abstract
-
Zhenyu Xu, Dayong Li, Xuliang Ma, Dequan Shi, Chaowei Han, Lihua Wang
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1928-1934
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Dissolved oxygen in molten iron is one of the most important metallurgical factors affecting nodularization effect and casting properties. In present paper, the metallurgical behaviors of active oxygen in molten iron are discussed during nodularization through a ZrO2 (MgO partly stabilized) solid electrolyte battery for ultra-low oxygen condition of nodularized iron liquid. Combining with the results of thermal analysis obtained almost after active oxygen content measurement, the optimization control of nodularization process for ductile iron is studied. Results show that nodularization extremely disturbs the metallurgy equilibrium in molten iron, over-nodularization promotes this non-equilibrium degree. Inoculation can decrease the non-equilibrium trend and improve the solidification model by graphite nucleation. Nodularization effect degeneration began with the inoculation fading, with the active oxygen content slight increase, the volume fraction of nodular graphite decreased with rounded morphology. Followingly, as the active oxygen content continuous increase, the nodularity began to decrease. Therefore, it is promising to achieve more accurate control of nodularization by this combined on-line measurement technique.
View full abstract
-
Xuan Meng, Yongbum Choi, Kazuhiro Matsugi, Zhefeng Xu, Wenchang Liu
Article type: Regular Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1935-1942
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
Carbon fiber reinforced pure Al, A336 alloy and carbon fiber-carbon nanofiber reinforced A336 alloy composites were successfully fabricated by low-pressure infiltration process, aiming for development the carbon fiber reinforced aluminum matrix composites with high thermal conductivity and mechanical property used as functional materials and structural materials, respectively. Carbon fiber of 10 vol% and hybrid carbon fiber-carbon nanofiber of 10 vol% were used to fabricated preforms for the low-pressure infiltration process. Afterwards, pure Al and Aluminum alloy under a temperature of 1073 K were infiltrated into the preforms under an applied pressure of 0.4 MPa in Ar environment. Microstructural and mechanical performances of the composites were investigated. Microstructure observations indicated that SiO2 binder was coated on the surface of carbon fiber and distributed at the corner of carbon fibers in carbon fiber preform. Carbon nanofibers were agglomerated at the corner of carbon fibers, and some were dispersed on the surface of carbon fiber in the hybrid preform. In composites, carbon fibers were homogeneously distributed in the matrix. Further Vickers hardness test results showed that the hardness of carbon fiber reinforced pure Al composite increased by 76% compared to pure Al, and carbon fiber reinforced A336 alloy composite increased by 11.1% compared to A336 alloy. The thermal conductivity (TC) test result illustrated that the thermal conductivity of carbon fiber reinforced pure Al and A336 alloy composite was 245.8 W/(m·K) and 113.5 W/(m·K), respectively, and the thermal conductivity of carbon fiber-carbon nanofiber reinforced A336 alloy composite was 98.4 W/(m·K).
View full abstract
-
Haipeng Lu, Junqi Qin, Changchun Di, Yuliang Yang, Ruikun Huo
Article type: Technical Article
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1943-1948
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
Advance online publication: October 19, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
By studying effect of different duty cycles on tungsten-cobalt film to improve its performances, tungsten-cobalt films were prepared on the surface of PCrNi3MoVA steel by electrodeposition under different duty cycles. The results show that grain size increases with increasing duty cycle but tungsten content, microhardness, film-based bond strength and TC(100) increase first and then decrease with increasing duty cycle. When the duty cycle is 30%, tungsten-cobalt films with highest tungsten content (43.37%), grain size (12.3 nm) and largest TC(100) (0.845) have highest microhardness (7.1 GPa) and strongest film-base bond (24 N), which results in lowest friction coefficient (0.31) and smallest wear rate (2 × 10−5 mm3N−1m−1) that is only 28.57% for the tungsten-cobalt film prepared under 100% duty cycle.
View full abstract
-
Mingqin Xu, Mingxu Xia, Qiaodan Hu, Jianguo Li
Article type: Rapid Publication
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1949-1951
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
As an important deoxidization agent, Al and its deoxidization products are rarely investigated in terms of nucleation catalyzer for liquid iron itself. Here, we tracked the atomic structure evolution of Al deoxidized liquid iron using in situ high energy X-ray diffraction method to figure out the effect of Al and its deoxidization product for the nucleation in liquid iron. The identified icosahedral short-range ordering (ISRO) and its enhancement with decreasing temperature in both the liquids investigated suggest that the type and number of ISRO is not the sole reason responsible for the variation of undercooling. A decreased nearest neighbor atomic distance (r1) of liquid was detected with the enhanced nucleation after adding 1 mass%Al for de-oxidization. It indicates that the difference between SRO structure of Fe–1 mass%Al liquid and the corresponding crystal structure becomes small, resulting in a lower undercooling.
View full abstract
-
Yoshihiko Hangai, Keita Takahashi, Ryohei Nagahiro, Kenji Amagai, Taka ...
Article type: Rapid Publication
2018Volume 59Issue 12 Pages
1952-1955
Published: December 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2018
JOURNAL
FREE ACCESS
FULL-TEXT HTML
A point group mold, whose surface consists of tips of pins arranged to form the desired shape, was newly used to fabricate Al foam with complex shapes. Although dimples formed by the pin tips were clearly observed, the surface of the Al foam retained the shape of the point group mold. No protrusion of the Al foam through the gaps between the pins during foaming was observed. Namely, the surface of the point group mold was transferred to the Al foam.
View full abstract


