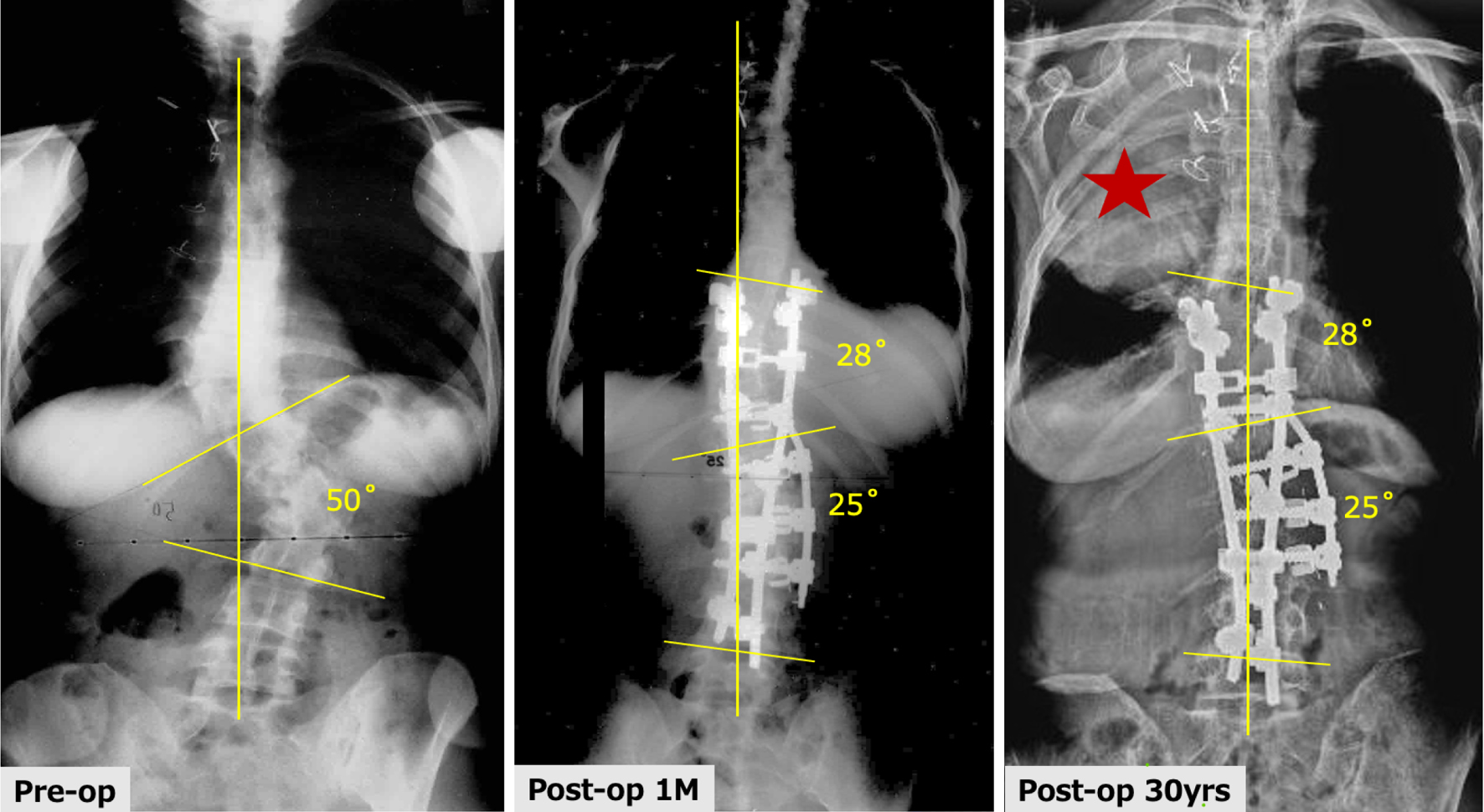
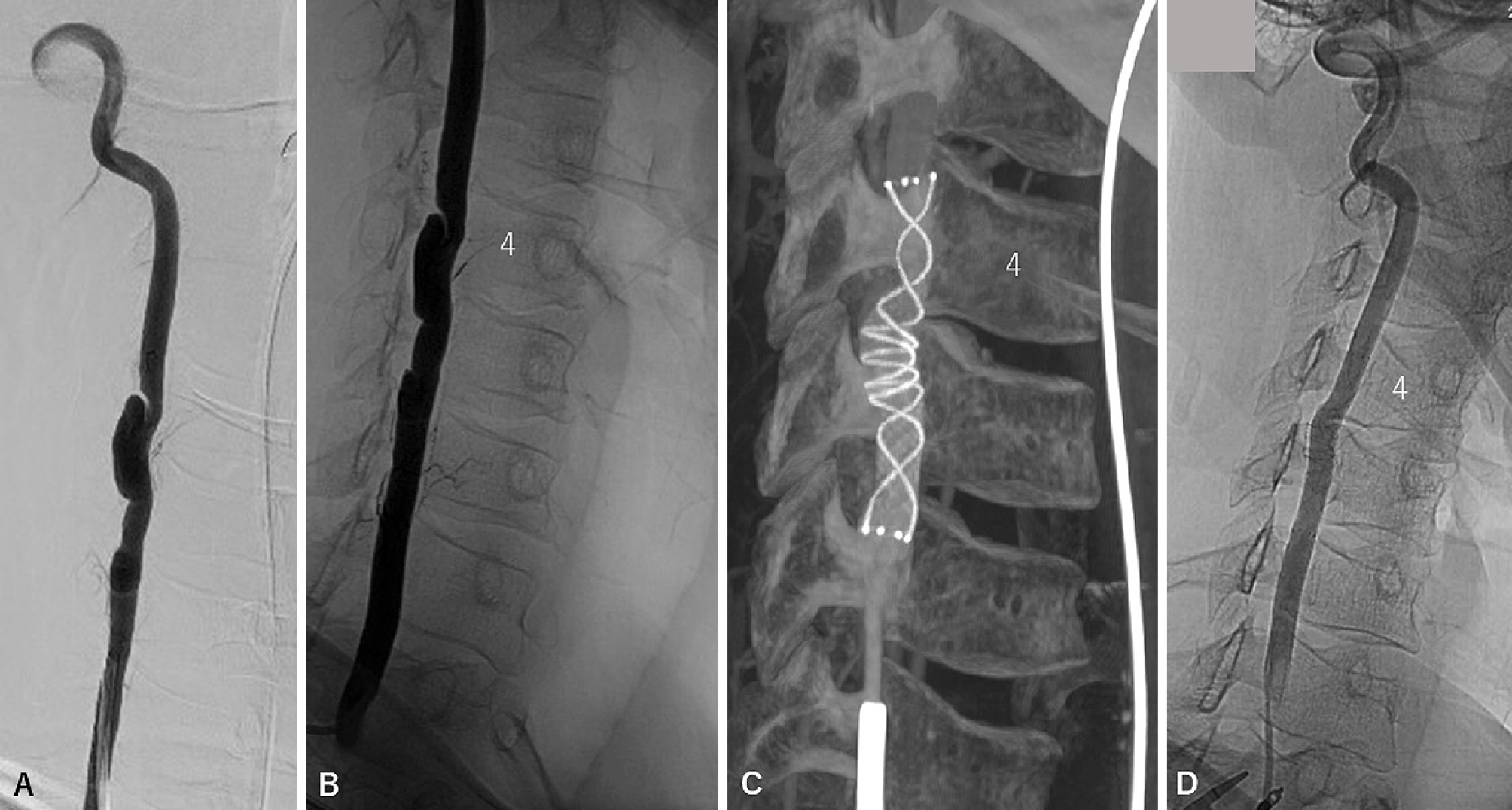
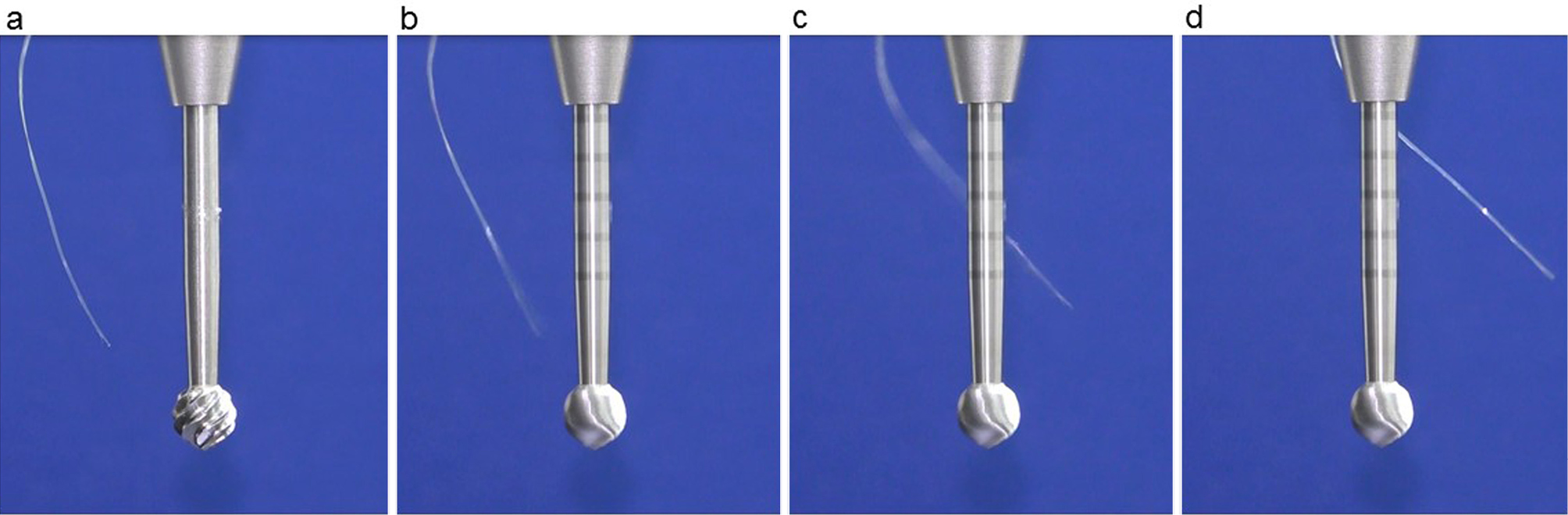
Volume 14, Issue 7
Displaying 1-16 of 16 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 984
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (292K)
-
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 985-991
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (1480K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 992-998
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (2175K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 999-1004
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (1296K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1005-1011
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (1658K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1012-1022
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (2992K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1023-1031
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (2796K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1032-1039
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (2122K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1040-1043
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (1014K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1044-1047
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (735K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1048-1054
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (1924K)
-
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1055-1060
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (1549K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1061-1066
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (1508K) -
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1067-1072
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (1808K)
-
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1073-1078
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (1268K)
-
2023Volume 14Issue 7 Pages 1079
Published: July 20, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 20, 2023
Download PDF (183K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|